引言
3/4/5-O-阿魏酰奎宁酸(3/4/5-O-feruloylquinic acid,3/4/5-O-FQA)是奎宁酸结合酚酸的衍生物,属于植物酚类物质,广泛存在于茶叶、竹笋等植物中,具有出色的抗氧化能力,对预防多种疾病和维持人体健康有益[1⇓-3].3/4/5-O-FQA常出现于咖啡豆中绿原酸的研究过程中[4⇓⇓⇓-8],Park等人从三种速溶咖啡品牌中分离出三个主要的绿原酸(3/4/5-O-caffeoylquinic acid,3/4/5-O-CQA)和一些次要的绿原酸(3/4/5-O-FQA),研究表明,这些绿原酸具有较好的2,2-联苯基-1-苦基肼(2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazy,DPPH)自由基清除活性[9⇓⇓-12].
3/4/5-O-FQA还可以从苦竹中提取,例如,Ao等人已从苦竹嫩芽中分离4种化合物,即3-O-coumaroylquinic acid和3/4/5-O-FQA,他们的研究结果表明3-O-FQA比4-O-FQA和5-O-FQA显示出更强的抗氧化能力,因此推测3-O-FQA将有助于开发新的抗氧化和抗炎物质[13].Ma等人结合相关文献分析一级质谱,确定白茅根中含有3-O-FQA[14].Deng等人研究小果博落回和土蜜树化学成分,采用有机溶剂萃取法、柱色谱以及重结晶法从小果博落回根85%乙醇提取物中分离得到了35个化合物,经1H、13C核磁共振(nuclear magnetic resonance,NMR)、质谱等方法分析,鉴定其中含有3-O-FQA[15].
分子结构决定分子的性质和应用价值.以上研究结果只能得出分子3/4/5-O-FQA的平面结构,推测相对构型,然而,其三维结构尚不清楚.NMR技术是研究分子结构最有效的实验手段之一.量子化学计算是理论研究分子结构的重要工具,能够帮助理解和解释实验现象.为了系统探讨3/4/5-O-FQA的三维结构,本文采用NMR实验与量子化学理论计算相结合的方法,研究了3/4/5-O-FQA分别在气相、D2O和DMSO-d6溶液中的三维精确结构和化学位移,探讨了溶剂化效应对分子结构的影响,有助于深入理解1H NMR实验结果,为进一步研究3/4/5-O-FQA的性质和应用价值提供参考和帮助.
1 实验部分
1.1 NMR实验
3/4/5-O-FQA样品均购于成都麦德生科技有限公司.1H NMR实验在Bruker Avance Ⅲ 500 MHz NMR波谱仪上进行,质子共振频率为500.13 MHz.溶剂为D2O时,实验采用zgpr脉冲序列,1H化学位移的标定选TSP为内参.溶剂为DMSO-d6时,实验采用zg脉冲序列,1H化学位移定标参照DMSO溶剂残余峰δ 2.50.所有实验均在25 ℃室温下进行.
