引言
核磁共振(Nuclear Magnetic Resonance,NMR)技术相较于其他检测方法,具有非侵入式和无损分析样品的显著优势,已在化学分析和医学影像领域得到了广泛应用[1-
近年来,国内外多个研究团队对磁共振微线圈进行了研究.Wu等[11]设计了一种基于印刷电路板(Printed Circuit Board,PCB)的平面微型线圈.该线圈采用螺旋结构,螺旋引线两端分别与两个焊盘相连,并通过引线键合技术,将焊盘与外部调谐电路进行有效连接.石英玻璃样品管则平放在PCB板上,并固定于螺旋线圈的中心区域,以确保样品与射频场的有效耦合.该方案降低了微线圈的制作难度,缩短了制作周期,但平面线圈结构产生的射频场均匀性较差,且螺旋线圈外层引线对中心区域射频场的贡献较小,却产生了较大电阻,从而增加了热噪声.另外,Davoodi等[12]采用高精度的微机电系统技术(Micro-Electro-Mechanical System,MEMS),在厚度为100 μm的玻璃基板上键合金线以形成线圈,该线圈未进行调谐,直接通过同轴线连接至射频前端.该设计通过去除调谐和匹配电路,以实现宽频探测,但未充分考虑线圈与功率放大器之间阻抗不匹配导致的功率反射问题.Murphree等[13]利用传输线特征阻抗在宽频范围内保持恒定的特性,设计了一种基于传输线的马鞍形宽带线圈.其制作方式是在柔性电路板的一面刻蚀马鞍形线圈走线,另一面则进行完整的覆铜,作为线圈的参考层,形成具有稳定特征阻抗的结构,最终将柔性电路板缠绕于样品管外部,以形成马鞍形线圈.该方案在未对线圈进行调谐的情况下,成功实现了多个元素的NMR信号检测.然而,由于传输线结构中的参考层限制了射频场的分布,射频激发区域主要集中在线圈走线附近,导致样品的中心区域部分未能被有效激发,从而显著降低了射频激发效率.
综合来看,尽管磁共振微型线圈领域的研究与设计已取得了一定进展,但进一步提升射频场均匀性、降低热噪声、优化射频激发效率和提高信噪比,仍然是实现微量样品高灵敏度探测的重要挑战.针对以上问题,本文提出了一种新型微线圈设计方案,利用PCB工艺制作了多层板微线圈,每层板上的线圈结构一致,不同板层上的线圈采用串联连接.单个板层上设计了多匝线圈,每匝线圈之间采用并联连接.这样的结构设计,在提高样品区域射频场均匀度的同时,减小了线圈的电阻和电感,以便能在宽频范围内更好地进行射频激发和磁共振信号探测.
1 设计方案
随着电磁场仿真软件的不断发展和日益完善,磁共振线圈的设计过程变得更加高效和精确.本研究采用有限元分析软件对线圈的射频激发效率、均匀度、电阻等关键参数进行了仿真分析,优化其信噪比和宽频激发效率,确保微型线圈能够实现高效的信号收发,从而满足高性能磁共振探测的需求.
1.1 宽频微线圈探头实现方法
目前,传统商业化宽频探头采用多谐振电路设计,使用电容和电感对线圈进行调谐与匹配,以实现对不同元素的检测.但多谐振电路的引入不仅使整体电路结构更加复杂,探头整体体积也更庞大.
本设计为避免额外引入电容和电感,且希望微线圈能在宽频范围内有效地发射射频功率.因此,在微线圈结构设计时,尽量减小线圈电感,使其阻抗在宽频范围内变化较小.在发射期间,通过将微线圈与一个阻性负载串联,共同构成一个接近50 Ω的终端负载,这样直接使用常规的射频放大器,就能在宽频范围内实现阻抗匹配,从而减少功率反射,提高传输效率;在接收期间,通过T/R开关控制断开阻性负载,使线圈接收到的NMR信号直接耦合至高输入阻抗的宽频前置放大器,这种设计避免了负载电阻对接收信噪比的不利影响,有效降低了系统噪声,提高了宽频检测的性能.
