
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 155-162.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212904
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
De-gang TANG1,2,Hong-chuang LI1,2,Xiao-ling LIU1,2,Lei SHI1,2,Hai-dong LI1,2,Chao-hui YE1,2,Xin ZHOU1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-04-01
Published:2022-06-05
Online:2021-05-15
Contact:
Xin ZHOU
E-mail:xinzhou@wipm.ac.cn
CLC Number:
De-gang TANG,Hong-chuang LI,Xiao-ling LIU,Lei SHI,Hai-dong LI,Chao-hui YE,Xin ZHOU. A Simulation Study on the Effect of the High Permittivity Materials Geometrical Structure on the Transmit Field
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

Fig.2
The schematic simulation model diagrams of high permittivity pads (dark grey) with different geometrical structures (all coils are hidden). (a) Without pads; (b) With a quartered cylindrical pad; (c) With four cuboid pads that surround the phantom symmetrically; (d) With three cuboid pads on the same side; (e) With a single annular sector column with a degree of 120°
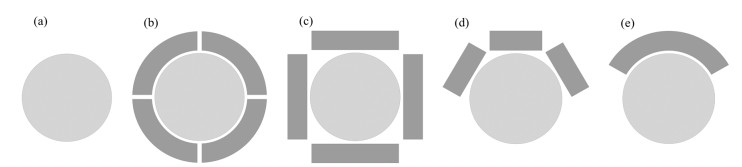

Fig.3
The simulated transmit efficiency maps in the central transverse plane of the phantom corresponding to high permittivity pads with different geometrical structures. (a) Without pads; (b) With a quartered cylindrical pad; (c) With four cuboid pads that surround the phantom symmetrically; (d) With three cuboid pads on the same side; (e) With a single annular sector column with a degree of 120°
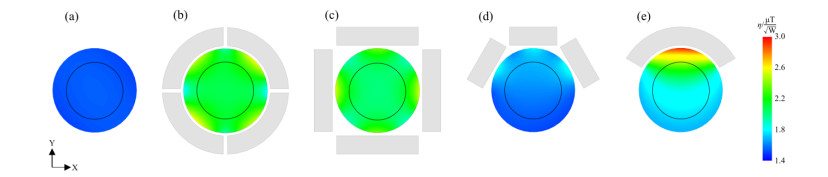
Table 1
The simulated average transmit efficiency η and $ B_1^ + $ inhomogeneity values (CV) in the ROI of different models corresponding to high permittivity pads with different geometrical structures
| 参数 | 无HPMs | 四等分圆筒状 | 四方块环绕 | 同侧三方块 | 120°扇环柱 |
| 发射效率η均值/ | 1.52 | 2.13 | 2.07 | 1.59 | 1.91 |
| CV/% | 0.30 | 1.37 | 1.23 | 2.23 | 9.28 |
| 1 |
UGURBIL K Imaging at ultrahigh magnetic fields: history, challenges, and solutions[J]. Neuroimage, 2018, 168, 7-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.07.007 |
| 2 |
YANG Q X, WANG J, ZHANG X, et al Analysis of wave behavior in lossy dielectric samples at high field[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2002, 47 (5):982-989.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.10137 |
| 3 |
SCHICK F Whole-body MRI at high field: technical limits and clinical potential[J]. Eur Radiol, 2005, 15 (5):946-959.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-005-2678-0 |
| 4 |
DIETRICH O, REISER M F, SCHOENBERG S O Artifacts in 3-T MRI: Physical background and reduction strategies[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2008, 65 (1):29-35.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.11.005 |
| 5 |
KANGARLU A, BAERTLEIN B A, LEE R, et al Dielectric resonance phenomena in ultra high field MRI[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 1999, 23 (6):821-831.
doi: 10.1097/00004728-199911000-00003 |
| 6 |
HUANG Q H, GAO Y, XIN X G Study on the law of B1 field homogeneity and SAR inside human body varying with field strength at high and ultra-high field MR[J]. Chin J Biological Eng, 2013, 32 (1):21-27.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2013.01.004 |
|
黄绮华, 高勇, 辛学刚 高场和超高场MR下人体内B1场均匀性及SAR随场强变化规律的研究[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2013, 32 (1):21-27.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2013.01.004 |
|
| 7 | OSCH M J P V, WEBB A G Safety of ultra-high field MRI: What are the specific risks?[J]. Curr Radiol Rep, 2014, 2 (8):1-8. |
| 8 |
DOTY F D, ENTZMINGER G, KULKARNI J, et al Radio frequency coil technology for small-animal MRI[J]. NMR Biomed, 2007, 20 (3):304-325.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.1149 |
| 9 |
GULSEN G, MUFTULER L T, NALCIOGLU O A double end-cap birdcage RF coil for small animal whole body imaging[J]. J Magn Reson, 2002, 156 (2):309-312.
