
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2025, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 249-264.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20253145cstr: 32225.14.cjmr20253145
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2025-02-17
Published:2025-09-05
Online:2025-03-27
Contact:
* Tel: 15776630256, E-mail: huyue@hit.edu.cn.CLC Number:
LI Peng, JI Yuping, HU Yue. High-quality MR Fingerprinting Reconstruction Based on Manifold Structured Data Priors[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 249-264.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

Fig. 3
(a) and (b) are the flip angles and repetition time patterns that were used in the experiment. (c), (d), (e) shows the spiral undersampling trajectory, pseudo radial Cartesian sampling mask, and the variable density spiral undersampling trajectory, respectively, used in one repetition time in the experiments
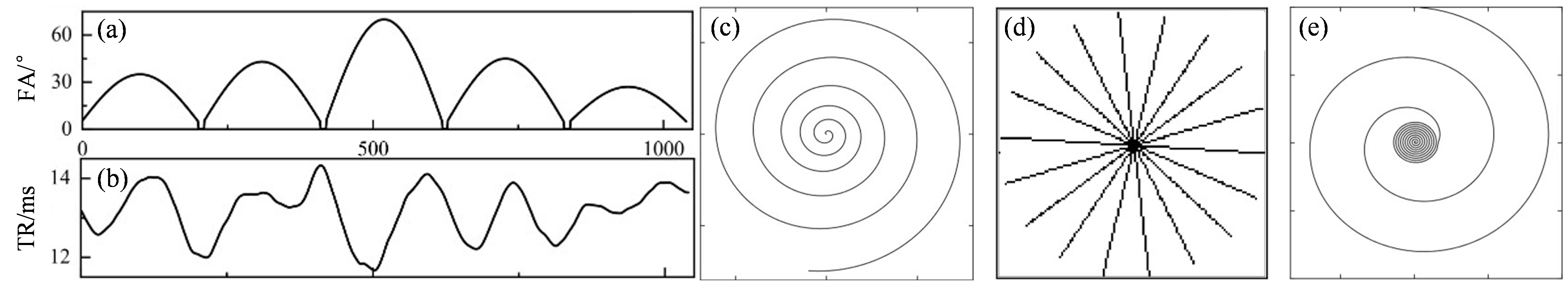
Table 2
The NMSEs of the reconstructed parameter maps by different methods using various acquisition lengths L
| L | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maps | T1 | T2 | PD | T1 | T2 | PD | T1 | T2 | PD | T1 | T2 | PD |
| BLIP | 0.0872 | 0.3789 | 0.0321 | 0.0682 | 0.2830 | 0.0311 | 0.0564 | 0.2080 | 0.0302 | 0.0453 | 0.1549 | 0.0291 |
| MBIR | 0.0345 | 0.3490 | 0.0369 | 0.0344 | 0.2310 | 0.0353 | 0.0328 | 0.1524 | 0.0347 | 0.0311 | 0.1160 | 0.0318 |
| FLOR | 0.0208 | 0.1676 | 0.0190 | 0.0143 | 0.1067 | 0.0131 | 0.0129 | 0.0680 | 0.0128 | 0.0104 | 0.0450 | 0.0101 |
| SL-SP | 0.0163 | 0.1417 | 0.0108 | 0.0112 | 0.0967 | 0.0105 | 0.0108 | 0.0667 | 0.0081 | 0.0102 | 0.0429 | 0.0075 |
| DG-LR | 0.0167 | 0.1421 | 0.0106 | 0.0109 | 0.1013 | 0.0104 | 0.0103 | 0.0659 | 0.0073 | 0.0075 | 0.0365 | 0.0045 |
| MS | 0.0219 | 0.1901 | 0.0180 | 0.0149 | 0.0991 | 0.0097 | 0.0137 | 0.0653 | 0.0082 | 0.0093 | 0.0406 | 0.0048 |
| LLR | 0.0186 | 0.1890 | 0.0132 | 0.0134 | 0.1117 | 0.0091 | 0.0120 | 0.0659 | 0.0088 | 0.0081 | 0.0400 | 0.0046 |
| MS-LLR(本文方法) | 0.0146 | 0.1374 | 0.0080 | 0.0094 | 0.0864 | 0.0046 | 0.0078 | 0.0603 | 0.0040 | 0.0052 | 0.0284 | 0.0027 |
Table 3
T1 and T2 values (ms, mean ± standard deviation) of several brain tissues measured on the corresponding regions (blue boxes) in Fig.7
| REF | BLIP | MBIR | FLOR | SL-SP | DG-LR | MS | LLR | MS-LLR(本文方法) | 文献[ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | GM | 1342.4±53.7 | 1328.4±242.2 | 1325.6±140.2 | 1319.2±95.6 | 1327.0±84.5 | 1322±79.3 | 1305.4±64.2 | 1331.4±75.7 | 1337.1±61.1 | 1286~1393 |
| WM | 797.6±35.3 | 806.7±104.9 | 807.2±74.4 | 810.0±61.2 | 805.6±56.4 | 805.8±56.8 | 789.3±45.5 | 804.7±50.2 | 801.2±42.1 | 788~898 | |
| CSF | 3412.0±157.8 | 3653.6±295.7 | 3528.0±244.1 | 3524.0±192.7 | 3452.0±180.4 | 3441.7±184.2 | 3143.5±174.1 | 3459.5±183.7 | 3432.6±168.5 | / | |
| T2 | GM | 78.4±6.0 | 93.3±19.8 | 85.2±17.1 | 82.8±12.4 | 80.8±11.2 | 80.6±11.8 | 76.8±8.9 | 80.3±13.5 | 79.5±7.8 | 78~117 |
| WM | 68.4±4.7 | 76.2±14.5 | 72.3±12.1 | 71.7±8.9 | 71.2±7.5 | 70.2±7.6 | 67.1±5.7 | 70.5±6.4 | 69.0±5.1 | 63~80 | |
| CSF | 816.0±171.3 | 857.8±313.6 | 830.0±248.2 | 798.6±217.7 | 802.4±202.9 | 804.4±195.1 | 790.1±189.3 | 807.3±193.9 | 811.6±187.7 | / |
Table 4
T1 and T2 values (ms, mean ± standard deviation) of several brain tissues measured on the corresponding regions (blue boxes) in Fig.8
