
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2025, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 221-230.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20243141cstr: 32225.14.cjmr20243141
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-12-23
Published:2025-09-05
Online:2025-01-22
Contact:
* Tel: 15726259486, E-mail: kouxinhui@qust.edu.cn.CLC Number:
KOU Xinhui, ZHANG Yubing. Study on the Enantiomeric Recognition of Chiral Ureas Containing Amino Acid Units[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 221-230.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
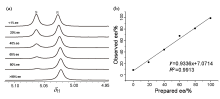
Fig. 5
(a) Selected region of the 1H NMR spectra of mandelic acid of various enantiomeric impurities in the presence of L-Phe-U and DMAP; (b) Correlation between prepared and observed ee values obtained by 400 MHz 1H NMR titrations of enantiomerically enriched mixtures of mandelic acid using L-Phe-U and DMAP in CDCl3
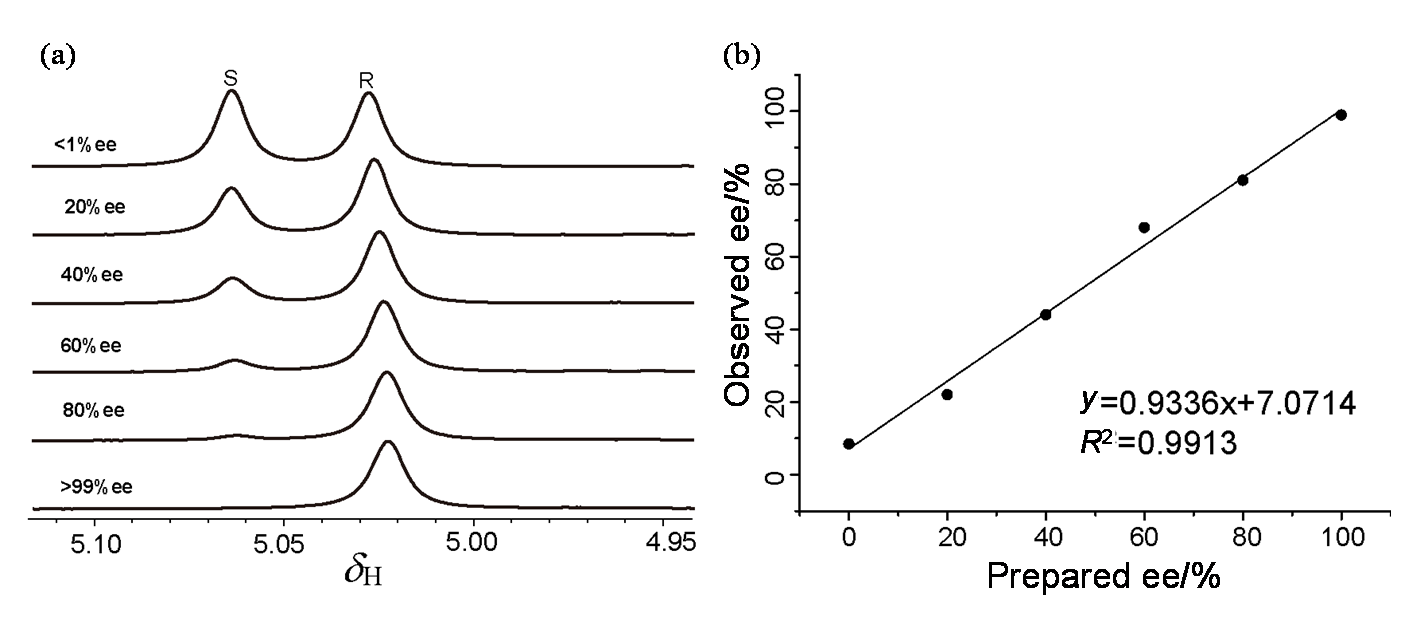
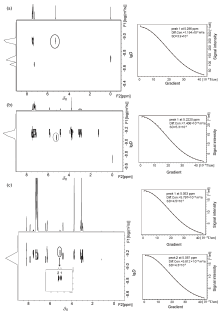
Fig. 6
Simulated diffusion decay curves of CαH (black circle) in (a) rac-MA, (b) rac-MA and L-Phe-U, (c) rac-MA, L-Phe-U and DMAP by varying the gradient strength from 2% to 95% with the same diffusion time and different diffusion gradient strength (Diff. Con. is for diffusion coefficient, and SD is for standard deviation)
| [1] | HUANG Z, YU S S, WEN K L, et al. Zn(II) promoted dramatic enhancement in the enantioselective fluorescent recognition of functional chiral amines by a chiral aldehyde[J]. Chem Sci, 2014, 5(9): 3457-3462. |
| [2] | MIYABE T, IIDA H, OHNISHI A, et al. Enantioseparation on poly(phenyl isocyanide)s with macromolecular helicity memory as chiral stationary phases for HPLC[J]. Chem Sci, 2012, 3(3): 863-867. |
