引言
神经元核内包涵体病(Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease,NIID)是一种相对罕见的慢性进展性神经退行性疾病[1],其病理特征为在多种系统的组织细胞中出现嗜酸性核内包涵体[2].NIID临床表现多样且无特异性,包括认知障碍、椎体系及椎体外系症状、小脑共济失调、肢体无力、感觉异常及自主神经功能紊乱等[3],常被误诊为脑炎或白质脑病等其他脑病.NIID目前常用的诊断依据主要有3点:脑磁共振成像(Magnetic Resonance Imaging,MRI)皮髓质交界区DWI高信号[4]、皮肤活检[5]和基因检测[6],其中以DWI成像上皮髓质交界处高信号作为最有力、最易获得的证据,可指导进一步的皮肤活检和诊断,因此早期识别NIID的影像学特征具有重要意义[7].但由于NIID的罕见性及患者发病时出现多系统的临床四不像现象,其典型的影像学表现很容易被忽视,从而导致漏诊或误诊,严重影响病人诊疗及时性和预后,亟需一种基于DWI的NIID智能分类方法辅助医生临床诊断.
随着医学影像和人工智能的不断发展,深度学习技术被越来越多地应用于医学图像处理[8],基于深度神经网络的方法可以实现一些基于脑MRI的疾病自动诊断.Qian等[9]探究了基于深度学习和影像的阿尔茨海默症分类,研究结果表明深度学习方法能够较好地用于辅助阿尔茨海默症自动分类.Calabrese等[10]将影像组学和深度学习模型相结合,从而实现了基于脑MRI的胶质瘤O6-甲基鸟嘌呤-DNA甲基转移酶(MGMT)甲基化状态预测.Xue等[11]提出一种改进后的卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)对基于磁共振血管造影的脑动脉瘤进行分类,取得良好效果.但这些深度学习方法往往建立在足够的数据量之上,而对于数据量通常较小的NIID一类罕见病,则需要构建特征提取能力更强、泛化性更好的模型.自监督学习主要是利用辅助任务从无监督数据中挖掘自身的监督信息,通过这种构造的监督信息对网络进行训练,可以学习到对分类任务有价值的表征,从而更好地提取特征进而完成分类[12],自监督学习方法已被证明在医学图像应用中有很大作用[13].Zhu等[14]提出一种基于扩散模型自监督表征学习的方法用于脑肿瘤图像分类,该自监督学习方法能够充分捕捉图像的细节特征,从而提高脑肿瘤图像分类准确率.Wang等[15]将自监督学习方法用于医学图像的分割任务中,取得较好分割效果.Xie等[16]建立了一个通用的医学自监督表示学习框架,在基于医学图像的分割和分类任务中均表现突出.目前常用的自监督学习方法通常仅使用了一种架构,即CNN或Transformer,且已有研究表明[17-18],同时使用CNN和Transformer的自监督学习架构特征提取能力更强,这主要是因为CNN和Transformer在训练过程中能够互相学习,从而实现特征交叉融合.
1 实验部分
1.1 数据及其预处理
1.1.1 数据集
本研究使用的数据集来源于徐州医科大学附属医院,入组标准为:(1)已经确诊的NIID患者;(2)治疗前MRI扫描包含DWI序列;(3)无严重运动伪影.最终被纳入数据集的NIID病例共有150例,作为对照组,本研究额外选取了99例非NIID人群的影像.所有影像数据采集时间为2012年9月至2023年10月,每例数据包含18张DWI影像,实验中去除不包含任何病灶的切片.本研究使用的数据均来源于临床常规工作,同时已获得徐州医科大学附属医院伦理委员会的批准(批准号:XYFY2019-KL059-01).249例数据以一定比例随机划分为训练集和测试集,其中训练集204例共2 472张影像(NIID 120例共960张影像,非NIID 84例共1 512张影像),测试集45例共510张影像(NIID 30例共240张影像,非NIID 15例共270张影像),样本具体信息如表1所示.所有数据采集自Philips、GE和TOSHIBA三种设备,不同仪器在采集DWI序列时的使用参数如表2所示.