1.2 计算方法
2 结果与讨论
2.1 1H NMR谱
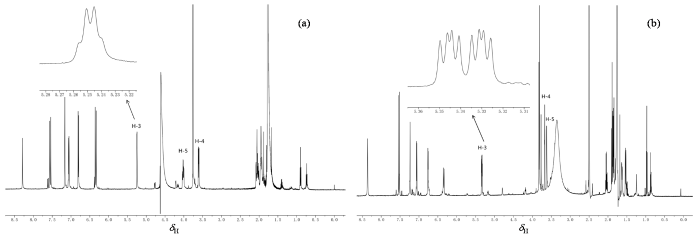
图1
图1
3-O-FQA的1H NMR谱. (a) D2O溶液;(b) DMSO-d6溶液. 插图为H-3谱峰的放大图
Fig. 1
1H NMR spectra of 3-O-FQA. (a) D2O solution; (b) DMSO-d6 solution. The inset shows an enlarged view of H-3 peaks
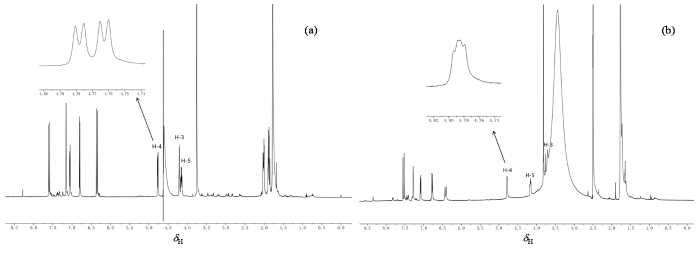
图2
图2
4-O-FQA的1H NMR谱. (a) D2O溶液;(b) DMSO-d6溶液. 插图为H-4谱峰的放大图
Fig. 2
1H NMR spectra of 4-O-FQA. (a) D2O solution; (b) DMSO-d6 solution. The inset shows an enlarged view of H-4 peaks
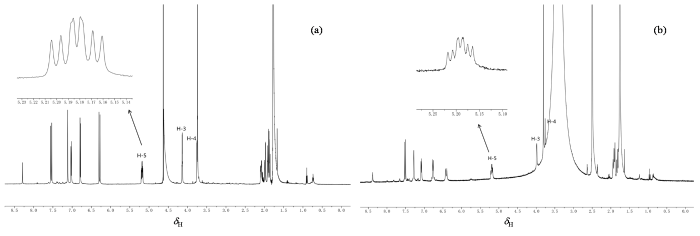
图3
图3
5-O-FQA的1H NMR谱. (a) D2O溶液;(b) DMSO-d6溶液. 插图为H-5谱峰的放大图
Fig. 3
1H NMR spectra of 5-O-FQA. (a) D2O solution; (b) DMSO-d6 solution. The inset shows an enlarged view of H-5 peaks
2.2 几何结构和分子振动频率
图4
表1 考虑H2O和DMSO溶剂化效应时3/4/5-O-FQA的10个最低分子振动频率
Table 1
| 频率/cm-1 | 3-O-FQA | 4-O-FQA | 5-O-FQA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | DMSO | H2O | DMSO | H2O | DMSO | |
| 12.47 | 1.93 | 15.38 | 15.19 | 12.58 | 12.85 | |
| 19.67 | 14.71 | 22.19 | 22.14 | 15.50 | 16.12 | |
| 31.81 | 29.02 | 25.61 | 25.43 | 29.57 | 30.10 | |
| 38.61 | 32.85 | 34.29 | 34.24 | 40.51 | 40.80 | |
| 53.25 | 50.29 | 54.94 | 55.32 | 44.85 | 45.36 | |
| 62.17 | 61.66 | 58.46 | 58.30 | 57.94 | 58.49 | |
| 72.09 | 71.09 | 64.52 | 64.65 | 69.16 | 69.59 | |