| [3] | METOLA P, ANSLYN E V, JAMES T D, et al. Circular dichroism of multi-component assemblies for chiral amine recognition and rapid determination[J]. Chem Sci, 2012, 3(1): 156-161. |
| [4] | MACHALSKA E, HACHLICA N, ZAJAC G, et al. Chiral recognition a stereo dynamic vanadium probe using the electronic circular dichroism effect in differential Raman scattering[J]. Phys Chem, 2021, 23(40): 23336-23340. |
| [5] | PU L. Enantioselective fluorescent sensors: A tale of BINOL[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2012, 45(2): 150-163. |
| [6] |
HALAY E, BOZKURT S. Enantioselective recognition of carboxylic acids by novel fluorescent triazine-based thiazoles[J]. Chirality, 2018, 30(3): 275-283.
doi: 10.1002/chir.22792 pmid: 29210117 |
| [7] | SPEYBROUCK D, HOWSAM M, LIPKA E. Recent developments in preparative-scale supercritical fluid- and liquid chromatography for chiral separations[J]. TRAC Trend Anal Chem, 2020, 133: 116090. |
| [8] |
SUN G L, LUO Y C, YAN Z H, et al. Chiral metal-organic frameworks-based materials for chromatographic enantioseparation[J]. Chinese Chem Lett, 2024, 35(12): 109787.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2024.109787 |
| [9] | MAMMONE F R, PANUSA A, RISOLUTI R, et al. Green HPLC enantioseparation of chemopreventive chiral isothiocyanates homologs on an immobilized chiral stationary phase based on amylose tris-[(S)-α-methylbenzylcarbamate][J]. Molecules, 2024, 29(12): 2895. |
| [10] |
MAAS A, LOSACKER M, HESS C. Chromatographic separation of R/S-enantiomers of amphetamine and methamphetamine: Pathways of methamphetamine synthesis and detection in blood samples by qualitative enantioselective LC-MS/MS analysis[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2018, 291: 138-143.