1.2 微线圈SNR分析
当微线圈被用来接收磁共振信号时,SNR是评估NMR波谱和成像质量的重要指标.在对样品施加90˚激励脉冲后,射频线圈的输出SNR为[14]:
(1)式中,
对于给定了核磁矩、主磁场和样品温度情况下,线圈SNR可表示为:
进一步,对于一个线圈直径为d、长度为l的螺线管线圈,其灵敏度可由以下公式表示[14]:
其中,
由(3)式可知,在样品体积
1.3 多层板微线圈结构设计与参数仿真
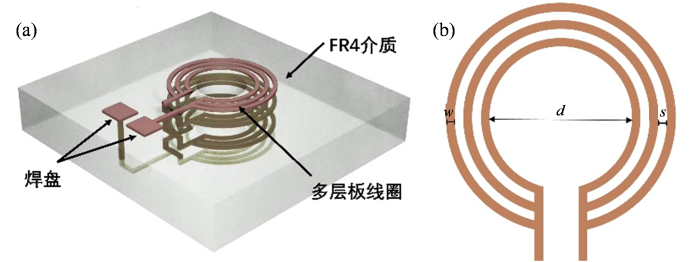
图1
图1
线圈结构示意图. (a)线圈立体结构;(b)单层微线圈平面结构
Fig.1
Schematic of the coil structure. (a) Three-dimensional structure of the coil; (b) Planar structure of the single-layer microcoil
多层板微线圈几何参数有线圈层数m、单层线圈并联匝数n、线圈厚度h、线宽w、单层线圈匝间距s和内径d.实验所采用样品管外径为0.65 mm,受到PCB工艺最小分辨率限制,d设计为1.1 mm.在保持d固定的情况下,随着s的增加,各匝线圈的半径也会随之增大,由于外匝线圈走线产生的射频场对样品中心的贡献较小,且随着线圈半径的增加,这一贡献进一步减弱,从而导致射频激发效率和SNR下降.为了提高射频激发效率,应尽可能减小线圈的s,因此设置s为0.1 mm.在磁共振波谱实验中,线圈的工作频率通常在数兆Hz到数百兆Hz之间,此时铜线圈的趋肤深度通常小于30 μm,增加线圈厚度无法有效降低线圈电阻,因此h设计为一盎司铜厚(35 μm).w的增加,能够有效降低线圈电阻,但各匝线圈的等效直径变大,降低了射频激发效率,因此折中选择w为0.1 mm.另外,随着n的增加,单层线圈的整体电阻降低,然而内层线圈的电流分配减少,导致其灵敏度下降,下文将对m和n的选择进行具体分析.
当样品量一定时,线圈信噪比由线圈射频场激发效率和电阻决定.因此,通过对多层板线圈在不同m和n下的射频场激发效率和电阻变化进行仿真分析,可以定量评估不同几何参数对线圈性能的影响.
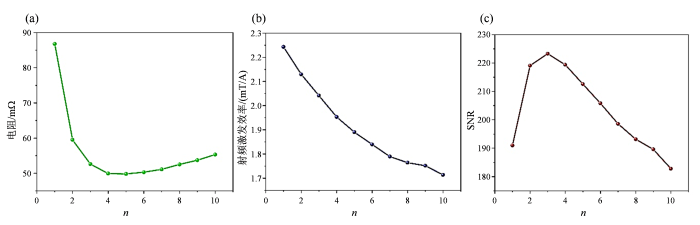
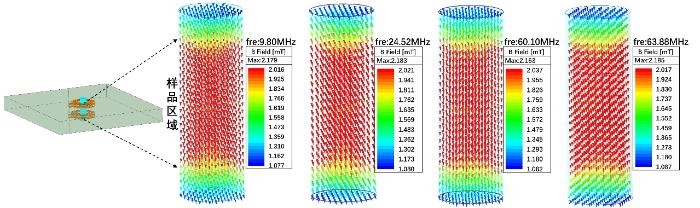
相比于每层线圈的n,m对射频场均匀性的影响更为显著.但是,增加电路板层数在提升射频场均匀性的同时,也会导致线圈电感增大,进而引起功率反射增加.为优化m,本研究对两层、四层和六层电路板线圈的射频场均匀度进行了仿真分析,三种线圈的每层并联匝数n保持三不变.仿真结果表明,两层、四层和六层板线圈的射频场均匀度[15]分别为27.5%、4.9%和3.1%.四层与六层板线圈的均匀性差异较小,且显著优于两层板线圈,但六层板线圈的电感是四层板线圈的两倍以上.因此,综合以上分析选择四层板线圈方案进行进一步优化.利用有限元电磁仿真软件对四层板线圈进行建模,设置线圈材料为铜,叠层材料为环氧玻璃纤维布阻燃板(Flame Retardant 4,FR4).采用大小为1 A、频率为63.88 MHz的电流进行激励.四层板的每层线圈采用多匝线并联结构,图2展示了线圈各项性能随四层板每层线圈并联匝数n变化的仿真结果.