引言
宫颈癌是女性常见的生殖系统恶性肿瘤之一,早期无典型症状,随着病情发展,患者可能出现阴道出血、阴道分泌物增多、尿频、便秘、疼痛等临床表现,多数患者确诊时病情已发展或达到中晚期阶段[1-2]. 有研究统计,宫颈癌的发病率逐年上升,且有低龄化趋势,死亡率位居妇科肿瘤之首,严重威胁女性的生活质量和生命健康[3]. 目前对宫颈癌的诊断方法主要包括宫颈活检及HPV病毒学等传统检查,由于宫颈癌发病的多灶性,以上检查方式仍有漏诊的可能性,故加强宫颈癌的早期诊治十分必要,有助于后期治疗方案的确定. 雌激素主要由卵巢分泌,具有维持女性特有的性功能、生殖功能及机体钙、磷和脂肪的正常代谢等功能,相关研究表明,雌二醇(estradiol,E2)能促进子宫内膜癌细胞的增殖,而促卵泡生成素(follicle stimulating hormone,FSH)、促黄体生成素(luteinizing hormone,LH)能够促进卵巢癌细胞迁移及侵袭,进一步加速肿瘤发展[4-5]. 血清肿瘤标志物相较于传统检查方式具有成本低廉、便捷、安全及定量、定性测定等优势,一项临床研究证实,血清肿瘤标志物的辅助检测可有效提高宫颈癌诊断的特异性与敏感度,临床已开始将其应用于宫颈癌诊断中[6]. 磁共振多期动态增强成像(dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging,DCE-MRI)是建立在快速扫描基础上的动态MRI技术,能够在早于形态学发生改变之前为肿瘤代谢物水平与微血管生成情况提供依据,在肿瘤早期诊断、早期放化疗疗效评价与监测等方面具有明显优势,其对肿瘤血供特点的评估已经得到公认[7]. 目前临床尚无雌激素相关标志物、肿瘤标志物联合磁共振多期动态增强成像诊断宫颈癌的定向研究,本文以此为创新点分析联合诊断对宫颈癌诊断的应用价值,为相关研究提供依据.
1 实验部分
1.1 实验数据
选取2020年1月~2023年12月在我院妇科经宫颈活检病理确诊的宫颈癌患者87例作为研究组,其中IV期19例,III期19例,II期24例,I期25例;鳞癌49例,腺癌31例,腺鳞癌7例. 纳入标准是年龄>18岁,均为女性;研究组符合宫颈癌的诊断标准[8];根据我国《宫颈癌防治指南》关于宫颈癌病变程度的判断标准进行分级,分为I~IV期[9];初次诊治,无既往手术史;无再生育要求;患者认知功能正常;配合依从性良好. 排除标准:妊娠或哺乳期妇女;有严重的药物滥用史、酒精依赖史;患有心、肝、肾等严重脏器病变;伴有其他恶性肿瘤者;存在呼吸、心血管等系统严重疾病;近期曾服用激素或避孕药;存在免疫系统及凝血功能障碍;患有甲状腺功能亢进;中途退出实验者. 另选取同期在我院经妇科常规及细胞学检查排除宫颈病变,MRI常规及DCE-MRI扫描宫颈大小、形态未见异常的女性63例作为对照组. 如表1所示两组患者一般资料具有可比性(P > 0.05). 所有患者已自愿签署知情同意书,且本研究已通过唐山市妇幼保健院伦理委员会审核(伦理批准号:2023-018-06).
表1 两组患者一般资料对比
Table 1
| 组别 | 样本数(n) | 年龄/岁 | BMI/(kg/m2) | 文化水平/例,括号内为百分占比 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 初中及以下 | 初中’高中 | 大学及以上 | ||||
| 对照组 | 63 | 47.95±3.26 | 25.61±0.88 | 12(19.05%) | 28(44.44%) | 23(36.51%) |
| 研究组 | 87 | 48.04±2.11 | 25.82±1.01 | 18(20.69%) | 37(42.53%) | 32(36.78%) |
| P | 0.838 | 0.187 | 0.804 | 0.815 | 0.973 | |
注:P<0.05表明差异有统计学意义.
