
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 320-331.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20223046
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Jiajun1,LU Yucheng2,BAO Yifang2,LI Yuxin2,GENG Chen3,4,#( ),HU Fuyuan1,§(
),HU Fuyuan1,§( ),DAI Yakang1,3,*(
),DAI Yakang1,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-16
Published:2023-09-05
Online:2023-03-03
Contact:
*Tel: 15850168495, E-mail: CLC Number:
ZHANG Jiajun, LU Yucheng, BAO Yifang, LI Yuxin, GENG Chen, HU Fuyuan, DAI Yakang. An Automatic Segmentation Method of Cerebral Arterial Tree in TOF-MRA Based on DBCNet[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 320-331.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
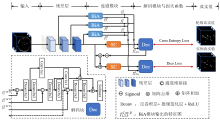
Fig. 3
The architecture diagram of DBCNet network. Where Dec is the decoding block of the network, BiA and SC are the branch decoupling module and deep feature extraction module proposed in this study. The final output feature maps $f_{i}^{\text{C}}$ and $f_{i}^{\text{D}}$ of the BiA module are obtained, where C and D represent the localization branch and the segmentation branch, respectively, and i takes 1, 2 and 3 to represent different BiA modules
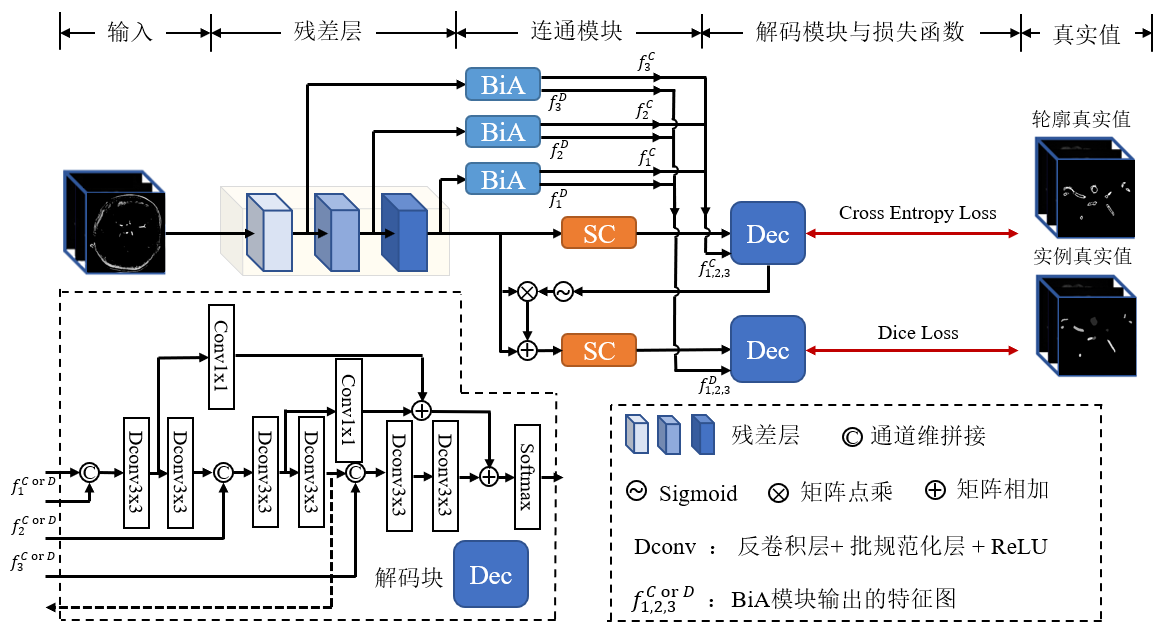
Fig. 6
3D reconstruction for DBCNet intracranial arterial tree region segmentation prediction results. Row A shows the arterial tree 3D reconstruction (threshold segmentation result of TOF-MRA), labeled real values and segmentation results of a healthy person; row B shows the arterial tree 3D reconstruction, labeled real values and segmentation results of a patient with intracranial aneurysm, the patient’s aneurysm is in the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) region. The visual effect of the real values and model segmentation results is different because the labeled real values are drawn manually using solid spheres, while the model segmentation results are obtained by up-sampling back to the original image size after voxel-level segmentation. Internal carotid arteries (ICA, blue), basilar artery (BA, green), vertebral artery (VA, purple), middle cerebral artery (MCA, yellow), anterior (ACA, red) and posterior cerebral artery (PCA, cyan)
