引言
磁共振成像(Magnetic Resonance Imaging,MRI)是一种利用强磁场和无线电波成像的医学影像技术,由于其不依赖于电离辐射(如X射线),因此相较于CT扫描和传统X光,具有更高的安全性,被广泛用于临床诊断和医学研究之中[1]. 虽然MRI技术在图像质量和诊断精度上具有无可替代的优势,然而其较长的扫描时间也给临床应用发展带来了挑战. 并行磁共振成像(Parallel Magnetic Resonance Imaging,PMRI)技术通过同时使用多个接收线圈来加快数据采集过程,缩短扫描时间,并在提高患者舒适度的同时,保持较高的图像质量,在多个临床应用场景中展现出巨大潜力[2]. 例如,磁共振心脏成像(Cardiac MRI,CMRI)需要使用心电门控并要求患者屏息,PMRI技术通过缩短扫描时间、减少屏息次数,提升了CMRI的可行性和舒适度,同时在儿童、老年人、无法保持静止的患者及急症场景中,降低了因长时间扫描而导致的运动伪影风险,提高了图像质量和诊断准确性. 合理的利用快速采集技术不但可以缩短MRI的检查时间,还可以大大提高检查质量,是当今磁共振技术发展的主流方向之一[3].
大多数临床扫描PMRI方法是利用灵敏度编码(Sensitivity Encoding,SENSE)[4]和广义自动校准部分并行采集(Generalized Auto Calibrating Partially Parallel Acquisitions,GRAPPA)[5]. 其中SENSE是一种基于图像域的并行成像方法,通过预扫描获取多个接收线圈的灵敏度图(Sensitivity Map),并结合这些信息来加速数据采集和图像重建. 而GRAPPA是一种基于K空间插值的并行成像算法,它通过使用自校准的部分采样数据来填补K空间中的缺失部分,从而加速扫描过程. 在GRAPPA的基础上,Zhao等[6]提出了基于GRAPPA的迭代重建方法,通过迭代地应用GRAPPA重新估计相位编码线并细化权重,从而减少了并行成像伪影. 此外,虚拟线圈概念(Virtual Coil Concept,VCC)不需要额外的物理硬件支持,通过数学建模生成额外接收通道,能够提升并行成像技术的加速因子,缩短扫描时间,并改善图像质量,在快速成像和高分辨率成像等应用场景中,虚拟线圈技术具有巨大的潜力. 例如Blaimer等[7]通过应用VCC到GRAPPA重建中,显著提升了并行成像技术的加速因子,实现了4~7倍加速成像. Wang等[8]利用磁共振线圈数据的复数共轭对称性质扩展了多层同时激发成像(Simultaneous Multi-Slice Imaging,SMS)所获取的多通道数据,实现了高质量的SMS图像重建.
近年来,随着深度学习技术的迅速发展,其在MRI中的应用逐渐得到深入探索. 目前为止,MRI重建的关键方法主要依赖于在大量数据集上进行训练,通常需要基于完全采样的数据构建大型训练数据库[9,10]. 由于训练过程对数据的需求量非常大,缺乏足够的高质量医学影像数据可能导致训练效果不理想,甚至可能导致重建图像的质量下降. 因此,如何有效利用有限的医学影像数据并提升重建精度,成为当前MRI重建研究中的一大挑战. 为了解决普遍性和数据可用性问题,Akçakaya等[11]提出了一种基于K空间插值的鲁棒性人工神经网络(Scan-specific Robust Artificial-neural-networks for K-space Interpolation,RAKI). 该算法无需借助外部数据库,而是通过利用特定扫描过程中额外采集的自动校准信号(Auto Calibration Signal,ACS)作为参考数据,进行欠采样数据与完整采样数据之间的映射学习,利用这种映射关系对欠采样的K空间进行恢复并重建. 基于RAKI算法的框架,Zhang等[12]提出了基于K空间插值的残差鲁棒人工神经网络(Residual Scan-specific Robust Artificial-neural-networks for K-space Interpolation,rRAKI). 该方法通过跳跃连接将非线性卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)与线性卷积结合,实现了针对特定扫描的深度学习网络重建,有效提高了图像重建的质量,并有效减小了高欠采样率下的卷褶伪影问题.