| 87.96 | 86.18 | 81.22 | 81.66 | 84.51 | 84.74 | |
| 89.33 | 89.63 | 118.58 | 118.16 | 102.86 | 102.94 | |
| 123.20 | 123.03 | 127.79 | 127.73 | 114.08 | 114.54 | |
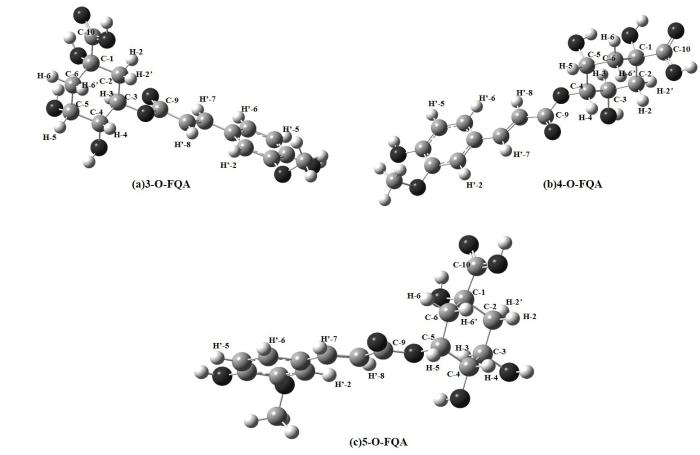
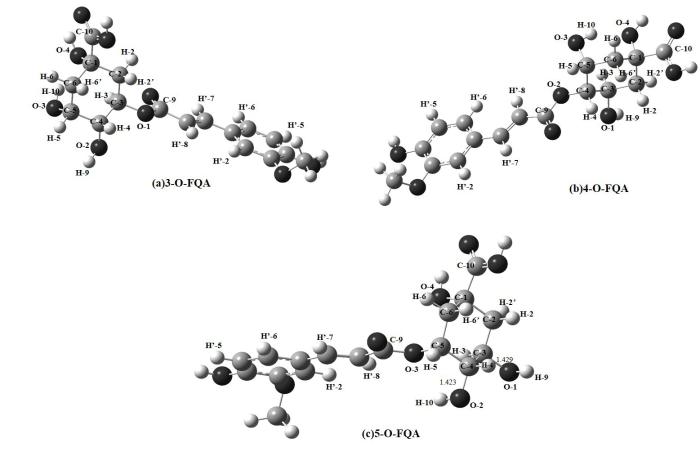
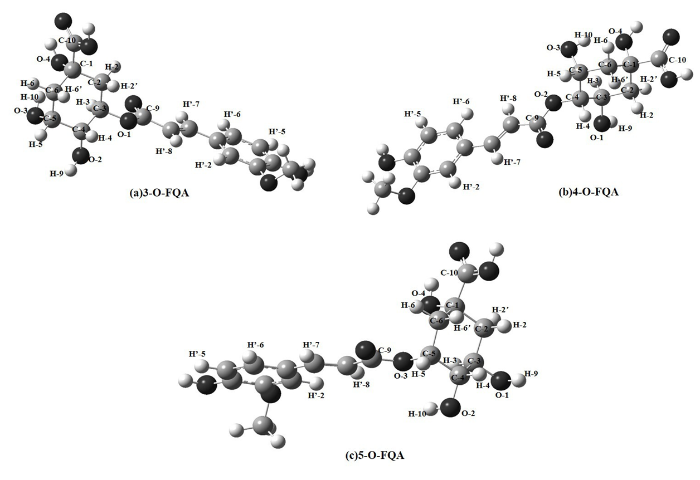
图5和6分别为考虑溶剂化效应时3/4/5-O-FQA在水溶液和DMSO溶液中优化后的三维结构.3/4/5-O-FQA结构分别对应(a)、(b)、(c),原子序号如图中所示.我们发现,3/4/5-O-FQA三种结构在不同溶液下的主要差别是酯化位H-3、H-4、H-5处二面角的差异.在H2O和DMSO两种溶液环境下,3/4/5-O-FQA在酯化位H-4、H-5处二面角相对差值约0.2˚,4/5-O-FQA在H-3处二面角相对差值约0.1˚~0.2˚,而3-O-FQA在H-3位置处的二面角τ (H3C3O1C9)在两种溶液下(H2O溶液下24.279˚,DMSO溶液下20.132˚)相对差值约4.147˚.可见,3-O-FQA中酯化位H-3附近的几何结构在两种溶液下有明显变化.
图5
图5
(a) 3-O-FQA、(b) 4-O-FQA和(c) 5-O-FQA在水溶液下的优化结构
Fig. 5
Optimized structures of (a) 3-O-FQA, (b) 4-O-FQA and (c) 5-O-FQA in water solution
图6
图6
(a) 3-O-FQA、(b) 4-O-FQA 和 (c) 5-O-FQA在DMSO溶液下的优化结构
Fig. 6
Optimized structures of (a) 3-O-FQA, (b) 4-O-FQA and (c) 5-O-FQA in DMSO solution
分子结构发生变化能够影响分子内动力学.分子振动频率的计算结果显示,3-O-FQA分子的最小振动频率对应于二面角τ (H3C3O1C9)的弯曲振动模式,且在H2O和DMSO两种溶液下,该振动频率分别为12.47 cm-1和1.93 cm-1,相差约10 cm-1.该频率差异说明两种溶液中3-O-FQA分子在二面角τ (H3C3O1C9)附近存在结构变化,并且相比于水溶液时,3-O-FQA在DMSO溶液中该弯曲振动变慢,对应分子内相互作用减弱,说明取代基H-3周围的电子密度减小,电荷屏蔽效应减弱.Mulliken电荷分析表明,3-O-FQA中 H-3原子在H2O与DMSO溶液中的净电荷分别为0.180和0.182.因电子带负电,由此可得在DMSO溶液中H-3周围的电荷密度较小,这与振动分析结论一致.