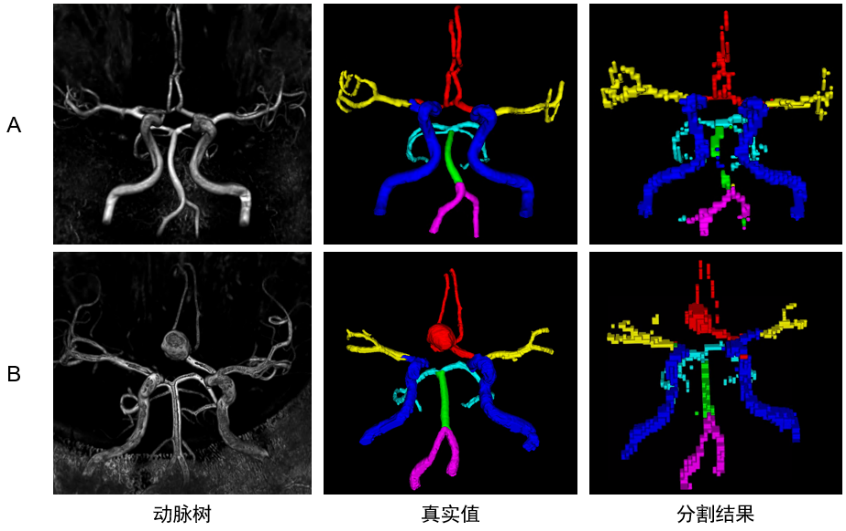
Table 2
Segmentation performance evaluation of each region of the intracranial arterial tree in the testing data set
| ACA | BA | ICA | MCA | PCA | VA | 平均 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dice/% | 86.32±4.59 | 81.56±3.54 | 92.52±1.25 | 86.53±3.44 | 81.66±3.15 | 82.92±6.28 | 74.72±3.36 |
| HD95/mm | 3.30±2.32 | 4.94±2.97 | 1.27±0.87 | 3.64±2.41 | 5.16±3.02 | 5.05±5.85 | 3.89±1.30 |
Table 3
Segmentation performance evaluation of each region of the intracranial arterial tree in the testing data set using DBCNet and other common deep learning networks
| ACA | BA | ICA | MCA | PCA | VA | 平均 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nnUNet | Dice/% | 52.18±2.29 | 0 | 80.03±5.93 | 57.00±2.15 | 45.00±15.81 | 0 | 26.78±3.91 |
| HD95/mm | 31.74±8.50 | 30 | 8.29±11.01 | 21.91±14.10 | 27.15±4.08 | 30 | 24.84±3.94 | |
| Modified UNet | Dice/% | 77.89±5.14 | 81.01±7.22 | 89.49±2.67 | 76.26±2.94 | 0 | 0 | 49.90±3.59 |
| HD95/mm | 6.48±4.48 | 8.49±14.01 | 4.95±10.67 | 7.99±3.32 | 30 | 30 | 14.65±2.69 | |
| VNet | Dice/% | 58.70±22.74 | 73.56±7.79 | 89.46±3.81 | 70.86±4.16 | 72.97±5.66 | 70.04±14.56 | 54.56±8.59 |
| HD95/mm | 13.56±8.43 | 12.59±14.59 | 5.16±11.03 | 15.76±4.84 | 22.81±6.57 | 14.33±6.69 | 14.04±8.69 | |
| DBCNet | Dice/% | 86.32±4.59 | 81.56±3.54 | 92.52±1.25 | 86.53±3.44 | 81.66±3.15 | 82.92±6.28 | 74.72±3.36 |
| HD95/mm | 3.30±2.32 | 4.94±2.97 | 1.27±0.87 | 3.64±2.41 | 5.16±3.02 | 5.05±5.85 | 3.89±1.30 |
| [1] |
GERI O, SHIRAN S I, ROTH J, et al. Vascular territorial segmentation and volumetric blood flow measurement using dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography of the brain[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2017, 37(10): 3446-3456.
doi: 10.1177/0271678X17702394 |
| [2] | TAHER F, PRAKASH N. Automatic cerebrovascular segmentation methods-a review[J]. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 10(3): 576. |
| [3] |
GAO X, UCHIYAMA Y, ZHOU X, et al. A fast and fully automatic method for cerebrovascular segmentation on time-of-flight (TOF) MRA image[J]. J Digit Imaging, 2011, 24(4): 609-625.