在PMRI中,理论上可实现的最大加速因子通常受到接收线圈数量的限制. 当前,二维MRI中常见的加速因子一般为2~4倍,随着加速因子的增加,较少的网络训练ACS参考数据可能导致噪声的显著放大,进而影响重建结果的质量[13]. 而较多的ACS会大幅度增加扫描时间. 在机器学习领域,针对有限训练数据的问题,常采用增强[14]、迁移学习[15]、生成对抗网络[16]学技术策略. 如何在ACS数量有限的情况下尽量提高加速倍率是亟待解决的问题[17-
1 理论与方法
1.1 VCC原理
VCC是一种在MRI领域中用于并行成像技术的创新概念,旨在通过数学模型或算法模拟出额外的接收线圈,从而提高成像速度和图像质量,而不需要物理上增加实际的线圈. 这种技术的核心在于利用现有的线圈信号和空间信息,通过算法合成出“虚拟”的接收通道,以优化并行成像过程,以此来减小噪声放大对重建图像质量的影响[7]. 具体来说,从线圈
其中,
其中*表示复共轭运算. 根据(2)式,信号可以被解释为来自一个虚拟线圈的信号,该线圈具有复敏感度分布
1.2 GRAPPA重建原理
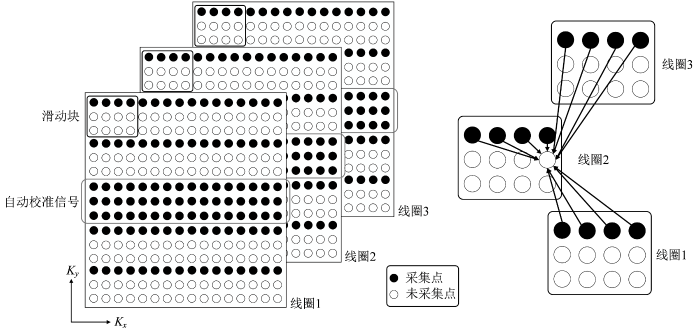
图1
通常,在重建线圈
上式中
1.3 RAKI重建原理
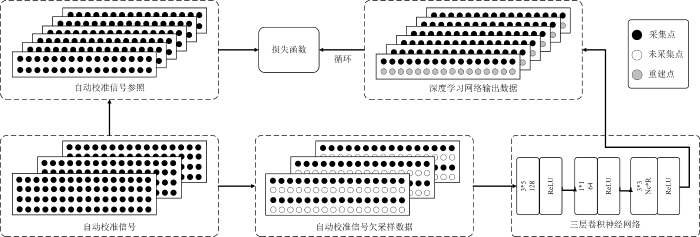
RAKI通过使用多个紧凑型CNN代替传统的线性卷积核,从而实现对特定扫描任务的非线性K空间插值. 算法的训练流程如图2所示. 具体而言,ACS在按照输入数据的欠采样率
图2
1.4 本文提出的网络框架
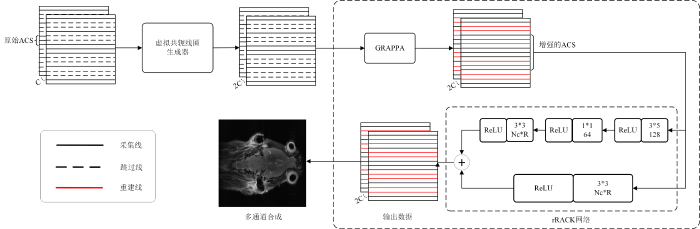
针对训练数据较为有限情况下的磁共振并行成像问题,本文提出了一种结合虚拟共轭线圈与GRAPPA增强网络的PMRI方法,其总体架构如图3所示.
图3
该方法的核心组成部分包括虚拟共轭线圈生成器、GRAPPA模块以及rRAKI网络. 具体而言,虚拟共轭线圈生成器首先利用输入的均匀欠采样K空间数据生成扩展数据,然后通过GRAPPA模块对扩展数据进行线性K空间插值,从而获得扩展增强的ACS. 这些增强后的ACS数据被输入到深度学习网络中进行训练,以建立输入数据与目标数据之间的映射关系. 网络部分
1.5 损失函数
所提算法所采用的损失函数为
其中,
1.6 所提方法伪代码表述
伪代码表示如下所示:
(1)对于一组多通道磁共振均匀欠采样数据
(2)利用磁共振K空间虚拟共轭特性生成多一倍的欠采样数据
(3)使用GRAPPA算法利用
(4)通过截取
(5)设迭代上限
(6)根据设置的迭代上限
(7)迭代训练循环完成后,获得的多通道插值数据
2 实验与结果分析
2.1 实验数据
为了验证所提方法的有效性,本研究使用了合肥综合性国家科学中心能源研究院自主研发的7 T MRI系统实机采集的K空间数据样本进行性能评估. 实验使用的为健康的小鼠,年龄约为8~10周,体重大约300~350 g. 通过快速自旋回波(FSE, Fast Spin Echo)序列对实验鼠进行约100次不同平面的扫描,序列的回波时间(Echo Time,TE)为39.87 ms,重复时间(Repetition Time,TR)为3 000 ms,切片厚度为1.0 mm,回波链长度(Echo Train Length,ETL)为8,扫描方向覆盖横断位(Axial)、矢状位(Sagittal)和冠状位(Coronal),激发次数(Number of Excitations,NEX)为2,以确保高质量的解剖图像. 单次扫描数据包含8个通道,每个通道采集样本的空间分辨率为
2.2 评价指标
本文采用了三种常用的图像质量评价指标对网络重建结果进行了评价,分别为标准化均方根误差(Normalized Root Mean Squared Error,NRMSE)、峰值信噪比(Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio,PSNR)和结构相似度指数(Structural Similarity,SSIM). 这些指标能够从不同角度全面反映重建图像的质量,涵盖了误差度量、信号保真度以及结构一致性等方面的评价标准.