表1 病例信息表
Table 1
| 特征 | 训练集 | 测试集 |
|---|---|---|
| 样本数量 | 204 | 45 |
| 年龄/岁 | 64.92±9.88 | 60.47±11.91 |
| 男性/女性 | 86/118 | 22/23 |
表2 数据采集参数表
Table 2
| 仪器 | 重复时间/ms | 回波时间/ms | 图像分辨率 | 层厚/mm | 翻转角 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Philips 3.0T | 2820.82 | 80.45 | 256×256×18 | 5 | 90° |
| GE 3.0T | 4880.00 | 78.10 | 256×256×18 | 6 | 90° |
| TOSHIBA 3.0T | 4000.00 | 100.00 | 256×256×18 | 6 | 90° |
1.1.2 数据预处理
本研究的数据预处理包括以下三个操作:
(1) 图像清洗.去除每个NIID病例影像序列的前5张及后5张切片,此部分不包含任何病灶.
(2) 重采样、标准化和归一化.重采样后每张图像大小为224×224,然后将所有图像的灰度值映射至[0,1]之间.
(3) 图像扩增.为了保证网络训练过程中有足够的数据量,本研究对训练集进行数据扩增操作,扩增方法为动态扩增,即每次训练前对训练集进行随机扩增,包括水平翻转(概率0.5)和随机仿射变换(角度±6˚)两种扩增方式,扩增倍数为3倍.如图1所示分别是DWI影像的NIID原图、水平翻转图、仿射变换图.
图1
图1
NIID图像扩增示例. 从左至右依次为原图、水平翻转图和仿射变换图
Fig. 1
An example of NIID image amplification. Left to right: original, horizontal flip, affine transformation
1.2 基于交叉自监督学习的NIID自动分类方法
1.2.1 实验方法
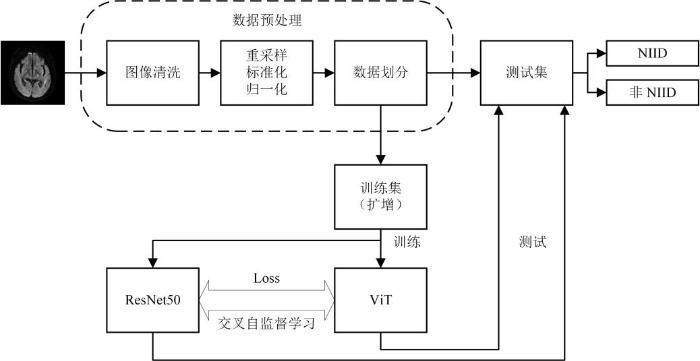
本文提出一种基于交叉自监督的NIID智能诊断模型,该模型主要由两部分组成,一部分为基于特征相似度的交叉自监督学习架构,用于优化特征提取,另一部分为自监督预训练后的模型,用于完成NIID自动分类.整个方法的具体流程如图2所示,首先对图像数据进行预处理,接着将预处理后的图像输入基于ResNet50和ViT的自监督学习架构,并保留ResNet50和ViT预训练权重,然后使用训练集对ResNet50或ViT进行微调训练得到最佳模型,最后在测试集上完成模型评估,输出分类结果.