doi: 10.1007/s10278-010-9326-1 pmid: 20824304 |
| [4] | CHEN M, GENG C, LI Y X, et al. Automatic detection for cerebral aneurysms in TOF-MRA images based on fuzzy label and deep learning[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(3): 267-277. |
| 陈萌, 耿辰, 李郁欣, 等. 基于模糊标签和深度学习的TOF-MRA影像脑动脉瘤自动检测[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(3): 267-277. | |
| [5] |
REN Y, CHEN G Z, LIU Z, et al. Reproducibility of image-based computational models of intracranial aneurysm: a comparison between 3D rotational angiography, CT angiography and MR angiography[J]. Biomed Eng Online. 2016, 15: 50.
doi: 10.1186/s12938-016-0163-4 pmid: 27150439 |
| [6] |
MU N, LYU Z, REZAEITALESHMAHALLEH M, et al. An attention residual U-Net with differential preprocessing and geometric postprocessing: Learning how to segment vasculature including intracranial aneurysms[J]. Med Image Anal, 2023, 84: 102697.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102697 |
| [7] | LI Y, NI J, ELAZAB A, et al. Multiple self-attention network for intracranial vessel segmentation[C]// International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Online: IEEE, 2021: 1-8. |
| [8] | BIZJAK Ž, CHIEN A, BURNIK I, et al. Novel dataset and evaluation of state-of-the-art vessel segmentation methods[J]. SPIE, 2022, 12032, 120322x. |
| [9] |
XIA L k, ZHANG H, WU Y, et al. 3D vessel-like structure segmentation in medical images by an edge-reinforced network[J]. Med Image Anal, 2022, 82: 102581.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102581 |
| [10] |
JONES J D, CASTANHO P, BAZIRA P, et al. Anatomical variations of the circle of Willis and their prevalence, with a focus on the posterior communicating artery: A literature review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Anat, 2021, 34(7): 978-990.
doi: 10.1002/ca.v34.7 |
| [11] | TAKEMURA A, SUZUKI M, HARAUCHI H, et al. Automatic segmentation method which divides a cerebral artery tree in time-of-flight MR-angiography into artery segments[J]. P Soc Photo Opt Instrum Eng, 2006, 6144: 1098-1106. |
| [12] |
NOWINSKI W L, VOLKAU I, MARCHENKO Y, et al. A 3D model of human cerebrovasculature derived from 3T magnetic resonance angiography[J]. Neuroinformatics, 2009, 7(1): 23-36.
doi: 10.1007/s12021-008-9028-8 pmid: 19016001 |
| [13] |
CHEN L, MOSSA-BASHA M, SUN J, et al. Quantification of morphometry and intensity features of intracranial arteries from 3D TOF MRA using the intracranial artery feature extraction (iCafe): A reproducibility study[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 57: 293-302.
doi: S0730-725X(18)30538-1 pmid: 30580079 |
| [14] |
CHEN L, SUN J, HIPPE D S, et al. Quantitative assessment of the intracranial vasculature in an older adult population using iCafe[J]. Neurobiology of Aging, 2019, 79: 59-65.
doi: S0197-4580(19)30077-6 pmid: 31026623 |
| [15] |
LIU L L, CHENG J H, QUAN Q, et al. A survey on U-shaped networks in medical image segmentations[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 409: 244-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.070 |
| [16] | QIU Y, NIE S D, WEI L. Segmentation of breast tumors based on fully convolutional network and dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance image[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(2): 196-207. |
| 邱玥, 聂生东, 魏珑. 基于全卷积网络的乳腺肿瘤动态增强磁共振图像分割[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(2): 196-207. | |
| [17] | FAN D P, JI G P, SUN G, et al. Camouflaged object detection[C]// Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 2777-2787 |
| [18] |
YANG Z, SOLTANIAN-ZADEH S, FARSIU S. BiconNet: An edge-preserved connectivity-based approach for salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recogn, 2022, 121: 108231.
doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108231 |
| [19] | LIU Z, LIN Y T, CAO Y, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]// International Conference on Computer Vision, China:IEEE, 2021: 10012-10022. |
| [20] |
YUSHKEVICH P, PIVEN J, HAZLETT H, et al. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability[J]. Neuroimage. 2006, 31(3): 1116-28.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.015 pmid: 16545965 |
| [21] |
INCI S, ERBENGI A, ÖZGEN T. Aneurysms of the distal anterior cerebral artery: report of 14 cases and a review of the literature[J]. Surg Neurol, 1998, 50(2): 130-140.