而对4/5-O-FQA而言,计算结果表明,分子较低的振动频率在两种溶液中相差不大,且取代位原子 H-4/H-5的净电荷在两种溶液中保持一致,即4-O-FQA中H-4的净电荷在两种溶液中均为0.173,5-O-FQA中H-5的净电荷在两种溶液中均为0.164.这些事实说明4/5-O-FQA分子在两种溶液中的三维结构具有保守性,与实验结果吻合.可见,理论计算结果与实验结果一致,并且能够帮助解释实验现象.
图7
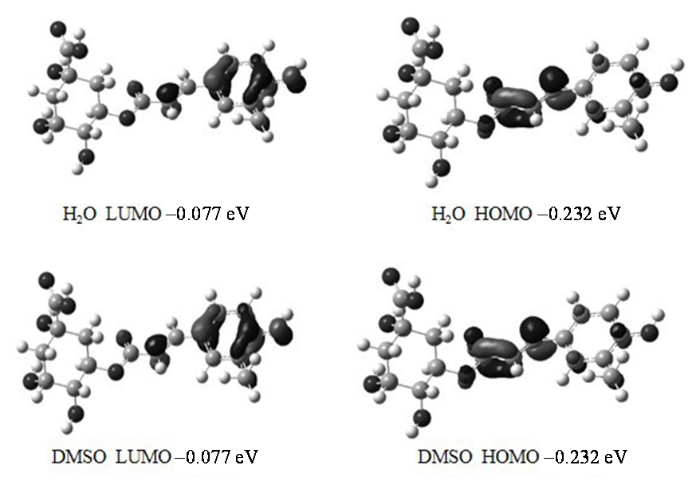
图7
3-O-FQA分别在H2O和DMSO溶液下的HOMO和LUMO轨道图
Fig. 7
HOMO and LUMO orbitals of 3-O-FQA in H2O and DMSO solutions
2.3 化学位移计算
为了深入理解体系的1H NMR谱,我们计算了3/4/5-O-FQA优化结构中的1H NMR化学位移.考虑溶剂化效应,我们以相同计算水平下四甲基硅烷(TMS)的1H NMR化学位移值来定标3/4/5-O-FQA中1H NMR化学位移计算值.为了确定计算化学位移的最佳电子结构方法,我们分别在B972/pcSseg-1、B3LYP/6-311++g(d,p)、revTPSS/pcSseg-1水平上采用GIAO方法计算了3-O-FQA在水溶液中1H NMR化学位移,计算结果见表2,原子编号如图4所示.将计算结果与实验数据比较可知,在B972/pcSseg-1、B3LYP/6-311++g(d,p)、revTPSS/pcSseg-1计算水平上,水溶液中3-O-FQA 1H NMR化学位移理论值与实验值的均方根误差分别为0.34 ppm、0.39 ppm、0.24 ppm.显然,revTPSS/pcSseg-1方法下的化学位移计算值与实验值偏差最小,即在这几种方法中revTPSS/pcSseg-1方法是最优的.因此,我们在revTPSS/pcSseg-1水平上采用GIAO方法分别计算了3/4/5-O-FQA在水溶液和DMSO溶液中的1H NMR化学位移.