1.2 实验方法
(1)E2、FSH、LH、糖链抗原125(carbohydrate antigen 125,CA125)、CA19-9检测方法:采集两组晨间空腹静脉血5 mL,室温下采用贝克曼AllograX-12台式离心机离心并分离血清,5 min后采用UniCel DxI 800全自动化学发光仪分别检测两组血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9水平,雌激素阳性标准[10]为 E2>200 pmol/L、FSH>40.13 mIU/mL、LH>24.9 mIU/mL,血清肿瘤标志物阳性标准为CA125>35 U/mL、CA19-9>35 U/mL.
(2)DCE-MRI诊断方法:检测前两组8 h禁食,适量饮水至膀光充盈后引导患者仰卧位于检测床上,采用飞利浦Ingenia 3.0 T超导型磁共振带有脂肪抑制技术的宫颈动态增强序列—T1高分辨扫描各向同性容积激发序列,向患者肘前静脉高压注射3 mL/s速率的钆特酸葡胺注射液(江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司,批准文号:国药准字H20153167,规格:15 mL : 5.654 g以钆特酸葡胺计)作为动态增强扫描对比剂,静止1 min后患者头先进,平稳呼吸,连续无间隔重复扫描4个时相(扫描时间均为65.4 s),重复4 mm,回波2 ms,参数设置为FOV 300 mm×300 mm~400 mm×400 mm,翻转角为12˚,扫描层数150,层厚3 mm,矩阵对应576×567,扫描完成后及时将数据上传,工作站接收数据并进行图像处理,在病灶实性部分早期强化最明显处勾画感兴趣区,观察定量参数Ktrans(容量转移常数)、Kep(速率常数)、Ve(血管外细胞外间隙容积分数)变化,所有定量参数测量3次并取其平均值. 宫颈体积明显增大,黏膜增厚,肿瘤病灶突向浆膜外,并侵犯阴道,宫颈间质消失,子宫旁出现病灶或坏死病灶,有淋巴结肿大或膀胱、直肠等邻近器官受浸润的现象即判断为阳性[11].
(3)联合诊断方法:分别采集两组血清性激素(E2、FSH、LH)和肿瘤标志物(CA125、CA19-9),再行DCE-MRI诊断,其中任一项检查结果呈阳性即提示为宫颈癌.
1.3 指标评价
检测两组患者血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9水平,并分析研究组不同临床分期患者血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9水平变化,采用受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC)分析血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9水平、DCE-MRI诊断及联合诊断方法对宫颈癌诊断的灵敏度和特异度.
1.4 实验设置
本文研究以SPSS26.0统计学软件分析数据,数据符合正态分布,以GraphPad Prism 8.0(美国GraphPad Software,Inc)软件制图,以均数±标准差(
2 实验结果
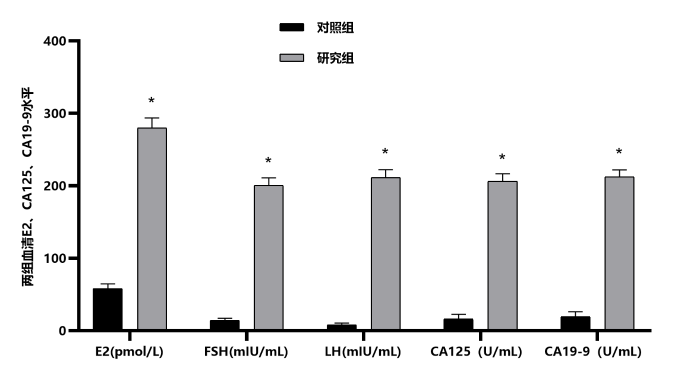
2.1 两组患者血清雌激素及肿瘤标志物水平比较
表2 两组患者血清雌激素及肿瘤标志物水平比较
Table 2
| 分组 | 样本数(n) | E2/(pmol/L) | FSH/(mIU/mL) | LH/(mIU/mL) | CA125/(U/mL) | CA19-9/(U/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 63 | 58.15±6.46 | 14.26±2.89 | 8.08±2.41 | 16.15±6.46 | 19.58±6.72 |
| 研究组 | 87 | 280.09±13.55 | 200.48±10.63 | 211.52±10.75 | 206.28±10.47 | 212.47±9.63 |
| t | 120.400 | 135.400 | 147.400 | 127.600 | 136.700 | |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
注:t值越大表明组间差异越大,P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义.