pmid: 9701118 |
| [22] | CANNY J. A computational approach to edge detection[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 1986, 8(6): 679-98. |
| [23] | HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]// Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, USA: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| [24] | WOO S H, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[J]. Computer Vision, 2018, 11211: 3-19. |
| [25] |
YEUNG M, SALA E, SCHÖNLIEB C B, et al. Unified focal loss: Generalising dice and cross entropy-based losses to handle class imbalanced medical image segmentation[J]. Comput Med Imag Grap, 2022, 95: 102026.
doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2021.102026 |
| [26] |
ISENSEE F, JAEGER P F, KOHL S A A, et al. nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation[J]. Nat Methods, 2021, 18(2): 203-211.
doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-01008-z pmid: 33288961 |
| [27] | ISENSEE F, KICKINGEREDER P, WICK W, et al. Brain tumor segmentation and radiomics survival prediction: Contribution to the BRATS 2017 Challenge[J]. Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries, 2017, 10670: 287-297. |
| [28] | MILLETARI F, NAVAB N, AHMADI S A, et al. V-Net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation[C]// International Conference on 3d Vision, 2016: 565-571. |
| [29] | ÇIÇEK Ö, ABDULKADIR A, LIENKAMP S S. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation[C]// Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 2016: 424-432. |
| [1] | CAO Fei, XU Qianqian, CHEN Hao, ZU Jie, LI Xiaowen, TIAN Jin, BAO Lei. An Intelligent Diagnosis Method for NIID Based on Cross Self-supervision and DWI [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 154-163. |
| [2] | XUE Peiyang, GENG Chen, LI Yuxin, BAO Yifang, LU Yucheng, DAI Yakang. A Classification Method for Cerebral Aneurysms in TOF-MRA Based on Improved 3D ResNet50 Model [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 56-66. |
| [3] | NING Xinzhou, HUANG Zhen, CHEN Xiqu, LIU Xinjie, CHEN Gang, ZHANG Zhi, BAO Qingjia, LIU Chaoyang. Research on Transformer Super-Resolution Reconstruction Algorithm for Ultrafast Spatiotemporal Encoding Magnetic Resonance Imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 454-468. |
| [4] | YANG Liming, WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress of Denoising Algorithms for Diffusion Tensor Images [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(3): 341-361. |
| [5] | Dai Junlong, He Cong, Wu Jie, Bian Yun. Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms Segmentation Network Combining Dual Decoding and Global Attention Upsampling Modules [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 151-161. |
| [6] | YANG Yu, CHEN Bo, WU Liubin, LIN Enping, HUANG Yuqing, CHEN Zhong. Spectrum Reconstruction for Laplace NMR: From Handcraft Regularization to Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 191-208. |
| [7] | CHANG Bo, SUN Haoyun, GAO Qingyu, WANG Lijia. Research Progress on Cardiac Segmentation in Different Modal Medical Images by Traditional Methods and Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 224-244. |
| [8] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [9] | LAI Jiawen, WANG Yuling, CAI Xiaoyu, ZHOU Lihua. Multidimensional Information Fusion Method for Meniscal Tear Classification Based on CNN-SVM [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 423-434. |
| [10] | WANG Hui, WANG Tiantian, WANG Lijia. Squeeze-and-excitation Residual U-shaped Network for Left Myocardium Segmentation Based on Cine Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 435-447. |
| [11] | Li Yijie, YANG Xinyu, YANG Xiaomei. Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction of Multi-scale Residual Unet Fused with Attention Mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 307-319. |
| [12] | LU Qiqi, LIAN Zifeng, LI Jialong, SI Wenbin, MAI Zhaohua, FENG Yanqiu. Magnetic Resonance R2* Parameter Mapping of Liver Based on Self-supervised Deep Neural Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 258-269. |
| [13] | TIAN Hui, WU Jie, BIAN Yun, ZHANG Zhiwei, SHAO Chengwei. Classification of Pancreatic Cystic Tumors Based on DenseNet and Transfer Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 270-279. |
| [14] | HUANG Min,LI Siyi,CHEN Junbo,ZHOU Dao. Progress of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting Technology and Its Clinical Application [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 207-219. |
| [15] | QIAN Chengyi,WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress on Imaging Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(2): 220-238. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||