doi: S0379-0738(18)30533-4 pmid: 30199817 |
| [11] | VALLAMKONDA B, SETHI S, SATTI P, et al. Enantiomeric analysis of chiral drugs using mass spectrometric methods: A comprehensive review[J]. Chirality, 2024, 36(8): e23705. |
| [12] | RAIKAR P, BANNIMATH G. Recent trends in chiral separation-a collective paradigm of selected chiral impurities[J]. Curr Pharm Anal, 2020, 16(5): 456-473. |
| [13] | WANG Z, WANG W, LUO A Q, et al. Recent progress for chiral stationary phases based on chiral porous materials in high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography separation[J]. J Sep Sci, 2024, 47(13): 2400073. |
| [14] | PARKER D. NMR Determination of enantiomeric purity[J]. Chem Rev, 1991, 91(7): 1441-1457. |
| [15] | SEO M-S, KIM H. 1H NMR chiral analysis of charged molecules via ion pairing with aluminum complexes[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2015, 137(44): 14190-14195. |
| [16] | SILVA M S. Recent advances in multinuclear NMR spectroscopy for chiral recognition of organic compounds[J]. Molecules, 2017, 22(2): 247. |
| [17] | WADHWA S, BUYENS D, KORVINK J G. Direct chiral discrimination with NMR[J]. Adv Mater, 2024, 36(40): 2408547. |
| [18] | CABRAL T L G, POGGETTO G D, DA SILVA J P B, et al. Determining the absolute configuration of small molecules by diffusion NMR experiments[J]. Angew Chem Int Edit, 2025, 64: e202418508. |
| [19] | ZENG Y, BAO W, GU G, et al. Enantiodifferentiation of chiral diols and diphenols via recognition-enabled chromatographic 19F NMR[J]. Magn Reson Lett, 2024, 4(4): 200112. |
| [20] | YANG Y, HUANG S H, FENG J W. Mechanisms underlying enantiomeric discrimination of its structural analogues with a diphenylethylenediamine derivative revealed by proton NMR spectroscopy[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2019, 36(4): 525-533. |
|
杨盈, 黄少华, 冯继文. 核磁共振氢谱中二苯基乙二胺衍生物手性识别其结构类似物[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2019, 36(4): 525-533.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20182703 |
|
| [21] |
WENZEL T J, CHISHOLM C D. Using NMR spectroscopic methods to determine enantiomeric purity and assign absolute stereochemistry[J]. Prog Nucl Mag Res Sp, 2011, 59(1): 1-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2010.07.003 pmid: 21600355 |
| [22] | BIAN G L, YANG S W, HUANG H Y, et al. A bisthiourea-based 1H NMR chiral sensor for chiral discrimination of a variety of chiral compounds[J]. Sensors Actuat B-Chem, 2016, 231: 129-134. |
| [23] | BIAN G, YANG S, HUANG H, et al. Chirality sensing of tertiary alcohols by a novel strong hydrogen-bonding donor-selenourea[J]. Chem Sci, 2016, 7(2): 932-938. |
| [24] | BOZKURT S, TURKMEN M B. New chiral oxo-bridged calix[2]arene[2]triazine for the enantiomeric recognition of alpha-racemic carboxylic acids[J]. Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 2016, 27(11-12): 443-447. |
| [25] |
ITO S, OKUNO M, ASAMI M. Differentiation of enantiomeric anions by NMR spectroscopy with chiral bisurea receptors[J]. Org Biomol Chem, 2018, 16(2): 213-222.
doi: 10.1039/c7ob02318a pmid: 29136083 |
| [26] | GUNAL S E, TUNCEL S T, DOGAN I. Enantiodiscrimination of carboxylic acids using single enantiomer thioureas as chiral solvating agents[J]. Tetrahedron, 2020, 76(18): 131141. |
| [27] | BALZANO F, UCCELLO-BARRETTA G, AIELLO F. Chapter 9-Chiral analysis by NMR spectroscopy: chiral solvating agents[M]// POLAVARAPU P L. Chiral Analysis (Second Edition). Elsevier, 2018: 367-427. |
| [28] | UCCELLO-BARRETTA G, BALZANO F. Chiral NMR solvating additives for differentiation of enantiomers[J]. Topics Curr Chem, 2016, 341: 69-131. |
| [29] | RECCHIMURZO A, MICHELETTI C, UCCELLO-BARRETTA G, et al. Thiourea derivative of 2-[(1R)-1-Aminoethyl]phenol: a flexible pocket-like chiral solvating agent (CSA) for the enantiodifferentiation of amino acid derivatives by NMR spectroscopy[J]. J Org Chem, 2020, 85(8): 5342-5350. |
| [30] | SIAU W Y, WANG J. Asymmetric organocatalytic reactions by bifunctional amine-thioureas[J]. Catal Sci Technol, 2011, 1(8): 1298-1310. |
| [31] |
SERDYUK O V, HECKEL C M, TSOGOEVA S B. Bifunctional primary amine-thioureas in asymmetric organocatalysis[J]. Org Biomol Chem, 2013, 11(41): 7051-7071.