NRMSE是均方误差(Mean Squared Error,RMSE)的归一化版本,旨在将误差相对于信号的幅度进行标准化. 它的计算公式为:
其中,
PSNR是衡量重建图像与原始图像之间信噪比的指标,通常用于评估图像压缩质量. 其计算公式为:
其中,
SSIM是一种评估两幅图像之间结构相似性的指标,考虑了亮度、对比度和结构三个方面. 其公式为:
其中,
2.3 实验环境与超参数设置
训练和测试过程在基于NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti显卡(4GB显存)的计算平台上进行.
在实验设置中,首先设置了GRAPPA算法的参数,根据实验,卷积核较低会使得GRAPPA重建结果出现过多未插值的数据行,而过大的卷积核(大于10×10)使得重建速度过慢,综合考虑设置卷积核大小为(8, 8),表示使用8×8的卷积核来进行插值操作;正则化因子设置为0.01,用于平衡数据拟合与平滑解之间的权重,从而避免过拟合. 对于深度学习网络参数,其中批次大小(Batch Size)为20,并采用Adam优化器进行参数优化,初始学习率设置为0.01. 此外,为了动态调整学习率,使用了StepLR学习率调度器. 在预定的训练轮次(Epoch)为15、40和45时,学习率将乘以衰减因子0.1,以实现逐步降低学习率的效果. 整个训练过程共进行100个epochs,每个epoch包含30次迭代,确保充分的模型训练和收敛.
2.4 实验结果
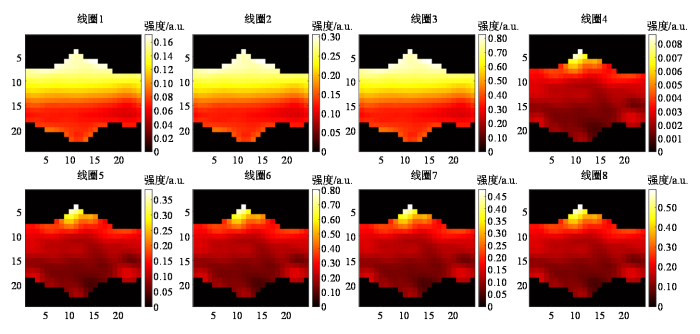
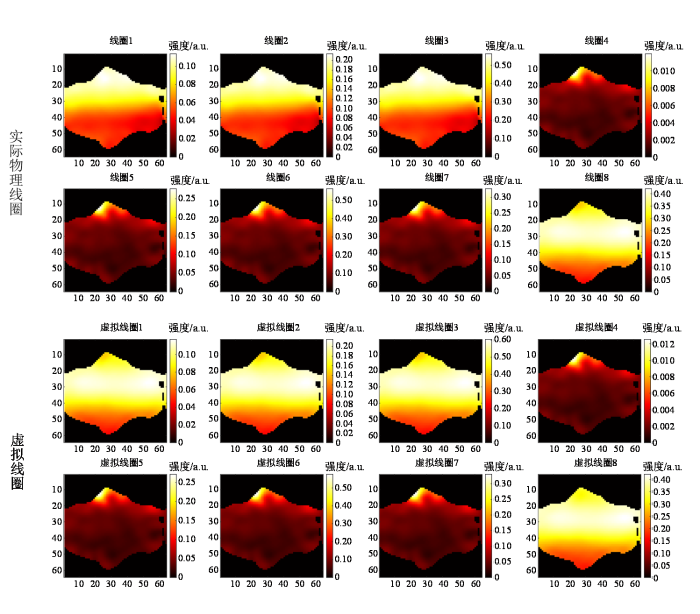
为了说明虚拟线圈扩充与GRAPPA增强方法对线圈灵敏度估计的提升效果,分别对ACS增强前后的线圈灵敏度图进行了展示. 在7 T MRI采集样本上,未使用所提方法前的欠采样K空间ACS数目为24,加速因子为8. 对ACS中间24×24区域的数据进行灵敏度计算,得到的8通道线圈灵敏度图如图4所示. 灵敏度计算过程如下:首先,利用该ACS区域,通过尺寸为m×m的滑动窗口提取各线圈数据,构造校准矩阵
图4
图5
在合肥综合性国家科学中心能源研究院7 T MRI采集样本(通过快速自旋回波序列采集的健康小鼠脑部横断位、冠状位和矢状位解剖图样本)上,对所提方法与其他先进重建方法进行了比较,测试条件包括不同的ACS数目和不同的R,测试结果如表1所示. 针对同一小鼠,我们分别获取了其在横断位、冠状位和矢状位上的数据. 文中所展示结果为每个解剖方位进行多次重复实验后计算的平均值,最优值已加粗显示. 实验结果表明,所提方法在各项性能指标上均表现出色,尤其在低ACS数目下,例如ACS = 10,R = 5,相比于rRAKI方法,所提方法的NRMSE显著降低了88.43%,SSIM提高了21.70%,PSNR提高了33.99%. 这些结果表明,所提方法通过虚拟共轭线圈生成额外的训练数据,并结合GRAPPA方法扩展了自动校准信号的数量,从而增强了数据的多样性和规模,这一改进有效提升了模型的泛化能力和鲁棒性,使得重建结果在图像质量上取得了显著提高.