doi: 10.1006/jmre.2002.2547 |
| 10 |
DARDZINSKI B J, LI S H, COLLINS C M, et al A birdcage coil tuned by RF shielding for application at 9.4 T[J]. J Magn Reson, 1998, 131 (1):32-38.
doi: 10.1006/jmre.1997.1334 |
| 11 |
LEE K H, CHENG M C, CHAN K C, et al Performance of large-size superconducting coil in 0.21 T MRI system[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2004, 51 (11):2024-2030.
doi: 10.1109/TBME.2004.831539 |
| 12 |
LIN I T, YANG H C, HSIEH C W, et al Human hand imaging using a 20 cm high-temperature superconducting coil in a 3 T magnetic resonance imaging system[J]. J Appl Phys, 2010, 107 (12):124701.
doi: 10.1063/1.3431538 |
| 13 | LIAO Z W, CHEN J F, YANG C S, et al A design scheme for 1H/31P dual-nuclear parallel MRI coil[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37 (3):273-282. |
| 廖志文, 陈俊飞, 杨春升, 等 1H/31P双核并行磁共振成像线圈的研究与设计[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37 (3):273-282. | |
| 14 | FENG T, CHEN J F, ZHANG Z, et al A design of short dead-time RF coil and RF switch for low-field NMR[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38 (1):1-11. |
| 冯涛, 陈俊飞, 张震, 等 低场核磁共振短死时间射频线圈与射频开关的设计[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38 (1):1-11. | |
| 15 |
WEBB A G, VAN DE MOORTELE P F The technological future of 7 T MRI hardware[J]. NMR Biomed, 2016, 29 (9):1305-1315.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.3315 |
| 16 |
ANDREYCHENKO A, BLUEMINK J J, RAAIJMAKERS A J E, et al Improved RF performance of travelling wave MR with a high permittivity dielectric lining of the bore[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 70 (3):885-894.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24512 |
| 17 |
YANG Q X, MAO W, WANG J, et al Manipulation of image intensity distribution at 7.0 T: Passive RF shimming and focusing with dielectric materials[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2006, 24 (1):197-202.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.20603 |
| 18 |
FRANKLIN K M, DALE B M, MERKLE E M Improvement in B1-inhomogeneity artifacts in the abdomen at 3 T MR imaging using a radiofrequency cushion[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2008, 27 (6):1443-1447.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.21164 |
| 19 |
DE HEER P, BRINK W M, KOOIJ B J, et al Increasing signal homogeneity and image quality in abdominal imaging at 3 T with very high permittivity materials[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2012, 68 (4):1317-1324.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24438 |
| 20 |
ZIVKOVIC I, TEEUWISSE W, SLOBOZHANYUK A, et al High permittivity ceramics improve the transmit field and receive efficiency of a commercial extremity coil at 1.5 tesla[J]. J Magn Reson, 2019, 299, 59-65.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2018.12.013 |
| 21 |
SICA C T, RUPPRECHT S, HOU R J, et al Toward whole-cortex enhancement with a ultrahigh dielectric constant helmet at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2020, 83 (3):1123-1134.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27962 |
| 22 |
LEE B Y, ZHU X H, RUPPRECHT S, et al Large improvement of RF transmission efficiency and reception sensitivity for human in vivo P-31 MRS imaging using ultrahigh dielectric constant materials at 7 T[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2017, 42, 158-163.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.07.019 |
| 23 |
RUPPRECHT S, SICA C T, CHEN W, et al Improvements of transmit efficiency and receive sensitivity with ultrahigh dielectric constant (uHDC) ceramics at 1.5 T and 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2018, 79 (5):2842-2851.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26943 |
| 24 |
VAN GEMERT J, BRINK W, REMIS R, et al A simulation study on the effect of optimized high permittivity materials on fetal imaging at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 82 (5):1822-1831.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27849 |
| 25 |
BRINK W M, WEBB A G High permittivity pads reduce specific absorption rate, improve B-1 homogeneity, and increase contrast-to-noise ratio for functional cardiac MRI at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2014, 71 (4):1632-1640.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24778 |
| 26 | SCHMIDT R, WEBB A A new approach for electrical properties estimation using a global integral equation and improvements using high permittivity materials[J]. J Magn Reson, 2016, 262, 814. |
| 27 |
VAN GEMERT J, BRINK W, WEBB A, et al High-permittivity pad design tool for 7 T neuroimaging and 3 T body imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 81 (5):3370-3378.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.27629 |
| 28 |
BRINK W M, REMIS R F, WEBB A G A theoretical approach based on electromagnetic scattering for analysing dielectric shimming in high-field MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2016, 75 (5):2185-2194.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.25783 |
| 29 | LUO M, HU C, ZHUANG Y, et al Numerical assessment of the reduction of specific absorption rate by adding high dielectric materials for fetus MRI at 3 T[J]. Biomed Eng-Biomed Tech, 2016, 61 (4):455-461. |
| 30 |
SEO J H, HAN S D, KIM K N Improvements in magnetic field intensity and uniformity for small-animal MRI through a high-permittivity material attachment[J]. Electron Lett, 2016, 52 (11):898-899.