图1
图1
两组患者血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9水平. *表示与对照组比较,P<0.05
Figure 1
Serum levels of E2, FSH, LH, CA125 and CA19-9 in two groups of patients.* indicates that compared with the control group, P<0.05
2.2 研究组不同临床分期宫颈癌患者血清雌激素及肿瘤标志物水平比较
与I期宫颈癌患者比较,II期宫颈癌患者血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9水平升高,与II期宫颈癌患者比较,III期宫颈癌患者血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9水平升高,组间比较具有统计学意义(P<0.05),III期与IV期宫颈癌患者比较,组间无统计学意义(P>0.05),结果见表3.
表3 研究组不同临床分期宫颈癌患者血清雌激素及肿瘤标志物水平比较
Table 3
| 分组 | 样本数(n) | E2/(pmol/L) | FSH/(mIU/mL) | LH/(mIU/mL) | CA125/(U/mL) | CA19-9/(U/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I期宫颈癌 | 25 | 268.88±2.15 | 191.72±1.87 | 201.09±0.25 | 195.92±0.08 | 205.02±2.18 |
| Ⅱ期宫颈癌 | 24 | 278.39±2.83* | 197.44±2.65* | 209.99±2.32* | 205.98±2.69* | 211.28±2.47* |
| Ⅲ期宫颈癌 | 19 | 289.87±3.35*# | 207.49±3.61*# | 219.08±3.21*# | 212.99±3.34*# | 218.34±3.62*# |
| Ⅳ期宫颈癌 | 19 | 287.16±5.94*# | 208.82±2.19*# | 219.56±0.16*# | 213.52±3.23*# | 217.91±4.19*# |
| F | 143.800 | 214.700 | 467.900 | 507.200 | 90.540 | |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
注:与I期宫颈癌比较,*P<0.05;与II期宫颈癌比较,#P<0.05;F和P表示组间差异性比较,F越大表示组间差异越大,P<0.05表示差异具有统计学意义.
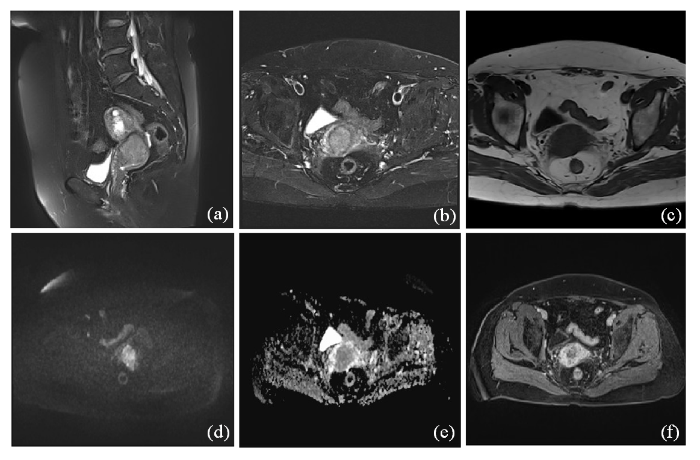
2.3 宫颈癌的DCE-MRI影像学表现
宫腔内类圆形肿块影,范围约2.0 cm×2.6 cm×1.2 cm,呈T1为等信号、T2为略高信号,扩散加权成像呈高信号,ADC图值约0.73×10-3 mm2/s,与宫体后壁分界不清. 经静脉注射对比剂后宫腔内肿块呈不均匀明显强化,延迟期呈相对肌层低信号,结果见图2.