表1 不同算法的评价指标对比结果
Table 1
| ACS | R | 算法 | NRMSE | SSIM | PSNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 4 | ZF | 0.3311 | 0.8475 | 23.8473 |
| GRAPPA | 0.0240 | 0.9248 | 35.2355 | ||
| RAKI | 0.0757 | 0.9282 | 30.2510 | ||
| rRAKI | 0.0702 | 0.9391 | 30.5825 | ||
| 本文方法 | 0.0108 | 0.9679 | 38.6888 | ||
| 10 | 5 | ZF | 0.6210 | 0.7924 | 21.1159 |
| GRAPPA | 0.0787 | 0.8544 | 30.0844 | ||
| RAKI | 0.2532 | 0.7941 | 25.0115 | ||
| rRAKI | 0.1954 | 0.7880 | 26.1367 | ||
| 本文方法 | 0.0226 | 0.9547 | 35.0208 | ||
| 18 | 6 | ZF | 0.2651 | 0.8599 | 24.2725 |
| GRAPPA | 0.1346 | 0.8069 | 27.7540 | ||
| RAKI | 0.0714 | 0.9071 | 29.9671 | ||
| rRAKI | 0.0967 | 0.8927 | 28.6522 | ||
| 本文方法 | 0.0229 | 0.9518 | 34.8806 | ||
| 24 | 8 | ZF | 0.3113 | 0.8669 | 24.1142 |
| GRAPPA | 0.1516 | 0.8021 | 27.2378 | ||
| RAKI | 0.1941 | 0.8215 | 26.1653 | ||
| rRAKI | 0.0984 | 0.8536 | 29.1153 | ||
| 本文方法 | 0.0599 | 0.9205 | 31.2673 | ||
| 30 | 10 | ZF | 0.3365 | 0.8723 | 23.7771 |
| GRAPPA | 0.1391 | 0.8205 | 27.6127 | ||
| RAKI | 0.2295 | 0.8084 | 25.4376 | ||
| rRAKI | 0.1906 | 0.7841 | 26.2441 | ||
| 本文方法 | 0.0982 | 0.9323 | 29.1251 | ||
| 30 | 15 | ZF | 0.3021 | 0.8749 | 24.1621 |
| GRAPPA | 0.1606 | 0.8219 | 26.9897 | ||
| RAKI | 0.2651 | 0.8748 | 24.7297 | ||
| rRAKI | 0.1834 | 0.8605 | 26.3309 | ||
| 本文方法 | 0.0781 | 0.9231 | 30.0419 |
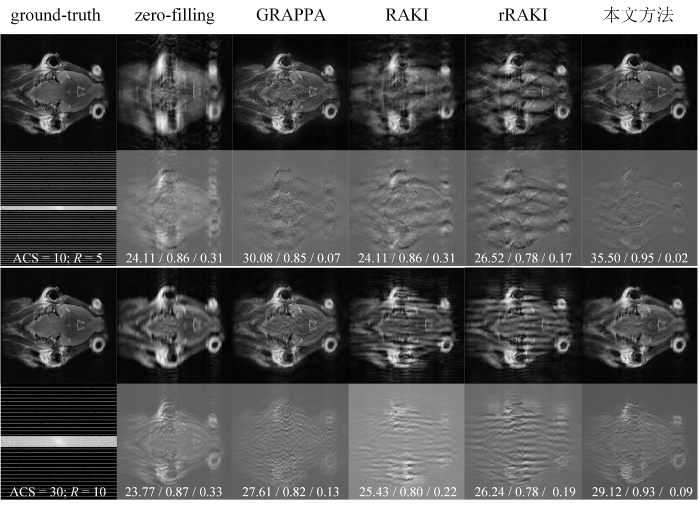
为了直观比较本文提出的算法与其他对比算法在重建效果上的表现,我们从小鼠脑部实验的多层扫描数据中随机选取了一层冠状位原始采集数据,并对ACS = 10、R = 5,以及ACS = 30、R = 10的均匀欠采样数据进行了重建. 重建结果及其误差图如图6所示. 其中,ground-truth表示未经欠采样处理的原始图像数据,zero-filling则指将欠采样数据进行零填充处理后的图像. 每个ground-truth图像下方展示的是相应的均匀欠采样K空间数据,各个算法重建结果图像下方则呈现了与ground-truth图像相减得到的误差图. 误差图中的三个数值分别为通过重建图与参考图像计算得到的PSNR、SSIM和NRMSE指标.
