
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2021, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 345-355.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212890
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ying-dan HU1,2,Yue CAI1,2,Xu-xia WANG1,2,Si-jie LIU1,2,Yan KANG1,2,Hao LEI1,2,Fu-chun LIN1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-02-23
Published:2021-09-05
Online:2021-03-31
Contact:
Fu-chun LIN
E-mail:fclin@wipm.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Ying-dan HU,Yue CAI,Xu-xia WANG,Si-jie LIU,Yan KANG,Hao LEI,Fu-chun LIN. Magnetic Resonance Imaging the Brain Structures Involved in Nicotine Susceptibility in Rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 345-355.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
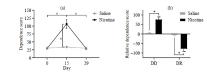
Fig.2
The effect of nicotine administration on the dependence score of rats. (a) The effect of nicotine administration and administration time on dependence score; (b) The effect of nicotine administration on the relative dependence score. The data are presented in the form of mean±standard deviation, *p < 0.000 1
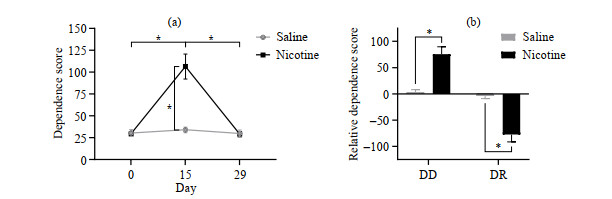
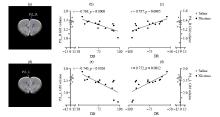
Fig.3
The PrL GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly correlated with DD and DR. (a) The PrL_R of rats in the Nic group; (b) PrL_R GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly negatively correlated with DD (r=-0.768, p=0.000 8); (c) PrL_R GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly positively correlated with DR (r=0.787, p=0.000 5); (d) The PrL_L of rats in the Nic group; (e) PrL_L GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly negatively correlated with DD (r=-0.740, p=0.001 6); (f) PrL_L GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly positively correlated with DR (r=0.752, p=0.001 2)
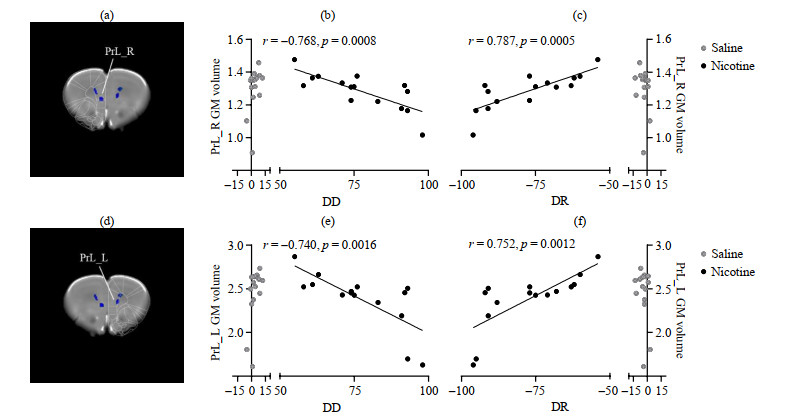
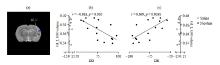
Fig.4
The GI_L GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly correlated with DD and DR. (a) The GI_L of rats in the Nic group; (b) GI_L GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly negatively correlated with DD (r=-0.683, p=0.005); (c) GI_L GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly positively correlated with DR (r=0.699, p=0.003 8)