图2
图2
方法流程图. Loss为余弦损失函数
Fig. 2
Flowchart of the method, where Loss is the cosine Loss function
1.2.2 基于交叉自监督的优化特征提取网络CO-ResNet50和CO-ViT
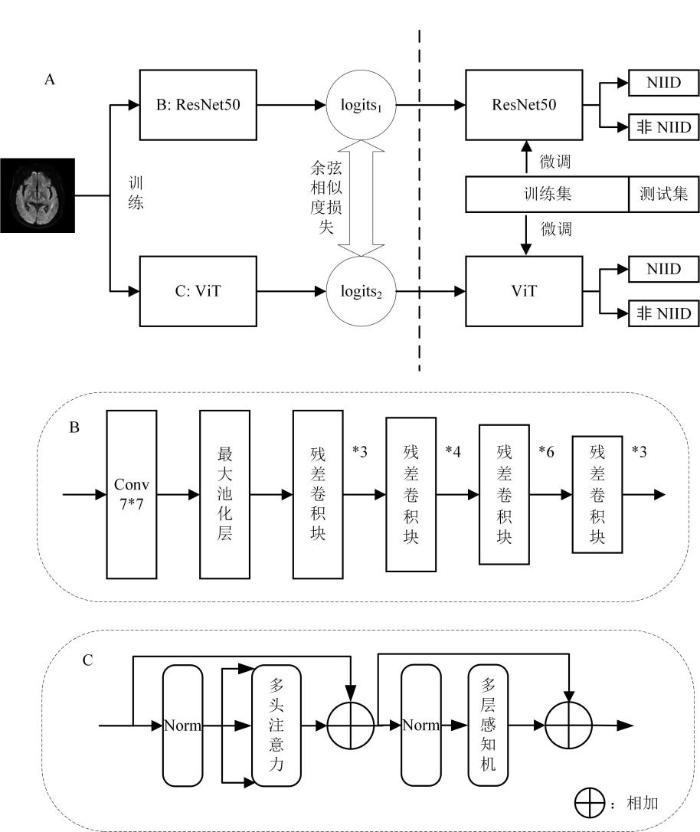
如图3所示,本研究使用的交叉自监督学习架构由一个ResNet50和一个ViT网络组成.在交叉自监督学习架构中,训练集将被同时输入ResNet50和ViT网络进行特征提取训练,且此时不需要任何标签,然后对比ResNet50和ViT网络的输出特征相似度,并以余弦相似度损失作为衡量标准,具体如(1)式和(2)式所示:
其中,x为输入向量,F(x)为模型全连接层输出向量,i和N表示计算过程中的特征图数量.R为ResNet50的输入向量,F(R)为ResNet50的全连接层输出,T为ViT的输入向量,F(T)为ViT的全连接层输出,Loss为余弦相似度损失.
图3
图3
交叉自监督学习架构. A为网络整体架构,B为ResNet50主体结构,C为ViT主体结构. logits1为ResNet50的输出,logits2为ViT的输出,Conv为卷积操作,Norm为归一化层
Fig. 3
Architecture of cross self-supervision. The part of A shows the overall network structure, while the part of B displays the main structure of ResNet50, the part of C displays the main structure of ViT. logits1 is the output of ResNet50, logits2 is the output of ViT, Conv is the convolution operation, and Norm is the normalization layer
和CNN相比,Transformer在所有层中的表示更加统一,且具有自注意功能,能够从浅层聚合全局信息,并跳过低层与高层的连接实现信息传递,但其低层和高层显示出更多的相似性,且较早的层中不会关注局部信息.CNN的感受野是逐渐扩大的,其局部感知性强、鲁棒性强、可拓展性强,但缺乏对全局信息的感知力.即CNN在处理局部特征方面表现出色,在处理全局信息时表现较弱,Transformer在处理全局信息方面具有优势,对于局部信息处理能力相对较弱.因此对于相同的输入,CNN中的ResNet50和Transformer中的ViT网络会提取不同的特征表示,我们通过交叉自监督学习将两者进行特征交叉融合,兼顾局部特征和全局特征,以优化特征提取,提高模型特征提取能力.具体地,将训练集分别输入ResNet50和ViT网络,以(1)式和(2)式对两者的输出特征向量做相似度对比计算,即经特征提取后,分别得到ResNet50和ViT的全连接层输出向量,然后将两者输出向量进行余弦相似度对比.经训练后当余弦相似度损失降低到一定程度时,即两个网络提取的特征向量达到一定相似度时,分别保存ResNet50和ViT模型权重,此时的网络称为Combine-ResNet50(CO-ResNet50)和Combine-ViT(CO-ViT).保存模型交叉自监督学习预训练权重后,以有标签训练集微调CO-ResNet50和CO-ViT网络,通过Softmax函数输出每张图像属于每个类别的概率,并计算每张图像的最大概率及其所属类别作为分类结果.微调训练完成后,再次分别保存ResNet50和ViT最佳模型用于后续分类测试,测试过程中不需要将测试集输入交叉自监督学习框架部分,这样的设计在保证分类准确率的同时能够最大程度节省分类时间,且保证了分类模型的独立性,使得保存预训练权重后的模型无需反复进行交叉自监督学习训练,具有灵活性和可迁移性.
