
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 366-380.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212962
• Review Articles & Perspectives • Previous Articles
Xiao CHANG1,Xin CAI1,Guang YANG2,Sheng-dong NIE1,*( )
)
Received:2021-12-06
Published:2022-09-05
Online:2022-02-18
Contact:
Sheng-dong NIE
E-mail:nsd4647@163.com
CLC Number:
Xiao CHANG,Xin CAI,Guang YANG,Sheng-dong NIE. Applications of Generative Adversarial Networks in Medical Image Translation[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 366-380.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
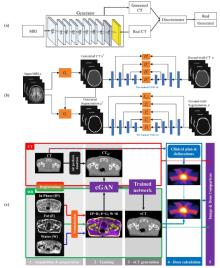
Fig.5
Three researches on translating magnetic resonance image to CT image. (a) Based on DCGAN, and the datasets include the public brain dataset in ADNI database and their own pelvic dataset[35]; (b) Segmentation and image translation are all achieved by GAN, and the dataset is also the public brain dataset in the ADNI database[36]; (c) MR-only guided radiotherapy[37]

Table 1
Summary of medical image translation research based on GAN
| 应用场景 | 文献 | 图像类型 | 网络架构 | 损失函数 | 评价标准 |
| 含噪图像 ↓ 去噪图像 | [ | CT | WGAN | LWGAN + Limage +Lperceptual | M8, 9, 14 |
| [ | CT | Pix2Pix+ | LGAN + Lperceptual | M5, 6, 8, 9 | |
| [ | CT | LSGAN, PatchGAN, LAPGAN | LGAN + Limage+Lperceptual | M7, 8, 9 | |
| [ | MRI | WGAN | LWGAN + Limage+Lperceptual | M8, 9 | |
| 低分辨图像 ↓ 高分辨图像 | [ | MRI | Pix2Pix+ | LGAN + Limage | M7, 8, 9 |
| [ | MRI | DCGAN | LGAN + L1 | M7, 8, 9, 10, 11 | |
| [ | PET | CGAN, U-Net | LGAN + L1 | M1, 7, 8 | |
| 模态转换 | [ | T1→FLAIR | CGAN | LGAN + Limage | M7, 8, 17 |
| [ | T1→T2,T1→FLAIR | CGAN | LGAN + Ledge | M7, 8, 9 | |
| [ | MRI→CT | DCGAN | LGAN + Limage + Lgradient | M7, 8 | |
| [ | MRI→CT | Pix2Pix+ | LGAN | M7, 8 | |
| [ | MRI→PET | CycleGAN | LGAN + Limage + Lcycle | M15 | |
| [ | MRI→PET | CGAN | LGAN | M1, 2, 3 | |
| [ | X-ray→CT | DCGAN, WGAN | LWGAN | M1 | |
| 小样本 ↓ 大样本 | [ | MRI | CGAN+PGGAN | LWGAN-GP | M12 |
| [ | MRI | PGGAN | LWGAN-GP | M12, 13, 16 | |
| [ | MRI | PGGAN | LGAN+Lcycle | M8, 9 | |
| [ | MRI | PGGAN | LGAN + LSSIM + L1 | M4, 16 | |
| [ | MRI | CGAN | LGAN + L1 + Lseg | M17 | |
| [ | 病理图像 | GAN | LGAN | M15 | |
| [ | X-ray | PGGAN | LGAN + Limage+Lfrequency | M15 | |
| [ | ECG | Pix2PixHD | LGAN+Limage+Lperceptual | - |
| 1 | GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative Adversarial Nets[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014: 2672-2680. |
| 2 | WANG T C, LIU M Y, ZHU J Y, et al. High-resolution image synthesis and semantic manipulation with conditional gans[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018: 8798-8807. |
| 3 | ZHU J Y, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2017: 2223-2232. |
| 4 | LI P L, LIANG X D, JIA D Y, et al. Semantic-aware grad-gan for virtual-to-real urban scene adaption[J]. 2018. arXiv: 1801.01726. |
| 5 | CHEN Y, LAI Y K, LIU Y J. Cartoongan: Generative adversarial networks for photo cartoonization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018: 9465-9474. |
| 6 | YI R, LIU Y J, LAI Y K, et al. Apdrawinggan: Generating artistic portrait drawings from face photos with hierarchical gans[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 10743-10752. |
| 7 | PARK T, LIU M Y, WANG T C, et al. GauGAN: semantic image synthesis with spatially adaptive normalization[C]//ACM SIGGRAPH 2019 Real-Time Live! 2019. |