doi: 10.1039/c3ob41403e pmid: 24057617 |
| [32] | FENG G S, CHEN M W, SHI L, et al. Facile synthesis of chiral cyclic ureas through hydrogenation of 2-hydroxypyrimidine/pyrimidin-2(1h)-one tautomers[J]. Angew Chem Int Edit, 2018, 57(20): 5853-5857. |
| [33] | LIU Y, WANG J, WEI Z, et al. Highly enantioselective synthesis of acyclic N,N'-acetals by chiral urea derived from quinine catalyzed the addition of aryl amines to isatin-derived ketimines[J]. Org Lett, 2019, 21(14): 5719-5724. |
| [34] |
RECCHIMURZO A, MICHELETTI C, UCCELLO-BARRETTA G, et al. A dimeric thiourea CSA for the enantiodiscrimination of amino acid derivatives by NMR spectroscopy[J]. J Org Chem, 2021, 86(11): 7381-7389.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c00340 pmid: 34019407 |
| [35] | DE LOS SANTOS Z A, YUSIN G, WOLF C. Enantioselective sensing of carboxylic acids with a bis (urea) oligo (phenylene) ethynylene foldamer[J]. Tetrahedron, 2019, 75(11): 1504-1509. |
| [36] | RECCHIMURZO A, BALZANO F, BARRETTA G U, et al. Bis-thiourea chiral sensor for the NMR enantiodiscrimination of N-acetyl and N-trifluoroacetyl amino acid derivatives[J]. J Org Chem, 2022, 87(18): 11968-11978. |
| [37] | KONRAD N, HORETSKI M, SIHTMAE M, et al. Thiourea organocatalysts as emerging chiral pollutants: en route to porphyrin-based (chir) optical sensing[J]. Chemosensors, 2021, 9(10): 278. |
| [38] | AIELLO F, RECCHIMURZO A, BALZANO F, et al. A Thiourea derivative of 2-[(1)-1-aminoethyl]phenol as a chiral sensor for the determination of the absolute configuration of N-3,5-dinitrobenzoyl derivatives of amino acids[J]. Molecules, 2024, 29(6): 1319. |
| [39] | MA M S, LEI X X. Chiral recognition of ibuprofen enatiomers by a chiral thiourea in the presence of DMAP using NMR[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2014, 31(4): 564-571. |
|
马敏山, 雷新响. 手性硫脲在DMAP条件下对布洛芬类药物的NMR手性识别[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2014, 31(4): 564-571.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20140410 |
|
| [40] | XU K X, LIU S Y, HE Y B, et al. Study on synthesis and chiral recognition of chiral hosts containing amino acid unit[J]. Acta Chim Sin, 2006, 64(21): 2205-2209. |
| 徐括喜, 刘顺英, 何永炳, 等. 含氨基酸单元的手性主体的合成及手性识别研究[J]. 化学学报, 2006, 64(21): 2205-2209. | |
| [41] | KOU X H, SHEN Y, LI Z B. Stereoselective ring-opening polymerization of rac-lactide using chiral urea/strong organobase binary catalyst system[J]. Acta Polym Sin, 2020, 51(10): 1121-1129. |
| 寇新慧, 沈勇, 李志波. 手性脲/有机碱二元体系协同催化外消旋丙交酯立构选择性开环聚合[J]. 高分子学报, 51(10): 1121-1129. | |
| [42] |
BIAN G, FAN H, YANG S, et al. A chiral bisthiourea as a chiral solvating agent for carboxylic acids in the presence of DMAP[J]. J Org Chem, 2013, 78(18): 9137-9142.