1.3 模型评估
本研究使用准确率(Accuracy)、曲线下面积(Area Under Curve,AUC)、精确率(Precision)、召回率(Recall)和F1分数(F1_Score)五种评价指标,来定量地衡量所提出的方法在NIID智能诊断上的性能表现.AUC表示的是受试者工作特征(Receiver Operating Characteristic,ROC)曲线下面积,取值范围介于0~1之间,AUC越接近1,一般认为模型性能越好.准确率是对于给定的测试数据集,分类器正确分类的样本数与总样本数之比:
精确率表示的是分类为NIID的样本中有多少是真正的NIID:
召回率表示的是NIID的样本中有多少被分类正确:
一般来说,当精确率高的时候,召回率一般很低;召回率高时,精确率一般很低. 而F1分数是精确率和召回率的调和均值,作用是对精确率和召回率进行调和:
其中,真阳性(True Positive,TP)是被模型正确分类为NIID的样本;真阴性(True Negative,TN)是被模型正确分类为非NIID的样本;假阳性(False Positive,FP)是被模型错误分类为NIID的样本;假阴性(False Negative,FN)是被模型错误分类为非NIID的样本.
1.4 训练环境与参数设置
本研究的模型训练基于显存32 GB的NVIDIA A40 GPU,主要软件环境为:CUDA 12.1、Python 3.9.18和PyTorch 2.2.0.相关参数设置如下:输入图像大小为224×224;批处理大小为64;优化器为Adam,初始学习率为1e-3,权重衰减为1e-4,学习率调整策略为余弦退火学习率;交叉自监督学习部分损失函数为余弦相似度损失,迭代次数100次;分类部分损失函数为交叉熵损失,迭代次数200次.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 基于交叉自监督学习的NIID自动分类结果
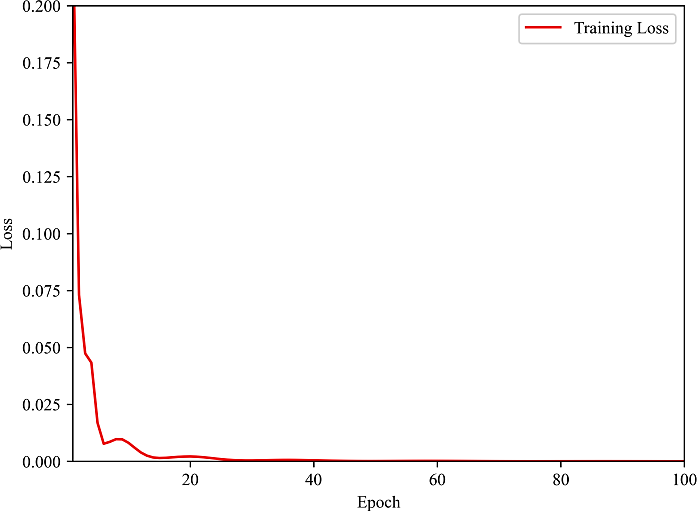
本研究首先使用训练集对基于ResNet50和ViT的交叉自监督学习部分进行特征提取训练,将训练集分别输入ResNet50和ViT模型,并对比两者提取的特征输出,当损失达到最小,即特征余弦相似度达到最高时停止训练.如图4所示是模型自监督学习训练过程,从图中可以看出模型自监督学习训练收敛较为快速和稳定,并达到了一个较好的收敛效果,可以认为ResNet50和ViT模型均提取到了最具代表性的特征,保留两者此时的模型权重.