| REF | BLIP | MBIR | FLOR | SL-SP | DG-LR | MS | LLR | MS-LLR(本文方法) | 文献[ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | GM | 1347.2±68.7 | 1327.2±249.5 | 1314.8±162.4 | 1321.6±121.9 | 1316.0±102.1 | 1324.7±105.4 | 1299.0±89.7 | 1309.1±97.6 | 1331.8±77.6 | 1286~1393 |
| WM | 805.6±79.1 | 850.1±325.1 | 852.8±195.5 | 824.0±127.4 | 813.6±109.1 | 816.3±102.1 | 791.1±58.5 | 809.5±76.8 | 804.5±52.3 | 788~898 | |
| CSF | 3596.0±183.5 | 3657.6±327.1 | 3692.0±285.1 | 3604.0±243.4 | 3632.0±224.9 | 3640.4±226.1 | 3343.2±212.6 | 3628.3±216.7 | 3583.3±203.1 | / | |
| T2 | GM | 80.1±4.8 | 92.9±24.2 | 86.6±14.7 | 83.4±12.9 | 82.6±10.4 | 82.8±9.2 | 77.6±7.1 | 81.8±9.1 | 80.9±6.2 | 78~117 |
| WM | 64.4±5.8 | 76.8±18.0 | 72.6±11.2 | 69.4±9.0 | 67.0±8.4 | 66.3±8.2 | 62.8±6.5 | 66.9±8.3 | 65.7±6.2 | 63~80 | |
| CSF | 804.0±109.1 | 852.4±225.5 | 831.2±201.2 | 828.0±172.2 | 823.2±160.5 | 819.8±157.2 | 783.8±142.4 | 819.7±145.6 | 814.9±125.6 | / |
Table 5
The NMSEs of the reconstructed parameter maps using different patch sizes
| Patch Size p | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radial | T1 | 0.00413 | 0.00404 | 0.00442 | 0.00313 | 0.00668 | 0.01026 |
| T2 | 0.02071 | 0.02453 | 0.02454 | 0.01377 | 0.02305 | 0.01973 | |
| PD | 0.00099 | 0.00090 | 0.00089 | 0.00088 | 0.00089 | 0.00090 | |
| Vds-spiral | T1 | 0.00595 | 0.00455 | 0.00408 | 0.00300 | 0.00329 | 0.00725 |
| T2 | 0.03690 | 0.02720 | 0.02472 | 0.01540 | 0.02178 | 0.02853 | |
| PD | 0.00310 | 0.00207 | 0.00173 | 0.00100 | 0.00103 | 0.00107 | |
Table 6
The NMSEs of the reconstructed parameter maps using different methods under various sampling patterns
| Spiral | Vds-spiral | Radial | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | PD | T1 | T2 | PD | T1 | T2 | PD | |
| BLIP | 0.0963 | 0.4682 | 0.0169 | 0.0320 | 0.1479 | 0.0248 | 0.0218 | 0.0983 | 0.0130 |
| MBIR | 0.0582 | 0.3763 | 0.0404 | 0.0276 | 0.0845 | 0.0254 | 0.0146 | 0.0809 | 0.0065 |
| FLOR | 0.0175 | 0.1024 | 0.0091 | 0.0102 | 0.0311 | 0.0067 | 0.0051 | 0.0274 | 0.0013 |
| SL-SP | 0.0154 | 0.0763 | 0.0083 | 0.0075 | 0.0282 | 0.0022 | 0.0027 | 0.0246 | 0.0010 |
| MS | 0.0169 | 0.0903 | 0.0107 | 0.0093 | 0.0406 | 0.0048 | 0.0049 | 0.0292 | 0.0018 |
| LLR | 0.0166 | 0.0864 | 0.0113 | 0.0067 | 0.0319 | 0.0037 | 0.0035 | 0.0285 | 0.0013 |
| MS-LLR(本文方法) | 0.0131 | 0.0534 | 0.0048 | 0.0030 | 0.0154 | 0.0010 | 0.0031 | 0.0138 | 0.0009 |
| [1] | MA D, GULANI V, SEIBERLICH N, et al. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting[J]. Nature, 2013, 495(7440): 187-192. |
| [2] | CHEN Y, LU L, ZHU T, et al. Technical overview of magnetic resonance fingerprinting and its applications in radiation therapy[J]. Med Phys, 2022, 49(4): 2846-2860. |
| [3] | DENG W, LI X H. Research progress of cardiac magnetic resonance fingerprint technology[J]. International Journal Of Medical Radiology, 2022, 45(2): 189-191;204. |
| 邓炜, 李小虎. 心脏磁共振指纹技术研究进展[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志, 2022, 45(2): 189-191,204. | |
| [4] | LENG Y J, WU Q W, LI, Y X, et al Quantitative measurement of brain tissue parameters based on magnetic resonance fingerprinting and its preliminary application in brain diseases[J], Chinese Journal of Clinical Neurosciences, 2020, 28(5): 579-583. |
| 冷一峻, 吴秋雯, 李郁欣, 等. 基于磁共振指纹技术的脑组织参数定量检测及在脑疾病中的初步应用[J]. 中国临床神经科学, 2020, 28(5): 579-583. | |