图2
图2
宫颈癌的DCE-MRI影像学表现. (a)矢状位T2WI抑脂序列示宫颈区肿块;(b) T2WI示肿块呈高信号,低信号基质环局部中断;(c) T1WI示肿块呈等信号;(d) DWI示肿块弥散受限呈高信号;(e) ADC呈低信号,值约0.73×10-3 mm2/s;(f)横断位T1WI脂肪抑制增强示肿块明显不均匀强化,静脉期及延迟期呈持续性强化,延迟期强化程度低于子宫肌层
Figure 2
DCE-MRI imaging findings of cervical cancer. (a) Sagittal T2WI lipid suppression sequence showed cervical mass; (b) The mass on T2WI showed high signal and local interruption of stromal ring with low signal; (c) T1WI showed equal-signal mass; (d) DWI showed limited mass diffusion with high signal; (e) The ADC is a low signal with a value of about 0.73×10-3 mm2/s; (f) Enhanced fat inhibition at transversal T1WI showed significant uneven enhancement of the mass, sustained enhancement in the venous phase and the delayed phase, and the degree of enhancement in the delayed phase was lower than that in the myometrium
2.4 研究组不同临床分期宫颈癌患者DCE-MRI定量参数比较
与I期宫颈癌患者比较,II期宫颈癌患者参数Ktrans、Kep水平升高,与II期宫颈癌患者比较,III期宫颈癌患者参数Ktrans、Kep水平升高,与III期宫颈癌患者比较,IV期宫颈癌患者参数Ktrans、Kep水平升高,不同临床分期宫颈癌患者参数Ve水平比较,组间无统计学意义(P > 0.05),结果见表4.
表4 研究组不同临床分期宫颈癌患者DCE-MRI定量参数比较
Table 4
| 分组 | 样本(n) | Ktrans/(min-1) | Kep/(min-1) | Ve |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I期宫颈癌 | 25 | 0.13±0.04 | 0.35±0.13 | 0.23±0.05 |
| Ⅱ期宫颈癌 | 24 | 0.19±0.08* | 0.46±0.26* | 0.25±0.04 |
| Ⅲ期宫颈癌 | 19 | 0.25±0.11*# | 0.59±0.17*# | 0.24±0.06 |
| Ⅳ期宫颈癌 | 19 | 0.31±0.15*#▲ | 0.87±0.21*#▲ | 0.26±0.07 |
| F | 13.330 | 26.780 | 1.210 | |
| P | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.311 |
注:与I期宫颈癌比较,*P<0.05;与Ⅱ期宫颈癌比较,#P<0.05;与Ⅲ期宫颈癌比较,▲P<0.05;F和P表示组间差异性比较,F越大表示组间差异越大,P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义.