图4
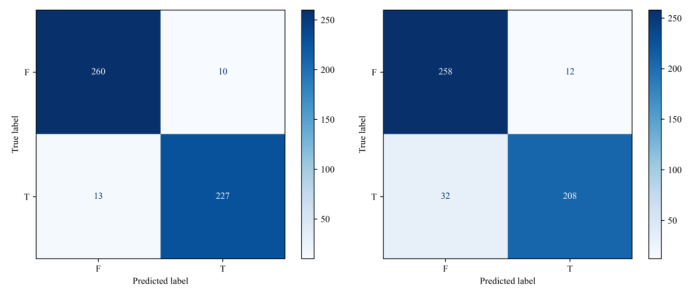
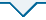
模型自监督学习训练完成后,使用训练集对保留模型权重的CO-ResNet50和CO-ViT模型微调训练,并使用测试集对微调后的模型进行评估.微调后的CO-ResNet50在测试集上的准确率、精确率、召回率、F1分数和AUC分别为95.49%、95.51%、95.44%、0.954 7和0.989 7;微调后的CO-ViT在测试集上的准确率、精确率、召回率、F1分数以及AUC分别为91.37%、91.76%、91.11%、0.912 9和0.970 4.图5是模型在测试集上预测结果的混淆矩阵,其左上和右下分别表示每个类别被正确预测的个数.实验结果表明,本研究提出的基于交叉自监督学习的优化特征提取方法对于NIID有较好的分类能力,能够做到NIID智能辅助诊断.
图5
图5
模型预测结果混淆矩阵. 左:CO-ResNet50,右:CO-ViT
Fig. 5
Confusion matrix of the prediction results of the models. Left: CO-ResNet50, Right: CO-ViT
2.2 不同模型的性能对比
在相同的实验数据和训练环境下,本研究进行了一些消融实验和对比实验,并比较不同模型在测试集中的分类性能.如图6所示是不同模型的ROC曲线,曲线的位置越高,AUC值越大,说明模型性能越好.从图6中可以看出,基于本研究交叉自监督学习方法的CO-ResNet50模型AUC值最大,为0.989 7,模型性能最佳.表3则展示了所有模型在测试集上的定量指标结果,从表中可以看出,CO-ResNet50在各项指标中表现均为最好;CO-ViT次之,其AUC值略低于基于掩膜自编码器(Masked Autoencoders,MAE)[21]的ViT方法;而消融实验中没有经过自监督学习的单独的ViT方法在各方面表现均为最差.实验结果表明,基于自监督学习的方法可以有效提高模型性能,而在本研究提出的交叉自监督学习方法中,后续分类任务采用ResNet50要好于采用ViT,这可能和数据量有关,ViT模型更适合数据量更大的情况.综合ROC曲线和各项指标表现,可以认为本研究提出的方法在基于DWI影像的NIID分类任务中表现最佳,模型各方面性能最好,可以有效完成NIID智能辅助诊断.
图6
图6
本文方法与对比模型的ROC曲线
Fig. 6
The ROC curves of the proposed method and other models
表3 本文方法与对比模型的性能比较
Table 3
| 方法 | 准确率/% | 精确率/% | 召回率/% | F1分数 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ViT | 82.75 | 82.80 | 82.55 | 0.8263 | 0.9304 |
| ResNet50 | 86.86 | 87.19 | 86.57 | 0.8673 | 0.9625 |
| MAE_ViT | 90.78 | 91.26 | 90.49 | 0.9068 | 0.9729 |
| CO-ViT | 91.37 | 91.76 | 91.11 | 0.9129 | 0.9704 |
| CO-ResNet50 | 95.49 | 95.51 | 95.44 | 0.9547 | 0.9897 |
2.3 讨论
本文提出一种基于交叉自监督的深度学习模型用于DWI影像的NIID智能诊断.该方法将ResNet50和ViT模型提取到的特征进行余弦相似度对比,优化特征提取,提高模型特征表达能力;同时考虑到ResNet50模型更适合提取局部特征、ViT模型更适合提取全局特征的特点,该方法兼顾局部特征和全局特征的提取.自监督学习完成后,利用自监督预训练保存的模型权重进行下游分类任务,可有效强化模型性能,提高模型分类准确率.此外,模型在训练过程中采用水平翻转、随机仿射变换等方法对训练集进行动态扩增,以保证数据量充足.模型训练完成后在测试集上进行测试和评估.