由图2(a)可知,随着n的增加,电阻先减小,随后增大.这一变化是由于n的增加,连接各匝线圈的走线长度增加,从而引起电阻增大.图2(b)显示了射频激发效率随n增加呈现下降趋势.这是由于内层线圈所分配的电流逐渐减少,而内层线圈在射频激发过程中起着至关重要的作用,因此其电流的降低直接影响了整体射频激发效率.图2(c)展示了随着每层线圈n的增加,其线圈信噪比的变化.其中,四层板三匝线圈表现出最佳信噪比.进一步对四层板三匝线圈的电阻和电感进行仿真,结果分别为52.64 mΩ和17.81 nH,电阻和电感均较小. 此外,考虑到趋肤效应的影响,频率不同的激励源可能会导致线圈中电流分布不同,从而影响射频场分布. 为评估这一影响,本研究在9.80 MHz、24.52 MHz、60.10 MHz和63.88 MHz四个频率激励下对四层板三匝线圈样品区域内的射频场分布进行仿真.如图3所示,四种激励源下的射频场均匀度都小于5%,表明不同频率下的射频场均匀性良好.以上仿真结果表明,四层板三匝线圈在信噪比与射频场均匀性上均表现出较好的特性,后续按此进行设计和加工,并进行测试和实验验证.
图2
图2
四层板线圈有限元电磁场仿真结果. (a)电阻、(b)射频激发效率和(c) SNR随n变化
Fig. 2
The finite element electromagnetic field simulation results for the four-layer coil. (a) Resistance, (b) RF excitation efficiency and (c) signal-to-noise ratio as a function of the number of parallel turns per layer coil
图3
图3
不同频率激励源下四层板三匝线圈B1场分布
Fig.3
The B1 field distribution of a three-turn coil on a four-layer PCB under different frequency excitations
2 探头制作与性能测试
2.1 探头制作
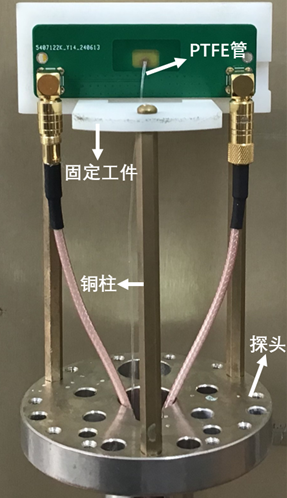
本设计中,线圈产生的射频场方向垂直于PCB板表面,为满足射频场对核自旋的高效激励,以及接收到最强的磁共振信号,主磁场方向应与射频场方向垂直,即平行于PCB板面.如图4所示,利用3D打印技术制作一个固定工件,电路板平放固定在工件上,工件通过三根铜柱与探头部分固定.聚四氟乙烯(Polytetrafluoroethylene,PTFE)管作为样品管,从线圈中心位置穿过PCB板,并利用医用无菌注射器将样品推至管内.
图4
2.2 线圈电性能测试
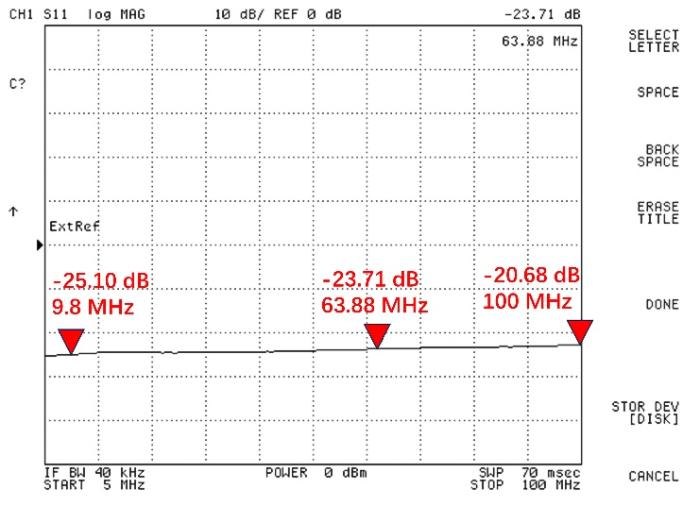
发射期间,为了确保射频功率能够高效地传输至线圈从而激发样品,利用网络分析仪(Agilent 4396B)在5~100 MHz对多层板微线圈的电性能进行测试.微线圈与48 Ω纯电阻负载串联共同构成终端负载,连接至网络分析仪的一端口进行测试. 由图5可知,在5~100 MHz范围内,S11都优于-20.68 dB,传输效率较高.