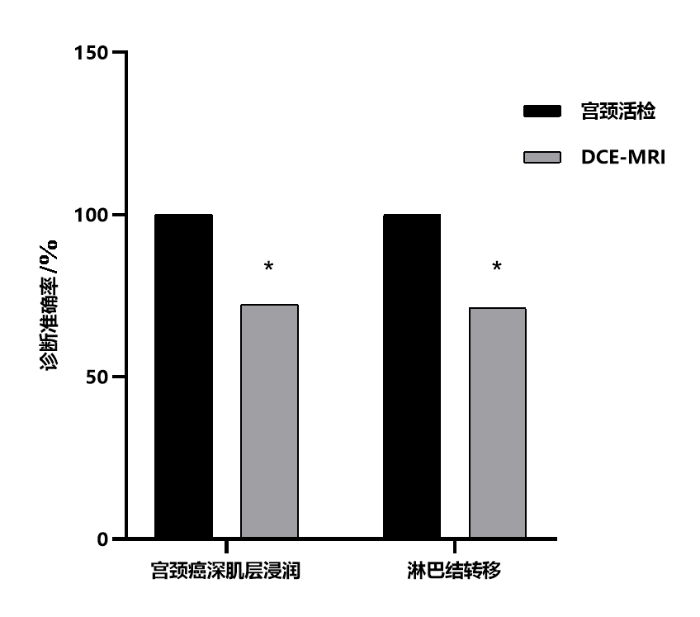
2.5 DCE-MRI对宫颈癌深肌层浸润、淋巴结转移的诊断准确率
表5 DCE-MRI对宫颈癌深肌层浸润、淋巴结转移的诊断情况
Table 5
| 宫颈活检 | 深肌层浸润 | 总计 | 淋巴结转移 | 总计 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性 | 阴性 | 阳性 | 阴性 | |||
| 阳性 | 72(82.76%) | 10(11.49%) | 82(94.25%) | 73(83.91%) | 10(11.49%) | 83(95.40%) |
| 阴性 | 4(4.60%) | 1(1.15%) | 5(5.75%) | 3(3.45%) | 1(1.15%) | 4(4.60%) |
| 总计 | 76(87.36%) | 11(12.64%) | 87(100.00%) | 76(87.36%) | 11(12.64%) | 87(100.00%) |
图3
图3
DCE-MRI对宫颈癌深肌层浸润、淋巴结转移的诊断准确率. *表示与宫颈活检结果比较,P<0.05
Figure 3
Diagnostic accuracy of DCE-MRI for deep muscle invasion and lymph node metastasis of cervical cancer. * indicates comparison with cervical biopsy results, P<0.05
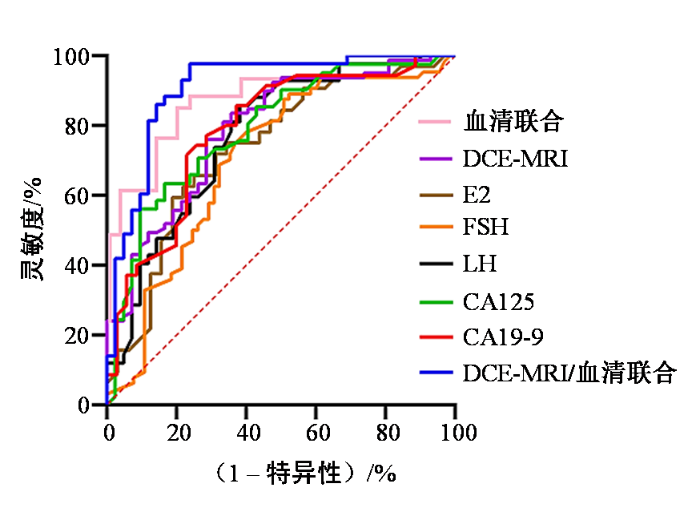
2.6 DCE-MRI联合血清雌激素及肿瘤标志物对宫颈癌的诊断价值
表6 ROC曲线分析诊断价值
Table 6
| 检查方式 | AUC | 灵敏度/(%) | 特异性/(%) | 约登指数 | 标准误 | P值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCE-MRI | 0.658 | 65.46 | 69.12 | 0.346 | 0.08 | <0.001 | 0.606~0.715 |
| E2 | 0.604 | 62.61 | 63.53 | 0.261 | 0.11 | <0.001 | 0.591~0.681 |
| FSH | 0.612 | 61.68 | 61.96 | 0.236 | 0.09 | <0.001 | 0.583~0.695 |
| LH | 0.599 | 62.08 | 64.97 | 0.271 | 0.13 | <0.001 | 0.552~0.637 |
| CA125 | 0.595 | 63.23 | 61.45 | 0.247 | 0.10 | <0.001 | 0.538~0.683 |
| CA19-9 | 0.586 | 63.26 | 62.85 | 0.251 | 0.08 | <0.001 | 0.574~0.652 |
| 血清指标 联合诊断 | 0.823 | 88.30 | 80.12 | 0.568 | 0.11 | <0.001 | 0.720~0.803 |
| DCE-MRI/ 血清指标 联合诊断 | 0.908 | 91.17 | 89.64 | 0.808 | 0.12 | <0.001 | 0.842~0.974 |
注:P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义,95%CI表示ROC曲线置信区间.