| 8 | QIU Y , NIE S D , WEI L . Segmentation of breast tumors based on full convolutional network and dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance image[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39 (2): 196- 207. |
| 邱玥, 聂生东, 魏珑. 基于全卷积网络的乳腺肿瘤动态增强磁共振图像分割[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39 (2): 196- 207. | |
| 9 | HU Y , WANG L J , NIE S D . Fine brain functional parcellation based on t-distribution stochastic neighbor embedding and automatic spectral clustering[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2021, 38 (3): 392- 402. |
| 胡颖, 王丽嘉, 聂生东. 融合t-分布随机邻域嵌入与自动谱聚类的脑功能精细分区方法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2021, 38 (3): 392- 402. | |
| 10 | MIRZA M, OSINDERO S. Conditional generative adversarial nets[J]. 2014. arXiv: 1411.1784. |
| 11 | MAO X D, LI Q, XIE H R, et al. Least squares generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2017: 2794-2802. |
| 12 | ADLER J, LUNZ S. Banach wasserstein GAN[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd international conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2018: 6755-6764. |
| 13 | GULRAJANI I, AHMED F, ARJOVSKY M, et al. Improved training of wasserstein gans[C]//Proceedings of the 31st international conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 5769-5779. |
| 14 | DENTON E L, CHINTALA S, SZLAM A, et al. Deep generative image models using a Laplacian pyramid of adversarial networks[C]//NIPS, 2015. |
| 15 | ISOLA P, ZHU J Y, ZHOU T H, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017: 5967-5976. |
| 16 | KARRAS T, AILA T, LAINE S, et al. Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation[J]. 2017, arXiv: 1710.10196. |
| 17 | RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 2015: 234-241. |
| 18 | YI Z L, ZHANG H, TAN P, et al. Dualgan: Unsupervised dual learning for image-to-image translation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2017: 2849-2857. |
| 19 | KIM T, CHA M, KIM H, et al. Learning to discover cross-domain relations with generative adversarial networks[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning, 2017: 1857-1865. |
| 20 |
YANG Q S , YAN P K , ZHANG Y B , et al. Low-dose CT image denoising using a generative adversarial network with wasserstein distance and perceptual loss[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2018, 37 (6): 1348- 1357.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2827462 |
| 21 |
SHAN H M , ZHANG Y , YANG Q S , et al. 3-D convolutional encoder-decoder network for low-dose CT via transfer learning from a 2-D trained network[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2018, 37 (6): 1522- 1534.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2832217 |
| 22 | LIAO H, HUO Z, SEHNERT W J, et al. Adversarial sparse-view CBCT artifact reduction[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 2018: 154-162. |
| 23 |
ZHANG Y K , HU D J , ZHAO Q L , et al. CLEAR: comprehensive learning enabled adversarial reconstruction for subtle structure enhanced low-dose CT imaging[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2021, 40 (11): 3089- 3101.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2021.3097808 |
| 24 |
ZHANG X , FENG C L , WANG A H , et al. CT super-resolution using multiple dense residual block based GAN[J]. Signal Image Video P, 2021, 15 (4): 725- 733.
doi: 10.1007/s11760-020-01790-5 |
| 25 |
HUANG Z X , LIU X F , WANG R P , et al. Considering anatomical prior information for low-dose CT image enhancement using attribute-augmented Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 428, 104- 115.
doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.10.077 |
| 26 |
RAN M S , HU J R , CHEN Y , et al. Denoising of 3D magnetic resonance images using a residual encoder-decoder Wasserstein generative adversarial network[J]. Med Image Anal, 2019, 55, 165- 180.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.05.001 |
| 27 | CHEN Y, SHI F, CHRISTODOULOU A G, et al. Efficient and accurate MRI super-resolution using a generative adversarial network and 3D multi-level densely connected network[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 2018: 91-99. |
| 28 |
SUN K , QU L Q , LIAN C F , et al. High-resolution breast MRI reconstruction using a deep convolutional generative adversarial network[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2020, 52 (6): 1852- 1858.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.27256 |
| 29 | XIE H Q , LEI Y , WANG T H , et al. Synthesizing high-resolution MRI using parallel cycle-consistent generative adversarial networks for fast MR imaging[J]. Med Phys, 2021, 49 (1): 357- 369. |
| 30 |
WANG Y , YU B T , WANG L , et al. 3D conditional generative adversarial networks for high-quality PET image estimation at low dose[J]. Neuroimage, 2018, 174, 550- 562.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.03.045 |
| 31 | KUDO A, KITAMURA Y, LI Y, et al. Virtual thin slice: 3D conditional GAN-based super-resolution for CT slice interval[C]//International Workshop on Machine Learning for Medical Image Reconstruction, 2019: 91-100. |
| 32 |
DE FARIAS E C , DI NOIA C , HAN C , et al. Impact of GAN-based lesion-focused medical image super-resolution on the robustness of radiomic features[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 1- 12.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79139-8 |
| 33 | YU B T, ZHOU L P, WANG L, et al. 3D CGAN based cross-modality MR image synthesis for brain tumor segmentation[C]//2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. 2018: 626-630. |
| 34 |
YU B T , ZHOU L P , WANG L , et al. Ea-GANs: edge-aware generative adversarial networks for cross-modality MR image synthesis[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2019, 38 (7): 1750- 1762.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2895894 |
| 35 | NIE D, TRULLO R, LIAN J, et al. Medical image synthesis with context-aware generative adversarial networks[C]//International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, 2017: 417-425. |
| 36 | ZHAO M Y, WANG L, CHEN J W, et al. Craniomaxillofacial bony structures segmentation from MRI with deep-supervision adversarial learning[C]//International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, 2018: 720-727. |
| 37 |
MASPERO M , SAVENIJE M H F , DINKLA A M , et al. Dose evaluation of fast synthetic-CT generation using a generative adversarial network for general pelvis MR-only radiotherapy[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2018, 63 (18): 185001.
doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aada6d |
| 38 | BI L, KIM J, KUMAR A, et al. Synthesis of positron emission tomography (PET) images via multi-channel generative adversarial networks (GANs)[M]//Springer: Molecular imaging, reconstruction and analysis of moving body organs, and stroke imaging and treatment. 2017: 43-51. |
| 39 | PAN Y S, LIU M X, LIAN C F, et al. Synthesizing missing PET from MRI with cycle-consistent generative adversarial networks for Alzheimer's disease diagnosis[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 2018: 455-463. |
| 40 |
WEI W , POIRION E , BODINI B , et al. Predicting PET-derived myelin content from multisequence MRI for individual longitudinal analysis in multiple sclerosis[J]. NeuroImage, 2020, 223, 117308.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117308 |
| 41 | LEWIS A, MAHMOODI E, ZHOU Y, et al. Improving tuberculosis (TB) prediction using synthetically generated computed tomography (CT) images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2021: 3265-3273. |
| 42 | CALIMERI F, MARZULLO A, STAMILE C, et al. Biomedical data augmentation using generative adversarial neural networks[C]//International conference on artificial neural networks, 2017, 626-634. |
| 43 | HAN C, HAYASHI H, RUNDO L, et al. GAN-based synthetic brain MR image generation[C]//2018 IEEE 15th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2018), 2018: 734-738. |
| 44 | HAN C, MURAO K, NOGUCHI T, et al. Learning more with less: Conditional PGGAN-based data augmentation for brain metastases detection using highly-rough annotation on MR images[C]//Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, 2019: 119-127. |
| 45 |
HAN C , RUNDO L , ARAKI R , et al. Combining noise-to-image and image-to-image GANs: Brain MR image augmentation for tumor detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 156966- 156977.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947606 |
| 46 |
HASSAN DAR S U I , YURT M , KARACAN L , et al. Image synthesis in multi-contrast MRI with conditional generative adversarial networks[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2019, 38 (10): 2375- 2388.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2901750 |
| 47 | APPAN K P, SIVASWAMY J. Retinal image synthesis for CAD development[C]//International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, 2018: 613-621. |
| 48 |
IQBAL T , ALI H . Generative adversarial network for medical images (MI-GAN)[J]. J Med Syst, 2018, 42 (11): 231.