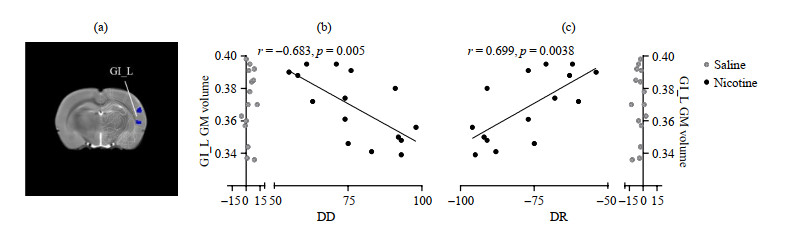
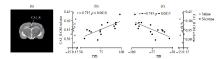
Fig.5
The CA1_R GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly correlated with DD and DR. (a) The CA1_R of rats in the Nic group; (b) CA1_R GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly positively correlated with DD (r = 0.735, p = 0.001 8); (c) CA1_R GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly negatively correlated with DR (r = -0.743, p = 0.001 5)
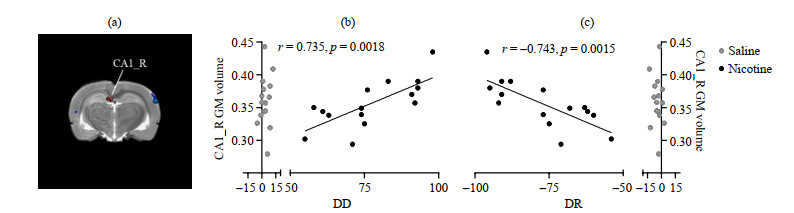

Fig.6
The Thalamus_L GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly correlated with DD and DR. (a) The Thalamus_L of rats in the Nic group; (b). Thalamus_L GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly positively correlated with DD (r=0.933, p < 0.000 1); (c) Thalamus_L GM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly negatively correlated with DR (r=-0.882, p < 0.000 1)
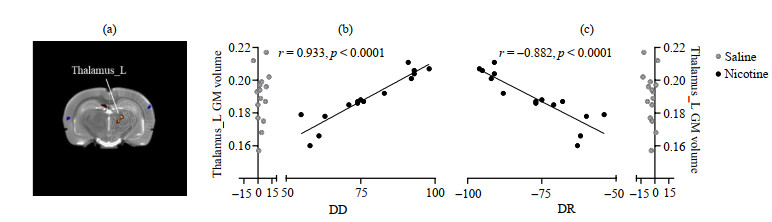
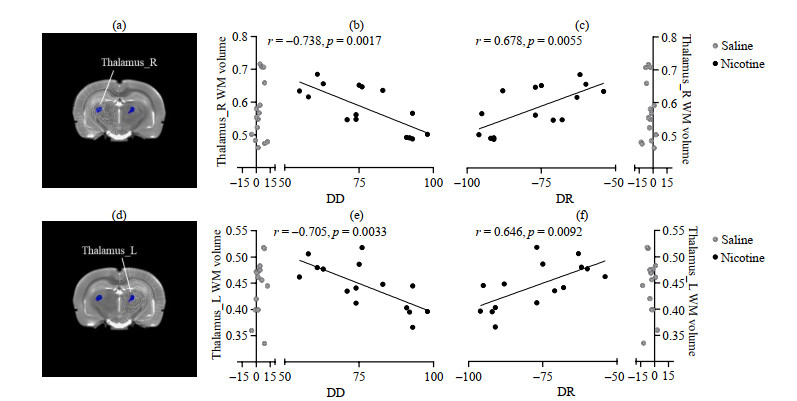
Fig.7
The volume of white matter (WM) in the thalamus of rats in the Nic group was significantly correlated with DD and DR. (a) The Thalamus_R of rats in the Nic group; (b) Thalamus_R WM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly negatively correlated with DD (r = -0.738, p=0.001 7); (c) Thalamus_R WM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly positively correlated with DR (r=0.678, p=0.005 5); (d) The Thalamus_L of rats in the Nic group; (e) Thalamus_L WM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly negatively correlated with DD (r = -0.705, p=0.003 3); (f) Thalamus_L WM volume of rats in the Nic group is significantly positively correlated with DR (r=0.646, p=0.009 2)
| 1 |
CHEN Z M , PETO R , ZHOU M G , et al. Contrasting male and female trends in tobacco-attributed mortality in China: evidence from successive nationwide prospective cohort studies[J]. The Lancet, 2015, 386 (10002): 1447- 1456.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00340-2 |
| 2 |
BRITTON J . Death, disease, and tobacco[J]. The Lancet, 2017, 389 (10082): 1861- 1862.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30867-X |
| 3 |
GARCIA-RIVAS V , DEROCHE-GAMONET V . Not all smokers appear to seek nicotine for the same reasons: implications for preclinical research in nicotine dependence[J]. Addic Biol, 2019, 24 (3): 317- 334.