图6
图6
不同算法重建结果和误差图
Fig. 6
Reconstruction results and error maps of different algorithms
通过对各算法重建结果的深入分析可见,基于深度学习的RAKI和rRAKI方法在训练数据较少的情况下,其重建图像存在明显的波浪形伪影,并且在细节恢复方面表现较差,导致重建图像与原始图像之间的差异较大. 相比之下,GRAPPA算法能够较好地减少伪影的产生,但重建图像中的噪声水平较高,误差图上表现出明显的噪声干扰. 与此不同,本文所提出的方法在较少的训练数据条件下,能够有效抑制伪影并较好地保留细节信息,重建图像在细节恢复和噪声控制方面表现优异,保持了与原始非欠采样图像较高的一致性. 总体而言,在训练数据较少的情况下,基于深度学习的重建算法往往面临更显著的性能退化问题,然而,所提方法能够在这些挑战性条件下保持较高的重建质量,不仅能够有效恢复图像细节,且误差较小,显示出更为优异的重建性能和较强的抗噪声能力. 进一步证明了其在更高加速因子的MRI图像重建任务中的适应能力.
2.5 消融实验
以基础的三层RAKI网络结构为基准,本研究通过逐步集成所提方法中的各个新组件,评估其在不同ACS数目和不同R条件下对整体重建性能的影响. 实验结果如表2所示,随着更多组件的引入,网络的重建性能得到了显著改善:具体而言,整体的NRMSE呈现持续下降趋势,PSNR持续上升,在ACS数量为10,R为2或者ACS数量为16,R为4的情况下各个组件对SSIM的指标影响不大,其它情况下,残差结构与虚拟共轭线圈生成对SSIM指标影响不大,但是迭代训练方法使SSIM的指标提升幅度较大. 这一结果验证了虚拟共轭线圈生成和迭代训练方法在提升模型重建性能方面的有效性. 特别地,在较少的ACS数量和较高加速因子的组合下(例如,ACS数目为10、R为5),引入迭代训练策略后,SSIM和PSNR显著提高了21.24%和46.01%,而NRMSE则显著降低至6.85%. 这一改善表明,迭代训练方法通过结合线性重建技术扩展ACS,并通过循环训练不断优化模型参数,能够有效提升模型在高加速因子和低ACS情况下的重建效果,显著提高了图像重建质量.
表2 消融实验对比结果
Table 2
| ACS | R | 残差结构 | 虚拟共轭 线圈生成 | 迭代训练方法 | NRMSE | SSIM | PSNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2 | × | × | × | 0.0032 | 0.9847 | 42.8324 |
| √ | × | × | 0.0031 | 0.9850 | 42.8832 | ||
| √ | √ | × | 0.0024 | 0.9855 | 43.9197 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 0.0020 | 0.9797 | 44.7016 | ||
| 10 | 5 | × | × | × | 0.1985 | 0.7845 | 24.9643 |
| √ | × | × | 0.1857 | 0.7850 | 25.0925 | ||
| √ | √ | × | 0.1684 | 0.7834 | 25.5169 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 0.0136 | 0.9512 | 36.4516 | ||
| 16 | 4 | × | × | × | 0.1456 | 0.9185 | 26.1477 |
| √ | × | × | 0.0962 | 0.9460 | 27.9456 | ||
| √ | √ | × | 0.0202 | 0.9693 | 34.7181 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 0.0084 | 0.9489 | 38.5150 | ||
| 24 | 8 | × | × | × | 0.2910 | 0.7816 | 23.1409 |
| √ | × | × | 0.2798 | 0.7844 | 23.3122 | ||
| √ | √ | × | 0.2347 | 0.7927 | 24.0741 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 0.0349 | 0.9246 | 32.3490 | ||
| 30 | 10 | × | × | × | 0.4402 | 0.6674 | 21.3433 |
| √ | × | × | 0.2402 | 0.7993 | 23.9745 | ||
| √ | √ | × | 0.2131 | 0.7791 | 24.4926 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 0.1285 | 0.9233 | 26.6901 |
3 结论
针对基于特定扫描的并行成像算法在有限数量的训练数据下出现混叠伪影的问题,提出了基于虚拟线圈和GRAPPA增强网络的PMRI方法. 其中,虚拟共轭线圈生成方法是利用磁共振K空间数据共轭对称的特性,生成原线圈采集数据的共轭对称数据,为原有数据提供了额外的相位敏感度信息;GRAPPA增强网络结合了GRAPPA和标准RAKI方法的优点,在应对更高加速因子和更少训练数据的情况下,展现出了较强的潜力,能够很好地抑制磁共振并行成像在较高加速因子情况下的噪声和残留伪影,从而获得更优的重建效果. 由于本文所提方法依赖于GRAPPA算法的插值结果输入到深度学习网络中进行训练,而GRAPPA算法的参数需要通过经验进行设置,这些参数可能并非最优值,因此可能对后续的深度学习训练产生影响. 未来的研究可以进一步优化这一流程,通过深度学习网络自动调节GRAPPA算法的参数,并实现二者更好的结合,从而提高重建结果的质量.