图5
2.3 磁共振波谱实验
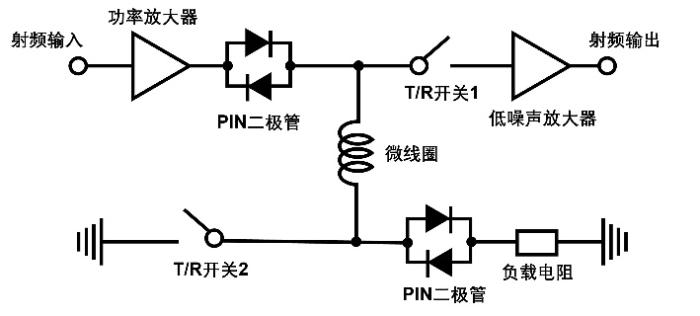
为测试该微线圈的性能,本研究在实验室的磁共振平台上进行了性能测试,测试设备包括上海康达卡勒幅医疗科技有限公司研发的1.5 T超导磁体、TOMCO公司BT00500-AlphaSA系列功率放大器和上海市磁共振重点实验室自研的宽频射频前端组件T/R开关[16]、自研Dispect谱仪和低噪声放大器.
实验测试框图如图6所示.发射期间,两个T/R开关同时断开,射频脉冲由谱仪发出,经过功率放大器放大后,最终主要被终端负载吸收,流经线圈的电流产生射频场以激发样品.接收期间,两个开关同时闭合,此时负载短路.由于磁共振信号极其微弱,无法导通PIN(Positive Intrinsic Negative)二极管,信号直接耦合至高阻前放以实现对磁共振信号的低噪声放大.
图6
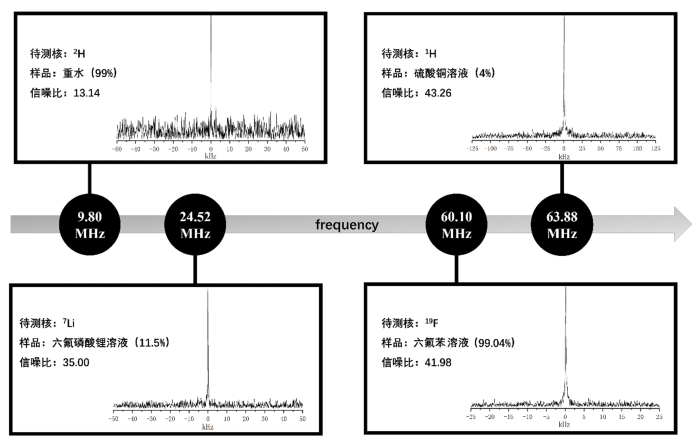
选取质量浓度为4%硫酸铜(CuSO4)水溶液(上海麦克林化科技有限公司)、11.5%六氟磷酸锂(LiPF6,上海麦克林化科技有限公司)溶液、99. 04%六氟苯(C6F6,上海麦克林化科技有限公司)溶液和99%重水(D2O,上海麦克林化科技有限公司)作为样品溶液,分别探测1H、7Li、19F和2H原子核的自由感应衰减信号.本实验待测样品体积为250 nL,实验过程中无需进行任何调谐和匹配操作,仅需更换待测样品.实验参数如表1所示,最终实验结果如图7所示,在9.80~63.88 MHz频率范围内依次记录了4种不同原子核的波谱.1H和19F在累加次数为50次的情况下,SNR分别为43.26和41.98.2H和7Li核分别在累加次数为100和500次的情况下,信噪比分别为13.14和35.00.通过实验测试和分析,验证了多层板微线圈良好的宽频性能.此外,本研究在无样品情况下对FR4材料中的1H信号进行采集.实验参数与检测硫酸铜溶液中的1H信号时保持一致(见表1).测试结果表明,未发现明显的1H信号,表明FR4对样品中的1H信号检测影响可忽略.