| [5] | TIPPAREDDY C, ZHAO W, SUNSHINE J L, et al. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting: an overview[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol I, 2021, 48(13): 4189-4200. |
| [6] | DAVIES M, PUY G, VANDERGHEYNST P, et al. A compressed sensing framework for magnetic resonance fingerprinting[J]. SIAM J Imaging Sci, 2014, 7(4): 2623-2656. |
| [7] |
ZHAO B, SETSOMPOP K, YE H, et al. Maximum likelihood reconstruction for magnetic resonance fingerprinting[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2016, 35(8): 1812-1823.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2531640 pmid: 26915119 |
| [8] | MAZOR G, WEIZMAN L, TAL A, et al. Low-rank magnetic resonance fingerprinting[J]. Med Phys, 2018, 45(9): 4066-4084. |
| [9] | ZHAO B, SETSOMPOP K, ADALSTEINSSON E, et al. Improved magnetic resonance fingerprinting reconstruction with low-rank and sssubspace modeling[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 79(2): 933-942. |
| [10] |
LIMA DA CRUZ G, BUSTIN A, JAUBERT O, et al. Sparsity and locally low rank regularization for MR fingerprinting[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 81(6): 3530-3543.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27665 pmid: 30720209 |
| [11] | HU Y, LI P, CHEN H, et al. High-quality MR fingerprinting reconstruction using structured low-rank matrix completion and subspace projection[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2021, 41(5): 1150-1164. |
| [12] |
NAGTEGAAL M, HARTSEMA E, KOOLSTRA K, et al. Multicomponent MR fingerprinting reconstruction using joint-sparsity and low-rank constraints[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 89(1): 286-298.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.29442 pmid: 36121015 |
| [13] |
MCGIVNEY D F, PIERRE E, MA D, et al. SVD compression for magnetic resonance fingerprinting in the time domain[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2014, 33(12): 2311-2322.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2337321 pmid: 25029380 |
| [14] |
YANG M, MA D, JIANG Y, et al. Low rank approximation methods for MR fingerprinting with large scale dictionaries[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 79(4): 2392-2400.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26867 pmid: 28804918 |
| [15] |
COHEN O, ZHU B, ROSEN M S. MR fingerprinting deep reconstruction network (DRONE)[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 80(3): 885-894.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27198 pmid: 29624736 |
| [16] | OKSUZ I, CRUZ G, CLOUGH J, et al. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting using recurrent neural networks[C]// 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019). IEEE, 2019: 1537-1540. |
| [17] |
FANG Z, CHEN Y, LIU M, et al. Deep learning for fast and spatially constrained tissue quantification from highly accelerated data in magnetic resonance fingerprinting[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2019, 38(10): 2364-2374.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2899328 pmid: 30762540 |
| [18] | SOYAK R, NAVRUZ E, ERSOY E O, et al. Channel attention networks for robust MR fingerprint matching[J]. IEEE T Bio-med Eng, 2021, 69(4): 1398-1405. |
| [19] |
TENENBAUM J B, SILVA V, LANGFORD J C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction[J]. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2319-2323.
doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2319 pmid: 11125149 |
| [20] | VAN DER MAATEN L, POSTMA E, VAN DEN HERIK J. Dimensionality reduction: a comparative[J]. J Mach Learn Res, 2009, 10: 66-71. |
| [21] | ALJABAR P, WOLZ R, RUECKERT D. Manifold learning for medical image registration, segmentation, and classification[M]// Machine learning in computer-aided diagnosis: Medical imaging intelligence and analysis, 2012: 351-372. |
| [22] | BOUMAL N. An introduction to optimization on smooth manifolds[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2023. |
| [23] | NAKARMI U, SLAVAKIS K, LYU J, et al. M-MRI: A manifold-based framework to highly accelerated dynamic magnetic resonance imaging[C]// 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017). IEEE, 2017: 19-22. |
| [24] | PODDAR S, JACOB M. Dynamic MRI using smoothness regularization on manifolds (SToRM)[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2015, 35(4): 1106-1115. |
| [25] |
PODDAR S, MOHSIN Y Q, ANSAH D, et al. Manifold recovery using kernel low-rank regularization: Application to dynamic imaging[J]. IEEE T Comput Imag, 2019, 5(3): 478-491.
doi: 10.1109/tci.2019.2893598 pmid: 33768137 |
| [26] | MOHSIN Y Q, PODDAR S, JACOB M. Free-breathing & ungated cardiac MRI using iterative SToRM (i-SToRM)[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2019, 38(10): 2303-2313. |
| [27] |
NAKARMI U, WANG Y, LYU J, et al. A kernel-based low-rank (KLR) model for low-dimensional manifold recovery in highly accelerated dynamic MRI[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2017, 36(11): 2297-2307.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2723871 pmid: 28692970 |
| [28] | SLAVAKIS K, SHETTY G N, CANNELLI L, et al. Kernel regression imputation in manifolds via bi-linear modeling: The dynamic-MRI case[J]. IEEE T Comput Imag, 2022, 8: 133-147. |
| [29] | DJEBRA Y, MARIN T, HAN P K, et al. Manifold learning via linear tangent space alignment (LTSA) for accelerated dynamic MRI with sparse sampling[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2022, 42(1): 158-169. |
| [30] |
ARBERET S, CHEN X, MAILHÉ B, et al. A parallel spatial and Bloch manifold regularized iterative reconstruction method for MR Fingerprinting[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2021, 82: 74-90.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2021.06.009 pmid: 34157408 |
| [31] | CANNON J W. Shrinking cell-like decompositions of manifolds. Codimension three[J]. Ann Math, 1979: 83-112. |
| [32] | DONG G, HINTERMÜLLER M, PAPAFITSOROS K. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging: From fingerprinting to integrated physics-based models[J]. SIAM J Imaging Sci, 2019, 12(2): 927-971. |
| [33] | BELKIN M, NIYOGI P. Laplacian eigenmaps for dimensionality reduction and data representation[J]. Neural Comput, 2003, 15(6): 1373-1396. |
| [34] | SRA S, NOWOZIN S, WRIGHT S J. Optimization for machine learning[M]. Mit Press, 2011. |
| [35] | MUCKLEY M J, STERN R, MURRELL T, et al. TorchKbNufft: A high-level, hardware-agnostic non-uniform fast Fourier transform[C]// ISMRM Workshop on Data Sampling & Image Reconstruction. 2020, 22. |
| [36] | LU H, ZHAO B. Accelerated magnetic resonance fingerprinting with low-rank and generative subspace modeling[C]// 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Workshops (ICASSPW). IEEE, 2023: 1-5. |
| [37] |
JIANG Y, MA D, SEIBERLICH N, et al. MR fingerprinting using fast imaging with steady state precession (FISP) with spiral readout[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2015, 74(6): 1621-1631.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.25559 pmid: 25491018 |
| [38] |
BIPIN MEHTA B, COPPO S, FRANCES MCGIVNEY D, et al. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting: a technical review[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 81(1): 25-46.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27403 pmid: 30277265 |
| [1] | HUANG Min, ZHU Junlin, KAO Yuchen, ZHOU Dao, TANG Qiling. Multi-Coil MRI Image Reconstruction Based on ISTAVS-Net of Physical Model [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 418-429. |
| [2] | HUANG Min,LI Siyi,CHEN Junbo,ZHOU Dao. Progress of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting Technology and Its Clinical Application [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 207-219. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