表2 基于B3LYP/6-31+g(d,p)方法优化后的结构,分别在B972/pcSseg-1、B3LYP/6-311++g(d,p)、revTPSS/pcSseg-1水平上用GIAO方法计算3-O-FQA分子在水溶液中的1H NMR化学位移值
Table 2
| Method | 1H NMR | RMSD | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH-2 | δH-2’ | δH-3 | δH-4 | δH-5 | δH-6 | δH-6’ | δH’-2 | δH’-5 | δH’-6 | δH’-7 | δH’-8 | ||
| B972/ pcSseg-1 | 2.41 | 2.19 | 5.28 | 3.68 | 3.79 | 2.17 | 2.17 | 8.08 | 7.24 | 7.52 | 7.88 | 6.61 | 0.34 |
| B3LYP/ 6-311++g(d,p) | 2.33 | 2.26 | 5.30 | 3.90 | 3.91 | 2.37 | 2.30 | 8.14 | 7.16 | 7.52 | 8.17 | 6.79 | 0.39 |
| revTPSS/ pcSseg-1 | 2.46 | 2.26 | 5.32 | 3.81 | 3.85 | 2.29 | 2.25 | 7.82 | 7.02 | 7.29 | 7.60 | 6.39 | 0.24 |
| EXPa | 2.13 | 2.11 | 5.31 | 3.67 | 4.08 | 2.20 | 1.95 | 7.23 | 6.82 | 7.12 | 7.61 | 6.41 | |
a. 重水溶液中实验值摘自文献[
表3为水溶液和DMSO溶液中3/4/5-O-FQA中H-3/4/5的化学位移实验值和理论计算值,其中括号内的数是理论计算值.质子化学位移是质子周围化学环境的反映.由表3可以看出,3/4/5-O-FQA中H化学位移的计算值与实验值的RMSD在水溶液中分别为 0.13 ppm、0.17 ppm、0.13 ppm,在DMSO溶液中分别为0.10 ppm、0.33 ppm、0.21 ppm,说明我们的理论计算结果与实验结果基本吻合.由表3还可以看出,无论是实验值还是理论计算值,对两种溶液中的3/4/5-O-FQA而言,均是酯化位质子的化学位移最大,即3-O-FQA中δH-3最大,4-O-FQA中δH-4最大,5-O-FQA中δH-5最大,说明酯化位质子周围的电子密度低,电子屏蔽效应弱.这些事实说明,我们的理论计算结果有助于人们理解实验现象.另外,化学位移的理论计算结果与实验结果之间存在一定差异,可能是因为计算时采用的隐形溶剂化模型对溶剂效应的描述尚不够准确.这也是目前从理论上精确计算溶液中质子化学位移的困难所在.
表3 3/4/5-O-FQA的化学位移实验值和理论计算值(括号内)
Table 3
| 3-O-FQA | 4-O-FQA | 5-O-FQA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2O | DMSO-d6 | D2O | DMSO-d6 | D2O | DMSO-d6 | |
| δH-3 | 5.25 (5.28) | 5.34 (5.42) | 4.21 (4.21) | 3.71 (4.21) | 4.14 (4.23) | 3.99 (4.23) |
| δH-4 | 3.61 (3.68 ) | 3.67 (3.68) | 4.77 (4.90) | 4.79 (4.90) | 3.75 (3.67) | 3.48 (3.67) |
| δH-5 | 4.02 (3.79) | 3.62 (3.78) | 4.16 (3.90) | 4.17 (3.90) | 5.18 (5.39) | 5.19 (5.40) |
| RMSD | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.13 | 0.21 |
不同的分子结构和电子分布能够引起NMR谱图的差异.由图1可知,3-O-FQA中H-3谱峰在D2O溶液中为dt裂分,而在DMSO-d6溶液中为ddd裂分.谱峰裂分对分子构型非常敏感.3-O-FQA在D2O溶液和DMSO-d6溶液中二面角τ (H3C3O1C9)具有显著差异(为4.147˚),导致了两种溶液中H-3谱峰的裂分模式不同.结合3-O-FQA在两种溶液中的结构差异,我们发现在DMSO-d6中,H-3与其邻位碳上的H-2、 H-2’和H-4之间的距离分别为2.470 Å、3.066 Å和3.054 Å,因此推测这三个质子与H-3发生核自旋耦合而使H-3谱峰展现出ddd裂分模式.