doi: 10.1007/s10916-018-1072-9 |
| 49 |
SHAKER A M , TANTAWI M , SHEDEED H A , et al. Generalization of convolutional neural networks for ECG classification using generative adversarial networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 35592- 35605.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974712 |
| 50 |
YANG H X , LIU J H , ZHANG L H , et al. ProEGAN-MS: A progressive growing generative adversarial networks for electrocardiogram generation[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 52089- 52100.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3069827 |
| 51 | WANG Y L , SUN L , SUBRAMANI S . CAB: Classifying arrhythmias based on imbalanced sensor data[J]. KSⅡ Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2021, 15 (7): 2304- 2320. |
| 52 | MADANI A, MORADI M, KARARGYRIS A, et al. Chest X-ray generation and data augmentation for cardiovascular abnormality classification[C]//Medical Imaging 2018: Image Processing, 2018, 10574105741M. |
| 53 | BAILO O, HAM D, MIN SHIN Y. Red blood cell image generation for data augmentation using conditional generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2019, 1039-1048. |
| 54 |
HALLAJI E , RAZAVI-FAR R , PALADE V , et al. Adversarial learning on incomplete and imbalanced medical data for robust survival prediction of liver transplant patients[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 73641- 73650.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3081040 |
| 55 | ALEX V , VAIDHYA K , THIRUNAVUKKARASU S , et al. Semisupervised learning using denoising autoencoders for brain lesion detection and segmentation[J]. J Med Imaging, 2017, 4 (4): 041311. |
| 56 | MADANI A, MORADI M, KARARGYRIS A, et al. Semi-supervised learning with generative adversarial networks for chest X-ray classification with ability of data domain adaptation[C]//2018 IEEE 15th International symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2018), 2018: 1038-1042. |
| 57 | JIANG J, HU Y C, TYAGI N, et al. Tumor-aware, adversarial domain adaptation from ct to mri for lung cancer segmentation[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 2018: 777-785. |
| 58 |
YOU C Y , LI G , ZHANG Y , et al. CT super-resolution GAN constrained by the identical, residual, and cycle learning ensemble (GAN-CIRCLE)[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2020, 39 (1): 188- 203.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2922960 |
| 59 |
WANG Z W , LIN Y , CHENG K T T , et al. Semi-supervised mp-MRI data synthesis with StitchLayer and auxiliary distance maximization[J]. Med Image Anal, 2020, 59, 101565.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.101565 |
| 60 |
LI W Y , LI J Y , POLSON J , et al. High resolution histopathology image generation and segmentation through adversarial training[J]. Med Image Anal, 2022, 75, 102251.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.102251 |
| 61 | ZHANG Y Z, YANG L, CHEN J X, et al. Deep adversarial networks for biomedical image segmentation utilizing unannotated images[C]//International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, 2017: 408-416. |
| 62 |
WOLTERINK J M , LEINER T , VIERGEVER M A , et al. Generative adversarial networks for noise reduction in low-dose CT[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2017, 36 (12): 2536- 2545.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2708987 |
| 63 | CHARTSIAS A, JOYCE T, DHARMAKUMAR R, et al. Adversarial image synthesis for unpaired multi-modal cardiac data[C]//International workshop on simulation and synthesis in medical imaging, 2017: 3-13. |
| 64 | WOLTERINK J M, DINKLA A M, SAVENIJE M H, et al. Deep MR to CT synthesis using unpaired data[C]//International workshop on simulation and synthesis in medical imaging, 2017: 14-23. |
| 65 | YANG H, SUN J, CARASS A, et al. Unpaired brain MR-to-CT synthesis using a structure-constrained CycleGAN[M]//Springer: Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support. 2018: 174-182. |
| 66 | BERMUDEZ C, PLASSARD A J, DAVIS L T, et al. Learning implicit brain MRI manifolds with deep learning[C]//Medical Imaging 2018: Image Processing, 2018: 10574105741L. |
| 67 |
MAHMOOD F , CHEN R , DURR N J . Unsupervised reverse domain adaptation for synthetic medical images via adversarial training[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2018, 37 (12): 2572- 2581.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2842767 |
| 68 |
LI X Y , ZHANG G X , QIAO H , et al. Unsupervised content-preserving transformation for optical microscopy[J]. Light-Sci Appl, 2021, 10 (1): 44.