图4
图4
ROC曲线分析观察指标的诊断价值
Figure 4
Diagnostic value of observation indexes in ROC curve
3 讨论
宫颈癌作为妇科常见的生殖系统恶性肿瘤,早期临床症状不明显,患者一旦确诊,常已发展至中晚期,预后较差[12]. 因此,强调提高宫颈癌早期诊断对延长患者生命十分必要. 雌激素由女性卵巢分泌,影响女性的生长及发育,有临床观察显示,降低雌激素水平有利于降低卵巢癌的发生风险,提示内分泌因素对于肿瘤的发生具有一定的作用[13]. 血清肿瘤标志物是早期预测癌症发生、治疗效果及预后的有效手段,然而评估其宫旁浸润、淋巴结转移等病变特征敏感性较低,仍有待通过影像学检查直观呈现[14]. 为进一步提升宫颈癌诊断正确率,本文又联用了DCE-MRI影像检查,DCE-MRI具有无辐射、成像软组织分辨率高、多方位及多参数成像等优势,在检查时会向体内注射对比剂,然后快速连续扫描感兴趣区域,得到一系列随时间变化的图像,这些图像能够反映组织的血流灌注情况和血管通透性等生理特性,因为不同组织对对比剂的吸收、分布和清除的过程存在差异,可对病变部位的形态、大小、周围浸润情况等准确诊断[15]. 本研究通过收集不同实验分组发现,采用血清雌激素、肿瘤标志物、DCE-MRI联合诊断的方法对提高诊断宫颈癌准确性具有较高的应用价值.
本文研究结果显示,与对照组比较,研究组患者血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9水平均显著升高,且不同临床分期的宫颈癌患者进行组间比较发现,血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9水平随病程迁延不断升高,提示血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9的检测可能对诊断宫颈癌具有一定临床价值. 宫颈癌患病年龄跨度较大,近年来≤ 35岁青年妇女的发病率有明显上升趋势,有研究认为机体内的激素水平影响着宫颈癌的发生和发展[16]. E2在人类内源性雌激素中活性最强,能够促进女性生殖器官发育,加速生殖器官的细胞增殖与分化,出现并维持女性的第二性征,并对蛋白质、脂肪、骨骼和水盐代谢产生广泛影响. 有研究发现,雌激素可能会导致机体对高危型人乳头瘤病毒(human papillomavirus,HPV)易感,协同刺激宫颈基底细胞异常增生发生病变,即E2进入细胞与雌激素受体结合后,可特异性结合HPV上相关应答元件,促进致癌基因E6、E7的表达,进而增加宫颈癌的风险[17]. 相关文献报道,FSH、LH与前列腺癌具有一定的相关性,前列腺癌组织中FSH受体的表达量明显高于良性前列腺增生组织[18]. CA125、CA19-9是主要分布于宫颈上皮、子宫内膜及输卵管等的高分子糖蛋白,是鉴别宫颈癌、胃癌、胰腺癌以及结肠癌等重要标志物. Chen等[19]研究表明,宫颈癌组织中重组人半乳糖凝集素3、CA19-9的表达明显高于宫颈健康女性,与宫颈间质浸润深度、淋巴结转移、病理分化程度呈正相关性. 该研究与本文研究结果相似,宫颈癌患者血清CA125、CA19-9水平明显高于健康对照组,宫颈癌分期程度越高,血清CA125、CA19-9水平越高. 研究认为宫颈癌患者血清肿瘤标志物CA125、癌胚抗原(CEA)明显高于健康女性,将血清肿瘤标志物应用于宫颈癌诊断中的临床价值理想,具有较高阳性检测率[20].