利益冲突
无
参考文献
Multi-coil MRI image reconstruction based on ISTAVS-Net of physical model
[J].
基于物理模型的ISTAVS-Net多线圈MRI图像重建
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20243109
[本文引用: 1]

提高磁共振成像速度是磁共振领域待解决的问题,采用多线圈扫描是一种常用加速方式.但在加速因子大于4时,传统压缩感知磁共振(CS-MRI)重建算法得到的图像质量不高.为此,本文提出一种基于物理模型的ISTAVS-Net多线圈MRI图像重建方法.将ISTA算法与VS-Net网络拆分思想相结合,提出ISTAVS算法,并展开成ISTAVS-Net网络.将每步迭代与网络模块结合,比黑盒U-Net网络的可解释性更强.网络中引入残差机制,增加了网络的非线性表达能力和稳定性. 稀疏变换、收缩阈值以及正则化参数在训练中自动学习,提高了重建的灵活性.采用Globus膝关节数据集的测试结果表明不同加速因子下ISTAVS-Net网络效果均优于传统的 L1-ESPIRiT和ISTA迭代算法,图像质量和性能指标比U-Net、ISTA-Net+和VS-Net网络提升明显,在高加速因子下对组织细节恢复能力更强.该网络鲁棒性强,更适合对临床扫描数据进行快速高质量重建,可拓宽MRI应用范围.
Parallel magnetic resonance imaging: past, present and future
[J].
并行磁共振成像的回顾、现状与发展前景
[J].
Parallel magnetic resonance imaging
[J].
SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI
[J].New theoretical and practical concepts are presented for considerably enhancing the performance of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) by means of arrays of multiple receiver coils. Sensitivity encoding (SENSE) is based on the fact that receiver sensitivity generally has an encoding effect complementary to Fourier preparation by linear field gradients. Thus, by using multiple receiver coils in parallel scan time in Fourier imaging can be considerably reduced. The problem of image reconstruction from sensitivity encoded data is formulated in a general fashion and solved for arbitrary coil configurations and k-space sampling patterns. Special attention is given to the currently most practical case, namely, sampling a common Cartesian grid with reduced density. For this case the feasibility of the proposed methods was verified both in vitro and in vivo. Scan time was reduced to one-half using a two-coil array in brain imaging. With an array of five coils double-oblique heart images were obtained in one-third of conventional scan time. Magn Reson Med 42:952-962, 1999.Copyright 1999 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA)
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mrm.10171
PMID:12111967
[本文引用: 2]

In this study, a novel partially parallel acquisition (PPA) method is presented which can be used to accelerate image acquisition using an RF coil array for spatial encoding. This technique, GeneRalized Autocalibrating Partially Parallel Acquisitions (GRAPPA) is an extension of both the PILS and VD-AUTO-SMASH reconstruction techniques. As in those previous methods, a detailed, highly accurate RF field map is not needed prior to reconstruction in GRAPPA. This information is obtained from several k-space lines which are acquired in addition to the normal image acquisition. As in PILS, the GRAPPA reconstruction algorithm provides unaliased images from each component coil prior to image combination. This results in even higher SNR and better image quality since the steps of image reconstruction and image combination are performed in separate steps. After introducing the GRAPPA technique, primary focus is given to issues related to the practical implementation of GRAPPA, including the reconstruction algorithm as well as analysis of SNR in the resulting images. Finally, in vivo GRAPPA images are shown which demonstrate the utility of the technique.Copyright 2002 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Iterative GRAPPA (iGRAPPA) for improved parallel imaging reconstruction
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mrm.21370
PMID:18383282
[本文引用: 1]

In this work an iterative reconstruction method based on generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA) reconstruction is introduced. In the new method the reconstructed lines are used to reestimate and refine the weights from all the acquired data by applying the GRAPPA procedure iteratively with regularization. Both phantom and in vivo MRI experiments demonstrated that, compared to GRAPPA, the iterative approach reduces parallel imaging artifacts and permits high-quality image reconstruction with a relatively small number of calibration lines and slight changes of GRAPPA weights.