doi: 10.1049/el.2016.0638 |
| 31 |
RUYTENBERG T, O'REILLY T P, WEBB A G Design and characterization of receive-only surface coil arrays at 3 T with integrated solid high permittivity materials[J]. J Magn Reson, 2020, 311, 106681.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2019.106681 |
| 32 |
CHEN W, LEE B Y, ZHU X H, et al Tunable ultrahigh dielectric constant (TuHDC) ceramic technique to largely improve RF coil efficiency and MR imaging performance[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2020, 39 (10):3187-3197.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.2988834 |
| 33 | 方俊鑫, 殷之文 电介质物理学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989. |
| 34 |
WEBB A G Dielectric materials in magnetic resonance[J]. Concepts Magn Reson Part A, 2011, 38A (4):148-184.
doi: 10.1002/cmr.a.20219 |
| 35 |
HOULT D I The principle of reciprocity in signal strength calculations—A mathematical guide[J]. Concepts Magn Reson, 2000, 12 (4):173-187.
doi: 10.1002/1099-0534(2000)12:4<173::AID-CMR1>3.0.CO;2-Q |
| 36 | 罗超. 基于超材料的3 T磁共振射频接收线圈性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2016. |
| 37 | 张巍巍. 基于1.5 T磁共振系统体线圈电磁参数分析及共振频率算法实现[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. |
| 38 |
XIN S X, HUANG Q, GAO Y, et al Fetus MRI at 7 T: B1 shimming strategy and SAR safety implications[J]. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2013, 61 (5):2146-2152.
doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2013.2247053 |
| [1] | MA Yingxue, ZHAO Yanqiang, YANG Xiaodong, JIANG Bin, TAO Cheng. Opportunities and Challenges of High-field and Ultra-high-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 334-344. |
| [2] | SUI Meiju, ZHANG Lei, WANG Ruifang, LUO Yingying, LI Sha, QIU Maosong, XU Qiuyi, CHEN Daiqin, CHEN Shizhen, ZHOU Xin. MRI-traceable Nanoenzyme for Cascade Catalysis-enhanced Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 231-248. |
| [3] | CHEN Qun, YANG Zijian, CHENG Xinyi, JIA Siyi, DU Xiaoxia, WANG Mengxing. Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technology in Pediatric Exercise Intervention Research [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 195-204. |
| [4] | PANG Qifan, WANG Zhichao, WU Yupeng, LI Jianqi. The Impact of K-Space Filling Strategy on Fat Artifacts in APT Imaging Based on FLASH Sequence [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 443-453. |
| [5] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [6] | LIU Ying, LIN Ling, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Research Progress of MRI Gradient Waveform Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 99-115. |
| [7] | LI Pan,FANG Delei,ZHANG Junxia,MA Debei. Magnetic Resonance Compatibility Analysis Method of Surgical Robotic System Based on Image Quality Evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 79-91. |
| [8] | Zhen-yu WANG, Ying-shan WANG, Jin-ling MAO, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Jie SHI, Hong-zhi WANG. Magnetic Resonance Images Segmentation of Synovium Based on Dense-UNet++ [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 208-219. |
| [9] | Yan MA, Cang-ju XING, Liang XIAO. Knee Joint Image Segmentation and Model Construction Based on Cascaded Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 184-195. |
| [10] | Jun LUO, Sheng-ping LIU, Xing YANG, Jia-sheng WANG, Ye LI. Design of a 5 T Non-magnetic Magnetic Resonance Radio Frequency Power Amplifier [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 163-173. |
| [11] | Ju-min ZHANG,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Dual-modal MRI T1-T2 Contrast Agent Based on Dynamic Organic Gadolinium Nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 11-19. |
| [12] | Zhi-chao WANG,Ji-lei ZHANG,Yu ZHAO,Ting HUA,Guang-yu TANG,Jian-qi LI. CEST Imaging of the Abdomen with Neural Network Fitting [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 33-42. |
| [13] | Han-wei WANG,Hao WU,Jing TIAN,Jun-feng ZHANG,Peng ZHONG,Li-zhao CHEN,Shu-nan WANG. The Diagnostic Value of Quantitative Parameters of T2/FLAIR Mismatch Sign in Evaluating the Molecular Typing of Lower-grade Gliomas [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 56-63. |
| [14] | Long XIAO,Xiao-lei ZHU,Ye-qing HAN,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Design and Application of Micellar Magnetic Resonance Imaging Molecular Probe [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 474-490. |
| [15] | Ying-dan HU,Yue CAI,Xu-xia WANG,Si-jie LIU,Yan KANG,Hao LEI,Fu-chun LIN. Magnetic Resonance Imaging the Brain Structures Involved in Nicotine Susceptibility in Rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 345-355. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||