doi: 10.1038/s41377-021-00484-y |
| [1] | WEI Zhihong, KONG Xudong, KONG Yan, YAN Shiju, DING Yang, WEI Xianding, KONG Dong, YANG Bo. Application of Generative Adversarial Networks Based on Global and Local Feature Information in Hippocampus Segmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 143-153. |
| [2] | CAO Fei, XU Qianqian, CHEN Hao, ZU Jie, LI Xiaowen, TIAN Jin, BAO Lei. An Intelligent Diagnosis Method for NIID Based on Cross Self-supervision and DWI [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 154-163. |
| [3] | XUE Peiyang, GENG Chen, LI Yuxin, BAO Yifang, LU Yucheng, DAI Yakang. A Classification Method for Cerebral Aneurysms in TOF-MRA Based on Improved 3D ResNet50 Model [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 56-66. |
| [4] | NING Xinzhou, HUANG Zhen, CHEN Xiqu, LIU Xinjie, CHEN Gang, ZHANG Zhi, BAO Qingjia, LIU Chaoyang. Research on Transformer Super-Resolution Reconstruction Algorithm for Ultrafast Spatiotemporal Encoding Magnetic Resonance Imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 454-468. |
| [5] | YANG Liming, WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress of Denoising Algorithms for Diffusion Tensor Images [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(3): 341-361. |
| [6] | Dai Junlong, He Cong, Wu Jie, Bian Yun. Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms Segmentation Network Combining Dual Decoding and Global Attention Upsampling Modules [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 151-161. |
| [7] | YANG Yu, CHEN Bo, WU Liubin, LIN Enping, HUANG Yuqing, CHEN Zhong. Spectrum Reconstruction for Laplace NMR: From Handcraft Regularization to Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 191-208. |
| [8] | CHANG Bo, SUN Haoyun, GAO Qingyu, WANG Lijia. Research Progress on Cardiac Segmentation in Different Modal Medical Images by Traditional Methods and Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 224-244. |
| [9] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [10] | LAI Jiawen, WANG Yuling, CAI Xiaoyu, ZHOU Lihua. Multidimensional Information Fusion Method for Meniscal Tear Classification Based on CNN-SVM [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 423-434. |
| [11] | WANG Hui, WANG Tiantian, WANG Lijia. Squeeze-and-excitation Residual U-shaped Network for Left Myocardium Segmentation Based on Cine Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 435-447. |
| [12] | Li Yijie, YANG Xinyu, YANG Xiaomei. Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction of Multi-scale Residual Unet Fused with Attention Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 307-319. |
| [13] | LU Qiqi, LIAN Zifeng, LI Jialong, SI Wenbin, MAI Zhaohua, FENG Yanqiu. Magnetic Resonance R2* Parameter Mapping of Liver Based on Self-supervised Deep Neural Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 258-269. |
| [14] | ZHANG Jiajun, LU Yucheng, BAO Yifang, LI Yuxin, GENG Chen, HU Fuyuan, DAI Yakang. An Automatic Segmentation Method of Cerebral Arterial Tree in TOF-MRA Based on DBCNet [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 320-331. |
| [15] | TIAN Hui, WU Jie, BIAN Yun, ZHANG Zhiwei, SHAO Chengwei. Classification of Pancreatic Cystic Tumors Based on DenseNet and Transfer Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 270-279. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||