Virtual coil concept for improved parallel MRI employing conjugate symmetric signals
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mrm.21652
PMID:19097211
[本文引用: 2]

A new approach for utilizing conjugate k-space symmetry for improved parallel MRI performance is presented. By generating virtual coils containing conjugate symmetric k-space signals from actual coils, additional image- and coil-phase information can be incorporated into the reconstruction process for parallel acquisition techniques. In that way the reconstruction conditions are improved, resulting in less noise enhancement. In particular in combination with generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA), the virtual coil concept represents a practical approach since no explicit spatial phase information is required. In addition, the influence of phase variations originating from the complex receiver coils as well as from the background is investigated. It is shown that there exist background phase distributions yielding an optimized pMRI reconstruction.
Reconstruction of simultaneous multi-slice MRI data by combining virtual conjugate coil technology and convolutional neural network
[J].
基于虚拟线圈和卷积神经网络的多层同时激发图像重建
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20202800
[本文引用: 1]

本文提出一种基于虚拟共轭线圈(Virtual Coil Concept,VCC)技术和k空间插值鲁棒人工神经网络(Robust Artificial-neural-networks for k-space Interpolation,RAKI)的图像重建方法,用于磁共振多层同时激发成像(Simultaneous Multi-Slice imaging,SMS),该方法能够有效提升重建图像的质量,被命名为VIRGINIA(VIRtual conjuGate coIls Neural-networks InterpolAtion).为了得到更高质量的SMS图像,本文提出的VIRGINIA方法利用磁共振线圈数据的复数共轭对称性质扩展了SMS所获取的多通道数据,并将扩展后的数据用于RAKI网络的训练,利用训练后的网络实现高质量的SMS图像重建.本文将VIRGINIA方法和其他SMS图像重建方法(RAKI和Slice-GRAPPA方法)进行了对比,并采用结构相似指数(Structural Similarity Index,SSIM)、峰值信噪比(Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio,PSNR)和均方根误差(Root Mean Square Error,RMSE)对不同方法的重建图像进行了量化对比分析.结果显示,在相同的SMS加速倍数下,使用VIRGINIA方法进行重建的图像质量均好于RAKI方法,且远好于传统Slice-GRAPPA方法.
Humus-net: Hybrid unrolled multi-scale network architecture for accelerated MRI reconstruction
[J].
Tc-kanrecon: High-quality and accelerated mri reconstruction via adaptive kan mechanisms and intelligent feature scaling
[J].
Scan-specific robust artificial-neural-networks for k-space interpolation (RAKI) reconstruction: database-free deep learning for fast imaging
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mrm.27420
PMID:30277269
[本文引用: 1]

To develop an improved k-space reconstruction method using scan-specific deep learning that is trained on autocalibration signal (ACS) data.Robust artificial-neural-networks for k-space interpolation (RAKI) reconstruction trains convolutional neural networks on ACS data. This enables nonlinear estimation of missing k-space lines from acquired k-space data with improved noise resilience, as opposed to conventional linear k-space interpolation-based methods, such as GRAPPA, which are based on linear convolutional kernels.The training algorithm is implemented using a mean square error loss function over the target points in the ACS region, using a gradient descent algorithm. The neural network contains 3 layers of convolutional operators, with 2 of these including nonlinear activation functions. The noise performance and reconstruction quality of the RAKI method was compared with GRAPPA in phantom, as well as in neurological and cardiac in vivo data sets.Phantom imaging shows that the proposed RAKI method outperforms GRAPPA at high (≥4) acceleration rates, both visually and quantitatively. Quantitative cardiac imaging shows improved noise resilience at high acceleration rates (rate 4:23% and rate 5:48%) over GRAPPA. The same trend of improved noise resilience is also observed in high-resolution brain imaging at high acceleration rates.The RAKI method offers a training database-free deep learning approach for MRI reconstruction, with the potential to improve many existing reconstruction approaches, and is compatible with conventional data acquisition protocols.© 2018 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Residual RAKI: A hybrid linear and non-linear approach for scan-specific k-space deep learning
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119248 URL [本文引用: 2]
Fast and high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging on high field system
[J].
基于高场磁共振的快速高分辨成像
[J].
Deep learning approaches for data augmentation in medical imaging: a review
[J].