3 结论
本文采用NMR波谱技术,结合量子化学计算方法,研究了3/4/5-O-FQA分别在气相、D2O溶液和DMSO-d6
溶液中的三维结构.NMR实验结果表明,3-O-FQA在D2O和DMSO-d6溶液下,1H NMR谱图中H-3裂分模式不同,而4/5-O-FQA在两种溶液中的1H NMR谱图类似.理论计算结果显示,3-O-FQA分子结构在水溶液和DMSO溶液中存在差异,主要表现在取代基H-3位置处二面角τ (H3C3O1C9)的改变,即相差4.147˚.这些结构变化导致了3-O-FQA在两种溶液中的1H NMR谱图H-3裂分模式不同,而4/5-O-FQA在两种溶液中的结构变化不明显.另外,基于优化结构的1H NMR化学位移计算、振动频率分析、Mulliken电荷分析均与实验结果一致,有助于人们深入理解实验现象.该工作给出了3/4/5-O-FQA的精确结构信息,能够为进一步研究其性质和应用价值提供参考和帮助.
利益冲突
无
致谢
我们感谢中国科学院精密测量科学与技术创新研究院刘红兵博士在NMR实验方面的帮助和讨论.
参考文献
Extraction, identification, and quantification of antioxidant phenolics from hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) shells
[J].
Bamboo shoots modulate gut microbiota, eliminate obesity in high-fat-diet-fed mice and improve lipid metabolism
[J].
A systematic review on the composition, storage, processing of bamboo shoots: Focusing the nutritional and functional benefits
[J].
Syntheses of 3-, 4-, and 5-O-feruloylquinic acids
[J].
4-O-feruloylquinic acid from green coffee beans
[J].
Chromatographic separation and identification of naturally occurring chlorogenic acids by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometry
[J].
Bioresponse-guided decomposition of roast coffee beverage and identification of key bitter taste compounds
[J].
In vitro antioxidative effects and tyrosinase inhibitory activities of seven hydroxycinnamoyl derivatives in green coffee beans
[J].
Isolation and quantification of major chlorogenic acids in three major instant coffee brands and their potential effects on H2O2-induced mitochondrial membrane depolarization and apoptosis in PC-12 cells
[J].
DOI:10.1039/c3fo60138b
PMID:24061869
[本文引用: 1]

Coffee is a most consumed drink worldwide, with potential health effects on several chronic diseases including neuronal degenerative diseases. Chlorogenic acids (CHAs) are phenolic compounds found in coffee and they are reported to have strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. However, the amounts of CHAs often vary in coffee drinks and their potential effects on ROS-induced neuronal cell death still require more investigation. Therefore, in this paper, major CHAs were isolated from three major instant coffee brands, confirmed and quantified using HPLC and NMR spectroscopic methods. Then, their antioxidant activities and protective effects on H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC-12 cells were investigated using radical scavenging, mitochondrial membrane potential and caspase assays. In the coffee samples, three major CHAs (3-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid, 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid) and some minor CHAs (3-O-feruloylquinic acid, 4-O-feruloylquinic acid, 5-O-feruloylquinic acid, 3,5-O-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3,4-O-dicaffeoylquinic acid, and 4,5-O-dicaffeoylquinic acid) were detected. The three major CHAs were further isolated and their chemical structures were confirmed using NMR spectroscopic techniques. Also, the amounts of the three major CHAs were individually quantified using a HPLC method. At the concentration of 10 μM, all three major CHAs quenched DPPH and/or xanthine oxidase-generated radical species by 21-51% (P < 0.014). They also inhibited H2O2-induced mitochondrial membrane depolarization and caspase-9 activation by 27% (P < 0.034) and 50% (P < 0.05), respectively. This study suggests that the major CHAs found in coffee are likely to be potent antioxidant compounds able to quench radical species as well as inhibit H2O2-induced apoptosis via suppressing mitochondrial membrane depolarization and caspase-9 activation in the cells.