表1 磁共振波谱宽频探测实验参数
Table 1
| 参数名称 | 参数设置 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原子核 | 2H | 7Li | 19F | 1H |
| 样品 | 99%重水 | 11.5%六氟磷酸锂溶液 | 99. 04%六氟苯溶液 | 4%硫酸铜溶液 |
| 中心频率 | 9.80 MHz | 24.52 MHz | 60.10 MHz | 63.88 MHz |
| 接收带宽 | 100 kHz | 100 kHz | 50 kHz | 250 kHz |
| 射频脉宽 | 45 μs | 28 μs | 15 μs | 15 μs |
| 发射功率 | 30% | 20% | 16% | 14.5% |
| 累加次数 | 100 | 500 | 50 | 50 |
图7
图7
磁共振波谱实验测试谱图
Fig. 7
Experimental test spectrum of magnetic resonance spectroscopy
3 结论
本文基于PCB工艺设计制作了一款具有射频场均匀性较好、电阻和电感均较小的宽频微线圈.该线圈未经过任何调谐匹配操作,即在9.80~63.88 MHz频率范围内探测到了多个元素的磁共振信号,初步验证了宽频微线圈性能.该设计方案大大降低了制作成本,且在保证性能的基础上,降低了检测的复杂性.后续本课题组考虑选用陶瓷材料作为PCB板介质层,以防止引入额外的干扰信号,并将设计低阻输出的射频功放,直接驱动低阻的微线圈,进一步降低功率消耗,提高发射效率.
利益冲突
无
参考文献
A roadmap to high-resolution standard microcoil MAS NMR spectroscopy for metabolomics
[J].
Hidden chemical order in disordered Ba7Nb4MoO20 revealed by resonant X-ray diffraction and solid-state NMR
[J].
NMR metabolomics methods for investigating disease
[J].DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04606 PMID:36625102 [本文引用: 1]
Investigation of dynamic structure of protein encountering complex with paramagnetic NMR
[J].
顺磁核磁共振技术研究蛋白质遭遇复合物的动态结构
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20223035
[本文引用: 1]

蛋白质依靠短程相互作用识别配体蛋白进而行使生物学功能,其相互作用界面仅占据蛋白质总表面积的一部分.因此,蛋白质与配体蛋白需要形成一系列遭遇复合物系综结构来减少构象搜索空间以加快结合速度.由于遭遇复合物在溶液体系中存在时间短、丰度低,因而很难被传统结构生物学技术捕捉到.本文选用组氨酸磷酸载体蛋白(HPr)和酶II(EIIA<sup>Glc</sup>)复合物为研究体系,采用顺磁弛豫增强(Paramagnetic Relaxation Enhancement,PRE)技术对遭遇复合物的系综结构及动力学性质进行表征,并用分子动力学模拟方法对实验结果进行验证,发现HPr在溶液体系中首先与EIIA<sup>Glc</sup>在3个方向上形成遭遇复合物,进而促进特异性复合物的形成.该方法不仅能够在溶液体系中观察遭遇复合物系综结构,还有望应用于生物大分子领域,揭示蛋白质在复杂生理网络中的相互作用机制及动力学行为.
Identification and structural characterization of an unknown trace degradation impurity in cabazitaxel injection by LC-DAD-SPE-NMR/MS
[J].
LC-DAD-SPE-NMR/MS技术用于卡巴他赛注射液中微量未知杂质的鉴定
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20243122
[本文引用: 1]

本研究采用液相色谱-二极管阵列检测器-固相萃取-核磁共振/质谱(LC-DAD-SPE-NMR/MS)联用技术,对卡巴他赛注射液中一个含量约为0.3%~0.4%的未知降解杂质完成化学结构解析. 卡巴他赛注射液中高含量的辅料吐温-80与该杂质在液相色谱分析中不能完全分离,直接制备高纯度杂质难度较大,因此难以采用先分离-后鉴定的传统策略鉴定该杂质. 本研究采用自动化的LC-DAD-SPE-NMR/MS联用技术,通过对萃取物溶液进行NMR谱详细分析,提取出降解杂质中氢-氢、氢-碳原子间相关信息,得到原子化学位移及连接关系,成功排除吐温-80谱峰的干扰,最终鉴定降解杂质为卡巴他赛中紫杉烷母核重排后的产物. 整个实验在48 h之内完成,并以混合物分析思路完成降解杂质结构解析. 本研究是LC-DAD-SPE-NMR联用技术在微量药物杂质分析领域的一次成功应用实例,为新药研究中杂质结构解析提供了新思路.
Planar microcoil arrays for in vitro cellular-level micromagnetic activation of neurons
[J].
Exploring multivalent carbohydrate-protein interactions by NMR
[J].