从图6和表3的测试结果中可以看出,CO-ResNet50和CO-ViT在准确率、精确率、召回率、F1分数和AUC指标上均有较好表现,以病例为单位其诊断准确率更是基本可达100%.基于MAE自监督学习方法的ViT(MAE_ViT)准确率较CO-ViT低了0.59%,F1分数低了0.006 1,AUC则高了0.002 5,模型综合性能在CO-ViT之下.而消融实验中,未经交叉自监督学习预训练的ResNet50,其准确率、F1分数和AUC分别比CO-ResNet50低了8.63%、0.087 4、0.027 2;未经交叉自监督学习预训练的ViT,其准确率、F1分数和AUC分别比CO-ViT低了8.62%、0.086 6、0.04.这些实验结果表明,本研究基于交叉自监督学习的方法可以显著提高模型特征提取能力,优化模型性能,使模型拥有更强的分类能力和更高的鲁棒性.此外,在同等条件下本研究中基于ResNet50的模型表现总是优于基于ViT的模型,这可能是因为ViT模型的训练往往需要更大量的数据集,而在面对类似于NIID的小样本罕见病时,模型表现则会差一些,但这并不妨碍其在交叉自监督学习中起到的优化特征提取的作用.
本研究在实验过程中使用的是NIID单模态的DWI影像,因此还存在一定局限性.下一步,本研究将纳入多模态数据,如CT影像、病历文本数据、实验室检验数据等,并考虑纳入多家医院数据,形成多中心研究,以进一步提高模型分类能力和模型泛化性.
3 结论
本文针对DWI影像的NIID智能辅助诊断提出一种基于交叉自监督的深度学习模型CO-ResNet50和CO-ViT,该方法可有效加强模型特征提取能力,提高模型性能.在测试集中的测试结果表明,CO-ResNet50可达到95.49%的准确率,CO-ViT也可达到91.37%的准确率.因此,可以认为本研究提出的方法有望辅助医生进行NIID诊断和治疗计划制定,提高医生临床诊疗效率,在类似的罕见病智能辅助诊断中应用前景广泛.
利益冲突
无
参考文献
MRI manifestations of adult-onset neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease
[J].
成人型神经元核内包涵体病脑MRI表现
[J].
MR findings of adult neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease: report of 8 cases and literature review
[J].
成人型神经元核内包涵体病的颅脑MR表现
[J].
Expanding the clinical spectrum of adult-onset neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease
[J].
Clinicopathological features of adult-onset neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease
[J].Neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease (NIID) is a slowly progressive neurodegenerative disease characterized by eosinophilic hyaline intranuclear inclusions in the central and peripheral nervous system, and also in the visceral organs. NIID has been considered to be a heterogeneous disease because of the highly variable clinical manifestations, and ante-mortem diagnosis has been difficult. However, since we reported the usefulness of skin biopsy for the diagnosis of NIID, the number of NIID diagnoses has increased, in particular adult-onset NIID. In this study, we studied 57 cases of adult-onset NIID and described their clinical and pathological features. We analysed both NIID cases diagnosed by post-mortem dissection and by ante-mortem skin biopsy based on the presence of characteristic eosinophilic, hyaline and ubiquitin-positive intanuclear inclusion: 38 sporadic cases and 19 familial cases, from six families. In the sporadic NIID cases with onset age from 51 to 76, dementia was the most prominent initial symptom (94.7%) as designated 'dementia dominant group', followed by miosis, ataxia and unconsciousness. Muscle weakness and sensory disturbance were also observed. It was observed that, in familial NIID cases with onset age less than 40 years, muscle weakness was seen most frequently (100%), as designated 'limb weakness group', followed by sensory disturbance, miosis, bladder dysfunction, and dementia. In familial cases with more than 40 years of onset age, dementia was most prominent (100%). Elevated cerebrospinal fluid protein and abnormal nerve conduction were frequently observed in both sporadic and familial NIID cases. Head magnetic resonance imaging showed high intensity signal in corticomedullary junction in diffusion-weighted image in both sporadic and familial NIID cases, a strong clue to the diagnosis. All of the dementia dominant cases presented with this type of leukoencephalopathy on head magnetic resonance imaging. Both sporadic and familial NIID cases presented with a decline in Mini-Mental State Examination and Frontal Assessment Battery scores. Based on these clinicopathological features, we proposed a diagnosis flow chart of adult-onset NIID. Our study suggested that the prevalence rate of adult-onset NIID may be higher than previously thought, and that NIID may be underdiagnosed. We should take NIID into account for differential diagnosis of leukoencephalopathy and neuropathy.© The Author (2016). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Skin biopsy is useful for the antemortem diagnosis of neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease
[J].