Botanical and geographical characterization of green coffee (Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora): chemometric evaluation of phenolic and methylxanthine contents
[J].
Profile and characterization of the chlorogenic acids in green Robusta coffee beans by LC-MSn: Identification of seven new classes of compounds
[J].
Impact of microarray technology in nutrition and food research
[J].Microarrays have become standard tools for gene expression profiling as the mRNA levels of a large number of genes can be measured in a single assay. Many technical aspects concerning microarray production and laboratory usage have been addressed in great detail, but it remains still crucial to establish this technology in new research fields such as human nutrition and food-related areas. The correlation between diet and inter-individual variation in gene expression is an important and relatively unexplored issue in human nutrition. Therefore, nutritionists changed their research field dramatically from epidemiology and physiology towards the "omics" sciences. Nutrigenomics as a field of research is based on the complete knowledge of the human genome and refers to the entire spectrum of human genes that determine the interactions of nutrition with the organism. Nutrigenetics is based on the inter-individual, genetically determined differences in metabolism. Nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics carry the hope that individualized diet can improve human health and prevent nutrition-related diseases. In this article we give an overview of current DNA and protein microarray techniques (including fabrication, experimental procedure and data analysis), we describe their applications to nutrition and food research and point out the limitations, problems and pitfalls of microarray experiments.
Extraction, isolation and identification of four phenolic compounds from Pleioblastus amarus shoots and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties in vitro
[J].
Analysis of compounds in Imperata cylindrical (Beauv. ) by UPLC-ESI-MS
[J].
UPLC-ESI-MSn法分析白茅根中的化学成分
[J].
Efficient implementation of the gauge-independent atomic orbital method for NMR chemical shift calculations
[J].
A solid-state NMR study of dimethylamine cation-doped MAPbBr3 perovskite materialss
[J].
二甲基胺阳离子掺杂甲胺铅溴钙钛矿材料的固体NMR研究
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20222994
[本文引用: 1]

本文利用氘核磁共振(<sup>2</sup>H NMR)技术对阳离子掺杂铅溴钙钛矿MA<sub>0.6</sub>DMA<sub>0.4</sub>PbBr<sub>3</sub>中内嵌阳离子的运动状态进行了较为深入的研究.通过对二甲基胺(DMA)和甲胺(MA)阳离子的选择性氘代,我们实现了对上述材料中不同内嵌阳离子的选择性NMR观测.研究结果显示,在低温下,该材料中的DMA与MA阳离子都接近于双重旋转模型;随着温度升高,DMA与MA阳离子的运动自由度增加,其运动逐步转变为快速各向同性运动.且在相同温度时,DMA阳离子比MA阳离子运动更快,表明该材料中阳离子运动状态不一致.在对阳离子运动研究的基础上,我们对该材料相结构转变的分子机制进行了探讨.
Hydrothermal crystallization of niobium oxide nanorods studied by 93Nb nuclear magnetic resonance
[J].
93Nb核磁共振研究铌酸纳米棒的水热晶化机理
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20233061
[本文引用: 1]

氧化铌(Nb<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub>)及其水合物铌酸(Nb<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub>·nH<sub>2</sub>O)代表了一类重要的多相催化剂,然而其水热合成过程和机理尚不明确.本文采用<sup>93</sup>Nb NMR,结合X射线粉末衍射、透射电镜等技术和量化计算,研究了以草酸铌铵为前驱体水热生成铌酸纳米棒的晶化过程.结果表明草酸铌铵水热晶化过程中发生了水解-聚合反应,先是草酸铌铵水解,接着铌氧单体之间发生缩水聚合反应,最终生成了层内无序、层间有序结构的固体铌酸纳米棒.晶化过程符合“液相成核”机理,层状结构铌酸纳米棒在180 ℃下1 h内即可生成,后续水热处理并未使其明显长大,新的固体产物不断由溶液中独立生成.