DOI:10.3390/jimaging9040081
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Deep learning has become a popular tool for medical image analysis, but the limited availability of training data remains a major challenge, particularly in the medical field where data acquisition can be costly and subject to privacy regulations. Data augmentation techniques offer a solution by artificially increasing the number of training samples, but these techniques often produce limited and unconvincing results. To address this issue, a growing number of studies have proposed the use of deep generative models to generate more realistic and diverse data that conform to the true distribution of the data. In this review, we focus on three types of deep generative models for medical image augmentation: variational autoencoders, generative adversarial networks, and diffusion models. We provide an overview of the current state of the art in each of these models and discuss their potential for use in different downstream tasks in medical imaging, including classification, segmentation, and cross-modal translation. We also evaluate the strengths and limitations of each model and suggest directions for future research in this field. Our goal is to provide a comprehensive review about the use of deep generative models for medical image augmentation and to highlight the potential of these models for improving the performance of deep learning algorithms in medical image analysis.
Transfer learning for medical images analyses: A survey
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.neucom.2021.08.159 URL [本文引用: 1]
Generative adversarial networks in medical image augmentation: a review
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105382 URL [本文引用: 1]
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) for low-data MRI reconstruction
[J].DOI:10.1038/s42256-019-0052-1 [本文引用: 1]
Enhanced magnetic resonance image synthesis with contrast-aware generative adversarial networks
[J].
DOI:10.3390/jimaging7080133
URL

A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exam typically consists of the acquisition of multiple MR pulse sequences, which are required for a reliable diagnosis. With the rise of generative deep learning models, approaches for the synthesis of MR images are developed to either synthesize additional MR contrasts, generate synthetic data, or augment existing data for AI training. While current generative approaches allow only the synthesis of specific sets of MR contrasts, we developed a method to generate synthetic MR images with adjustable image contrast. Therefore, we trained a generative adversarial network (GAN) with a separate auxiliary classifier (AC) network to generate synthetic MR knee images conditioned on various acquisition parameters (repetition time, echo time, and image orientation). The AC determined the repetition time with a mean absolute error (MAE) of 239.6 ms, the echo time with an MAE of 1.6 ms, and the image orientation with an accuracy of 100%. Therefore, it can properly condition the generator network during training. Moreover, in a visual Turing test, two experts mislabeled 40.5% of real and synthetic MR images, demonstrating that the image quality of the generated synthetic and real MR images is comparable. This work can support radiologists and technologists during the parameterization of MR sequences by previewing the yielded MR contrast, can serve as a valuable tool for radiology training, and can be used for customized data generation to support AI training.
Research on transformer super-resolution reconstruction algorithmfor ultrafast spatiotemporal encoding magnetic resonance imaging
[J].
用于超快时空编码MRI的Transformer超分辨率重建算法研究
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20243110
[本文引用: 1]

时空编码(SPEN)磁共振成像(MRI)是一种超快MRI技术,通过该技术采集获得的原始图像空间分辨率较低,需要基于序列物理原理进行超分辨率重建以提高其原始图像的分辨率,而现有的基于深度学习SPEN超分辨率重建算法在提取图像像素长距离依赖关系上的能力有限.为了解决此问题,本文提出了一种基于Transformer的SPEN MRI超分辨率重建算法.该算法采用编码器-解码器结构,并引入Transformer模块以提取特征图的局部上下文信息和长距离依赖关系.实验结果表明,本文所提的重建算法可以在不增加额外采样点的情况下从SPEN低分辨率图像中重建出高空间分辨率、无混叠伪影的超分辨率图像.与现有的超分辨率算法相比,本文提出的算法在临床前以及临床数据集上都取得了更好的重建效果.
Optimized fast GPU implementation of robust artificial-neural-networks for k-space interpolation (RAKI) reconstruction
[J].
The NMR phased array
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mrm.1910160203
PMID:2266841
[本文引用: 1]

We describe methods for simultaneously acquiring and subsequently combining data from a multitude of closely positioned NMR receiving coils. The approach is conceptually similar to phased array radar and ultrasound and hence we call our techniques the "NMR phased array." The NMR phased array offers the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and resolution of a small surface coil over fields-of-view (FOV) normally associated with body imaging with no increase in imaging time. The NMR phased array can be applied to both imaging and spectroscopy for all pulse sequences. The problematic interactions among nearby surface coils is eliminated (a) by overlapping adjacent coils to give zero mutual inductance, hence zero interaction, and (b) by attaching low input impedance preamplifiers to all coils, thus eliminating interference among next nearest and more distant neighbors. We derive an algorithm for combining the data from the phased array elements to yield an image with optimum SNR. Other techniques which are easier to implement at the cost of lower SNR are explored. Phased array imaging is demonstrated with high resolution (512 x 512, 48-cm FOV, and 32-cm FOV) spin-echo images of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Data were acquired from four-element linear spine arrays, the first made of 12-cm square coils and the second made of 8-cm square coils. When compared with images from a single 15 x 30-cm rectangular coil and identical imaging parameters, the phased array yields a 2X and 3X higher SNR at the depth of the spine (approximately 7 cm).
Adaptive reconstruction of phased array MR imagery
[J].DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1522-2594 URL [本文引用: 1]