DOI:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182166e13
PMID:21411744
[本文引用: 1]

Neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease (NIID) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease characterized by eosinophilic hyaline intranuclear inclusions in neuronal and somatic cells. Because of the variety of clinical manifestations, antemortem diagnosis of NIID is difficult.Seven skin biopsy samples from patients with familial NIID were evaluated histochemically, and the results were compared with those of skin samples from normal control subjects and from patients with other neurologic diseases. We also examined skin biopsy samples from patients with NIID by electron microscopy.In NIID skin biopsy samples, intranuclear inclusions were observed in adipocytes, fibroblasts, and sweat gland cells. These inclusions were stained with both anti-ubiquitin and anti-SUMO1 antibodies. Electron microscopy revealed that the features of the intranuclear inclusions in adipocytes, fibroblasts, and sweat gland cells were identical to those of neuronal cells. Approximately 10% of adipocytes showed intranuclear inclusions. No intranuclear inclusions were identified in the skin samples from normal control subjects and patients with other neurologic diseases.Skin biopsy is an effective and less invasive antemortem diagnostic tool for NIID.
Noncoding CGG repeat expansions in neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease, oculopharyngodistal myopathy and an overlapping disease
[J].
DOI:10.1038/s41588-019-0458-z
PMID:31332380
[本文引用: 1]

Noncoding repeat expansions cause various neuromuscular diseases, including myotonic dystrophies, fragile X tremor/ataxia syndrome, some spinocerebellar ataxias, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsies. Inspired by the striking similarities in the clinical and neuroimaging findings between neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease (NIID) and fragile X tremor/ataxia syndrome caused by noncoding CGG repeat expansions in FMR1, we directly searched for repeat expansion mutations and identified noncoding CGG repeat expansions in NBPF19 (NOTCH2NLC) as the causative mutations for NIID. Further prompted by the similarities in the clinical and neuroimaging findings with NIID, we identified similar noncoding CGG repeat expansions in two other diseases: oculopharyngeal myopathy with leukoencephalopathy and oculopharyngodistal myopathy, in LOC642361/NUTM2B-AS1 and LRP12, respectively. These findings expand our knowledge of the clinical spectra of diseases caused by expansions of the same repeat motif, and further highlight how directly searching for expanded repeats can help identify mutations underlying diseases.
Clinical and multimodal imaging features of adult-onset neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s10072-024-07699-y
PMID:39023713
[本文引用: 1]

This study aimed to analyze the clinical and multimodal imaging manifestations of adult-onset neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease (NIID) patients and to investigate NIID-specific neuroimaging biomarkers.Forty patients were retrospectively enrolled from the Qilu Hospital of Shandong University. We analyzed the clinical and imaging characteristics of 40 adult-onset NIID patients and investigated the correlation between these characteristics and genetic markers and neuropsychological scores. We further explored NIID-specific alterations using multimodal imaging indices, including diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), and brain age estimation. In addition, we summarized the dynamic evolution pattern of NIID by examining the changes in diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) signals over time.The NIID patients' ages ranged from 31 to 77 years. Cognitive impairment was the most common symptom (30/40, 75.0%), while some patients (18/40, 45.0%) initially presented with episodic symptoms such as headache (10/40, 25.0%). Patients with cognitive impairment symptoms had more cerebral white matter damage (χ2 = 11.475, P = 0.009). The most prevalent imaging manifestation was a high signal on DWI in the corticomedullary junction area, which was observed in 80.0% (32/40) of patients. In addition, the DWI dynamic evolution patterns could be classified into four main patterns. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) revealed extensive thinning of cerebral white matter fibers. The estimated brain age surpassed the patient's chronological age, signifying advanced brain aging in NIID patients.The clinical manifestations of NIID exhibit significant variability, usually leading to misdiagnosis. Our results provided new imaging perspectives for accurately diagnosing and exploring this disease's neuropathological mechanisms.© 2024. The Author(s).