doi: 10.1111/adb.12607 |
| 4 |
LIU M Z , JIANG Y , WEDOW R , et al. Association studies of up to 1.2 million individuals yield new insights into the genetic etiology of tobacco and alcohol use[J]. Nat Genet, 2019, 51 (2): 237- 244.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0307-5 |
| 5 |
LI S F , YANG Y H , HOFFMANN E , et al. CYP2A6 genetic variation alters striatal-cingulate circuits, network hubs, and executive processing in smokers[J]. Biol Psychiat, 2017, 81 (7): 554- 563.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.09.013 |
| 6 |
HONG L E , HODGKINSON C A , YANG Y , et al. A genetically modulated, intrinsic cingulate circuit supports human nicotine addiction[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010, 107 (30): 13509- 13514.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004745107 |
| 7 |
HSU L M , KEELEY R J , LIANG X , et al. Intrinsic insular-frontal networks predict future nicotine dependence severity[J]. J Neurosci, 2019, 39 (25): 5028- 5037.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0140-19.2019 |
| 8 | CAI W Q , WANG Y J . Advances in construction of human brain atlases from magnetic resonance images[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37 (2): 241- 253. |
| 蔡文琴, 王远军. 基于磁共振成像的人脑图谱构建方法研究进展[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37 (2): 241- 253. | |
| 9 |
ZHANG X , SALMERON B J , ROSS T J , et al. Factors underlying prefrontal and insula structural alterations in smokers[J]. Neuroimage, 2011, 54 (1): 42- 48.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.08.008 |
| 10 |
FRITZ H C , WITTFELD K , SCHMIDT C O , et al. Current smoking and reduced gray matter volume-a voxel-based morphometry study[J]. Neuropsychopharmacol, 2014, 39 (11): 2594- 2600.
doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.112 |
| 11 |
LIAO Y H , TANG J S , LIU T Q , et al. Differences between smokers and non-smokers in regional gray matter volumes: a voxel-based morphometry study[J]. Addict Biol, 2012, 17 (6): 977- 980.
doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2010.00250.x |
| 12 |
PAN P L , SHI H C , ZHONG J G , et al. Chronic smoking and brain gray matter changes: evidence from meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies[J]. Neurol Sci, 2013, 34 (6): 813- 817.
doi: 10.1007/s10072-012-1256-x |
| 13 |
HANLON C A , OWENS M M , JOSEPH J E , et al. Lower subcortical gray matter volume in both younger smokers and established smokers relative to non-smokers[J]. Addict Biol, 2016, 21 (1): 185- 195.
doi: 10.1111/adb.12171 |
| 14 |
WANG K C , YANG J Y , ZHANG S Y , et al. The neural mechanisms underlying the acute effect of cigarette smoking on chronic smokers[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9 (7): e102828.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102828 |
| 15 |
STOECKEL L E , CHAI X J , ZHANG J H , et al. Lower gray matter density and functional connectivity in the anterior insula in smokers compared with never smokers[J]. Addict Biol, 2016, 21 (4): 972- 981.
doi: 10.1111/adb.12262 |
| 16 |
BRYNILDSEN J K , NAJAR J , HSU L M , et al. A novel method to induce nicotine dependence by intermittent drug delivery using osmotic minipumps[J]. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 2016, 142, 79- 84.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2015.12.010 |
| 17 |
WU H , WANG X , GAO Y , et al. NMDA receptor antagonism by repetitive MK801 administration induces schizophrenia-like structural changes in the rat brain as revealed by voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging[J]. Neuroscience, 2016, 322, 221- 233.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.043 |
| 18 | XIN H T , WU G Y , WEN Z , et al. Effects of antiretroviral therapy on brain gray matter volumes in AIDS patients[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38 (1): 69- 79. |
| 辛红涛, 吴光耀, 文之, 等. 抗逆转录病毒治疗对艾滋病患者脑灰质体积的影响[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38 (1): 69- 79. | |
| 19 |
HAYASHI T , KO J H , STRAFELLA A P , et al. Dorsolateral prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortex interactions during self-control of cigarette craving[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013, 110 (11): 4422- 4427.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212185110 |
| 20 |
LI Y D , YUAN K , CAI C X , et al. Reduced frontal cortical thickness and increased caudate volume within fronto-striatal circuits in young adult smokers[J]. Drug Alcohol Depen, 2015, 151, 211- 219.
doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.03.023 |
| 21 |
PICARD F , SADAGHIANI S , LEROY C , et al. High density of nicotinic receptors in the cingulo-insular network[J]. Neuroimage, 2013, 79, 42- 51.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.074 |
| 22 |
NAQVI N H , RUDRAUF D , DAMASIO H , et al. Damage to the insula disrupts addiction to cigarette smoking[J]. Science, 2007, 315 (5811): 531- 534.
doi: 10.1126/science.1135926 |
| 23 |
MORALES A M , GHAHREMANI D , KOHNO M , et al. Cigarette exposure, dependence, and craving are related to insula thickness in young adult smokers[J]. Neuropsychopharmacol, 2014, 39 (8): 1816- 1822.
doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.48 |
| 24 | LIN F C , WU G Y , ZHU L , et al. Region-specific changes of insular cortical thickness in heavy smokers[J]. Front Hum Neurosci, 2019, 13, 265. |
| 25 |
TSAI P J , KEELEY R J , CARMACK S A , et al. Converging structural and functional evidence for a rat salience network[J]. Biol Psychiat, 2020, 88 (11): 867- 878.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.06.023 |
| 26 | KENNEY J W , GOULD T J . Modulation of hippocampus-dependent learning and synaptic plasticity by nicotine[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2008, 38 (1): 101- 121. |
| 27 |
LIN F C , WU G Y , ZHU L , et al. Altered brain functional networks in heavy smokers[J]. Addict Biol, 2015, 20 (4): 809- 819.
doi: 10.1111/adb.12155 |
| 28 |
SHEN Z J , HUANG P Y , QIAN W , et al. Severity of dependence modulates smokers' functional connectivity in the reward circuit: a preliminary study[J]. Psychopharmacology, 2016, 233 (11): 2129- 2137.
doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4262-5 |
| 29 | WANG L , NEGREIRA A , LAVIOLETTE P , et al. Intrinsic interhemispheric hippocampal functional connectivity predicts individual differences in memory performance ability[J]. Hippocampus, 2010, 20 (3): 345- 351. |
| 30 |
BRODY A L , MANDELKERN M A , LONDON E D , et al. Cigarette smoking saturates brain α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors[J]. Arch Gen Psychiat, 2006, 63 (8): 907- 914.
doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.8.907 |
| [1] | MA Yingxue, ZHAO Yanqiang, YANG Xiaodong, JIANG Bin, TAO Cheng. Opportunities and Challenges of High-field and Ultra-high-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 334-344. |
| [2] | SUI Meiju, ZHANG Lei, WANG Ruifang, LUO Yingying, LI Sha, QIU Maosong, XU Qiuyi, CHEN Daiqin, CHEN Shizhen, ZHOU Xin. MRI-traceable Nanoenzyme for Cascade Catalysis-enhanced Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 231-248. |
| [3] | CHEN Qun, YANG Zijian, CHENG Xinyi, JIA Siyi, DU Xiaoxia, WANG Mengxing. Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technology in Pediatric Exercise Intervention Research [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 195-204. |
| [4] | PANG Qifan, WANG Zhichao, WU Yupeng, LI Jianqi. The Impact of K-Space Filling Strategy on Fat Artifacts in APT Imaging Based on FLASH Sequence [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 443-453. |
| [5] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [6] | LIU Ying, LIN Ling, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Research Progress of MRI Gradient Waveform Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 99-115. |
| [7] | LI Pan,FANG Delei,ZHANG Junxia,MA Debei. Magnetic Resonance Compatibility Analysis Method of Surgical Robotic System Based on Image Quality Evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 79-91. |
| [8] |
De-gang TANG,Hong-chuang LI,Xiao-ling LIU,Lei SHI,Hai-dong LI,Chao-hui YE,Xin ZHOU.
A Simulation Study on the Effect of the High Permittivity Materials Geometrical Structure on the Transmit Field |
| [9] | Zhen-yu WANG, Ying-shan WANG, Jin-ling MAO, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Jie SHI, Hong-zhi WANG. Magnetic Resonance Images Segmentation of Synovium Based on Dense-UNet++ [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 208-219. |
| [10] | Yan MA, Cang-ju XING, Liang XIAO. Knee Joint Image Segmentation and Model Construction Based on Cascaded Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 184-195. |
| [11] | Jun LUO, Sheng-ping LIU, Xing YANG, Jia-sheng WANG, Ye LI. Design of a 5 T Non-magnetic Magnetic Resonance Radio Frequency Power Amplifier [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 163-173. |
| [12] | Ju-min ZHANG,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Dual-modal MRI T1-T2 Contrast Agent Based on Dynamic Organic Gadolinium Nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 11-19. |
| [13] | Zhi-chao WANG,Ji-lei ZHANG,Yu ZHAO,Ting HUA,Guang-yu TANG,Jian-qi LI. CEST Imaging of the Abdomen with Neural Network Fitting [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 33-42. |
| [14] | Han-wei WANG,Hao WU,Jing TIAN,Jun-feng ZHANG,Peng ZHONG,Li-zhao CHEN,Shu-nan WANG. The Diagnostic Value of Quantitative Parameters of T2/FLAIR Mismatch Sign in Evaluating the Molecular Typing of Lower-grade Gliomas [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 56-63. |
| [15] | Long XIAO,Xiao-lei ZHU,Ye-qing HAN,Shi-zhen CHEN,Xin ZHOU. Design and Application of Micellar Magnetic Resonance Imaging Molecular Probe [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(4): 474-490. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||