DOI:10.1039/d2cs00983h
PMID:36753338
[本文引用: 1]

Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) has been widely employed to assess diverse features of glycan-protein molecular recognition events. Different types of qualitative and quantitative information at different degrees of resolution and complexity can be extracted from the proper application of the available NMR-techniques. In fact, affinity, structural, kinetic, conformational, and dynamic characteristics of the binding process are available. Nevertheless, except in particular cases, the affinity of lectin-sugar interactions is weak, mostly at the low mM range. This feature is overcome in biological processes by using multivalency, thus augmenting the strength of the binding. However, the application of NMR methods to monitor multivalent lectin-glycan interactions is intrinsically challenging. It is well known that when large macromolecular complexes are formed, the NMR signals disappear from the NMR spectrum, due to the existence of fast transverse relaxation, related to the large size and exchange features. Indeed, at the heart of the molecular recognition event, the associated free-bound chemical exchange process for both partners takes place in a particular timescale. Thus, these factors have to be considered and overcome. In this review article, we have distinguished, in a subjective manner, the existence of multivalent presentations in the glycan or in the lectin. From the glycan perspective, we have also considered whether multiple epitopes of a given ligand are presented in the same linear chain of a saccharide (, poly-LacNAc oligosaccharides) or decorating different arms of a multiantennae scaffold, either natural (as in multiantennae -glycans) or synthetic (of dendrimer or polymer nature). From the lectin perspective, the presence of an individual binding site at every monomer of a multimeric lectin may also have key consequences for the binding event at different levels of complexity.
Three-dimensional NMR microscopy: improving SNR with temperature and microcoils
[J].It is widely held that the spatial resolution achievable by NMR microscopic imaging is limited in biological systems by diffusion to approximately 1-5 microns. However, these estimates were developed for specific imaging techniques and represent practical rather than fundamental limits. NMR imaging is limited by the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Diffusion effects on spatial resolution can be made arbitrarily small in principle by increasing the gradient strength. The exponential signal attenuation from random spin motion in a gradient, however, will reduce the signal far below the noise level when the voxel size is reduced much below 5 microns. Two factors can be optimized to improve the SNR: (1) the inductive linkage between microscopic samples and the detection apparatus and (2) the temperature of the rf probe. In this work, the filling factor was optimized using inductors with diameters less than 1 mm. It is furthermore shown that probe circuit cooling results in significant improvements in SNR, whereas cooling of the preamplifier is of little value when proper noise matching between the resonant circuit and preamplifier is accomplished. Using three-dimensional Fourier imaging techniques, we have obtained images of single-cell organisms with spatial resolution of approximately 6 microns. Practical limitations include mechanical stability of the apparatus, thermal shielding between the sample and probe, and the magnetic susceptibility of the sample.
In vivo magnetic resonance microscopy at 5 μm
[J].
Nuclear magnetic resonance microscopy with 4 μm resolution: Theoretical study and experimental results
[J].
Untuned broadband spiral micro-coils achieve sensitive multi-nuclear NMR TX/RX from microfluidic samples
[J].
DOI:10.1038/s41598-021-87247-2
PMID:33833324
[本文引用: 1]

The low frequency plateau in the frequency response of an untuned micro-resonator permits broadband radio-frequency reception, albeit at the expense of optimal signal-to-noise ratio for a particular nucleus. In this contribution we determine useful figures of merit for broadband micro-coils, and thereby explore the parametric design space towards acceptable simultaneous excitation and reception of a microfluidic sample over a wide frequency band ranging from C to H, i.e., 125-500 MHz in an 11.74 T magnet. The detector achieves 37% of the performance of a comparably sized, tuned and matched resonator, and a linewidth of 17 ppb using standard magnet shims. The use of broadband detectors circumvents numerous difficulties introduced by multi-resonant RF detector circuits, including sample loading effects on matching, channel isolation, and field distortion.
An easily constructed, tuning free, ultra-broadband probe for NMR
[J].We have developed an easy to construct, non-resonant wideband NMR probe. The probe is of the saddle coil geometry and is designed such that the coil itself forms a transmission line. The probe thus requires no tuning or matching elements. We use the probe with a spectrometer whose duplexer circuitry employs a simple RF switch instead of the more common lambda/4 lines, so the entire probe and spectrometer perform in an essentially frequency-independent manner. Despite being designed with electro- and magnetostatic formulas, the probe performs well at frequencies up to 150 MHz and beyond. We expect that with additional design effort, the probe could be modified for use at significantly higher frequencies. Because our construction method relies on commercial circuit fabrication techniques, identical probes can be easily and accurately produced.
Design and analysis of microcoils for NMR microscopy
[J].
A balanced T/R switch for wideband NMR front-end
[J].