Automatic detection for cerebral aneurysms in TOF-MRA images based on fuzzy label and deep learning
[J].
基于模糊标签和深度学习的TOF-MRA影像脑动脉瘤自动检测
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20223004
[本文引用: 1]

脑动脉瘤破裂造成的蛛网膜下腔出血致死致残率极高,借助深度学习网络辅助医生实现高效筛查具有重要意义.为提高基于时间飞跃法磁共振血管造影(Time of Flight-Magnetic Resonance Angiography,TOF-MRA)的脑动脉瘤自动检测的精度,本文基于模糊标签方式,提出一种基于变体3D U-Net和双分支通道注意力(Dual-branch Channel Attention,DCA)的深度神经网络DCAU-Net,DCA模块可以自适应地调整通道特征的响应,提高特征提取能力.首先对260例病例的TOF-MRA影像预处理,将数据集分为174例训练集、43例验证集和43例测试集,然后使用处理后的数据训练和验证DCAU-Net,测试集实验结果表明DCAU-Net可以达到90.69%的敏感度,0.83个/例的假阳性计数和0.52的阳性预测值,有望为动脉瘤筛查提供参考.
Research progress on imaging classification of Alzheimer’s disease based on deep learning
[J].
基于深度学习的阿尔兹海默症影像学分类研究进展
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20223013
[本文引用: 1]

随着全球老龄化的加剧与深度学习的发展,基于深度学习的阿尔兹海默症(AD)影像学分类成为当前的一个研究热点.本文首先阐述了AD影像学分类任务中常用的深度学习模型、评估标准及公开数据集;接着讨论了不同图像模态在AD影像学分类中的应用;然后着重探讨了应用于AD影像学分类的深度学习模型改进方法;进一步引入了对模型可解释性研究的探讨;最后总结并比较了文中提及的分类模型,归纳了与AD影像分类相关的大脑区域,并对该领域未来的研究方向进行了展望.
Combining radiomics and deep convolutional neural network features from preoperative MRI for predicting clinically relevant genetic biomarkers in glioblastoma
[J].
A Classification Method for Cerebral Aneurysms in TOF-MRA Based on Improved 3D ResNet50 Model
[J].
基于改进的3D ResNet50模型的TOF-MRA脑动脉瘤分类方法
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20243119
[本文引用: 1]

脑动脉瘤的不规则形态,尤其是子瘤的存在,是动脉瘤破裂风险的关键因素.临床上对子瘤的评估主要是通过时间飞跃法磁共振血管造影(Time of Flight-Magnetic Resonance Angiography,TOF-MRA)进行图像重建及基于医生视觉和经验的判断,这限制了诊断的效率和准确性.本文提出了一种基于3D ResNet50改进的并行多尺度注意力融合网络(Parallel Multiscale Attention Fusion Networks,PMAF-Net)的子瘤自动分类方法,PMAF-Net采用多尺度卷积并加权融合通道和空间注意力权重以提高特征提取能力.实验所用TOF-MRA数据291例,其中训练集128例,验证集32例,测试集131例.与其他分类网络比较,PMAF-Net在测试集上表现最好,准确率为83.97%,召回率为84.48%,精确率为80.33%,F1分数为0.823 5,受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)也显示出模型最佳的分类性能(AUC为0.900 8).实验结果表明该网络能更准确地识别出子瘤型动脉瘤,有望对动脉瘤破裂风险评估和量化提供支持.
Big self-supervised models advance medical image classification
[C]//
Contrastive self-supervised learning from 100 million medical images with optional supervision
[J].
Research on brain tumor medical image classification based on diffusion self-supervised representation learning
[J].
基于扩散模型自监督表征学习的脑瘤医学图像分类研究
[J].
Self-supervised Learning for Multi-modal Medical Image Segmentation
[J].
基于自监督学习的医学影像异常检测
[J].
UniMiSS: universal medical self-supervised learning via breaking dimensionality barrier
[C]//
CMKD: CNN/Transformerbased cross-model knowledge distillation for audio classification
[J].
CASS: Cross architectural self-supervision for medical image analysis
[J].
Deep residual learning for image recognition
[C]//
An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale
[C]//
Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners
[C]//