doi: 10.1021/jo4013546 pmid: 24050150 |
| [43] | GAMBHIR D, KUMAR K, MURUGESAN P, et al. Amino acid-based molecular and membranous chiral tools for enantiomeric recognition[J]. Langmuir, 2024, 40(5): 2745-2753. |
| [44] | CIOS P, ROMANSKI J. Enantioselective recognition of sodium carboxylates by an 1,8-diaminoanthracene based ion pair receptor containing amino acid units[J]. Tetrahedron Lett, 2016, 57(34): 3866-3869. |
| [1] | DU Qunjie. Experimental Study on Accurate Determination of Shale Porosity by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 275-284. |
| [2] | SHEN Zhiqiang, DENG Yabo, YANG Peiju, HU Xiaoxue, HUANG Xiaojuan, XU Chuanzhi, SONG Huanling. Design and Application of an in situ NMR Device for Light-Induced Reaction Systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 22-33. |
| [3] | XU Xiaojie, CHEN Yan’an, LI Xufei, ZHANG Yuncai, ZHANG Yong, ZHAN Dongkai, PAN Ting. Structural Elucidation of Hybutimibe [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 43-55. |
| [4] | WANG Feng, LIU Tingwei, XU Yajie, YU Peng, WANG Ya, PENG Bowen, YANG Xiaodong. A Miniaturised NMR RF Probe Design with External Field-locking Channel [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 332-340. |
| [5] | WANG Yuanfang,WANG Xiaohua,SHU Chang,ZHANG Xu,LIU Maili,ZENG Danyun. The Aggregation of ATAD2 Bromodomain in Solution [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 169-178. |
| [6] | ZHAO Chang,GONG Zhou. Investigation of Dynamic Structure of Protein Encountering Complex with Paramagnetic NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 148-157. |
| [7] | ZHAN Jianhua,HU Qin,ZHU Qinjun,JIANG Bin,ZHANG Xu,LIU Maili. Track the Conformational Change of Unlabeled Yeast Cytochrome c in Cell Homogenate Using NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 22-29. |
| [8] | CI Jie,YANG Xue,XIN Jiaxiang,WEI Daxiu,YAO Yefeng. Preparation and Lifetime Studies of the Singlet State of Five Spins in Hexene Molecules Used to Guide the Preservation of the Parahydrogen-induced Nuclear Polarization State [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 30-38. |
| [9] | Yun-shan PEI, Cai ZHANG, Xiao-li LIU, Kai CHENG, Ze-ting ZHANG, Cong-gang LI. Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by the Interaction Between Protein Disulfide Isomerase and α-Synuclein [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 381-392. |
| [10] | Xiao-yang ZHANG, Shou-quan YAO, Jun-cheng XU, Yu JIANG. Magnetic Field Locking System Based on Fluxgate and Time Domain Digital Frequency Discrimination [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 448-458. |
| [11] | Han HU,Wei-yu WANG,Jun XU,Feng DENG. 1, 3-Butadienen Hydrogenation on Supported Pd-Sn Bimetallic Catalysts Investigated by Parahydrogen-induced Polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 133-143. |
| [12] | Qian XU,Lang CHEN,Xiang-ying HU,Cong-gang LI,Yi-xiang LIU,Ling JIANG. The Effect of T69E-mimicked Phosphorylation on the Interaction Between Bcl-2 and Nur77 [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 87-95. |
| [13] | Xiao-qing LIN,Shi-jia DU,Hao-lin ZHAN,Yu-qing HUANG,Zhong CHEN. Two-Dimensional Homonuclear Orthogonal-Pattern Phase-Sensitive J-Resolved NMR Spectroscopy Based on Pure Shifts [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 448-459. |
| [14] | Yao XIAO,Chang-jiu XIA,Xian-feng YI,Feng-qing LIU,Shang-bin LIU,An-min ZHENG. Progress in the Studies on Sn-Zeolites by Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 571-584. |
| [15] | Xiao-dong HU,Wen-xian LAN,Chun-xi WANG,Chun-yang CAO. Research Advance and NMR Studies of Anti-Cancer Small Molecules Targeting c-MYC G4-DNA [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 503-513. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