本文以宫颈活检结果为金标准,DCE-MRI对宫颈癌深肌层浸润、淋巴结转移的诊断准确率分别为83.91%、85.06%,提示DCE-MRI诊断价值明显,为验证该结果,本文通过ROC曲线分析不同诊断方法的预测价值,研究结果显示联合诊断ROC曲线中AUC面积为0.908(95%CI:0.842~0.974),ROC曲线分析血清E2、FSH、LH、CA125、CA19-9、DCE-MRI对宫颈癌的诊断价值发现灵敏度、特异性及AUC相差不大,联合诊断价值最高,进一步说明联合诊断具有较高应用价值. DCE-MRI可通过定量参数分析肿瘤组织中的血流信息来辅助判断肿瘤的浸润程度,对宫颈等软组织的分辨能力强,可以清楚地显示宫颈的各层结构,更容易发现病变的确切位置和范围,除了反映形态学特征外,还能通过对比剂的动态变化获得如血流速度、血管通透性等多种功能参数,从多个角度评估肿瘤的特性. 再联合患者血清肿瘤标志物的变化,增强对宫颈癌的诊断准确性,利于开展更具针对性的治疗策略,促进患者生存质量的提高[21-22]. 本研究还发现,与I期、II期、III期、IV期宫颈癌患者DCE-MRI定量参数Ktrans、Kep水平逐渐升高,进一步提示DCE-MRI对宫颈癌分期的评估价值. Ktrans、Kep分别表示对比剂从血管内进入血管外细胞外间隙的速度和从血管外细胞外间隙反流至血管内的速度,宫颈癌的新生血管多,血流速度快,肿瘤新生血管基底膜不完整,导致内皮细胞间隙增宽,血管通透性增加,进而发生对比剂进出血管的速度加快,Ktrans、Kep水平升高. 有文献报道,MRI联合血清鳞状细胞癌抗原(SCCA)、CA125诊断宫颈癌宫旁浸润与盆腔淋巴结转移具有一定诊断价值,可通过MRI明确观察到癌灶导致的宫颈结构破坏与盆腔淋巴结形态变异,进而为肿瘤标志物提供解剖结构方面的诊断信息补充[23]. ROC曲线中AUC面积可作为疾病诊断的相关指标,当AUC面积为0.5~0.7之间表明诊断价值较低,0.7~0.9为中等价值,而>0.9表示价值较好[24]. Li[25]认为乳腺癌患者血清E2水平高于良性乳腺肿瘤患者,III~IV期乳腺癌患者入院次日血清E2水平高于I~II期患者,经ROC曲线分析AUC为0.736,血清E2水平检测在乳腺癌诊断中具有一定的价值. Jiang[26]发现MRI与肿瘤标志物联合诊断卵巢癌的AUC为0.914,敏感度为93.33%,认为MRI联合肿瘤标志物对卵巢癌的诊断价值显著.
本研究采用雌激素多指标综合评估提高了宫颈癌诊断的准确性,而血清肿瘤标志物在不同临床分期中的水平有变化规律,能辅助判断病程,联合DCE-MRI具有无辐射、成像软组织分辨率高、多方位及多参数成像等优势,可直观呈现病变部位形态、大小、周围浸润情况等,还能通过定量参数分析肿瘤组织血流信息辅助判断浸润程度,对宫颈各层结构分辨清晰,联合诊断能从多维度评估肿瘤特性,利于制定针对性治疗策略. 然而,本研究也存在局限性:首先,研究样本可能存在局限性,样本来源范围及数量可能影响结果的普遍性与代表性,可能对结果产生一定影响,未来将扩大样本来源地区范围、增加样本量,结果将更具说服力,此外,联合诊断的长期随访及预后评估方面研究不足,后续研究将进一步探讨该联合诊断方法对宫颈癌患者长期生存质量、复发率等方面的影响,以便更全面地评估其临床价值. 综上所述,雌激素、肿瘤标志物联合DCE-MRI检测对于宫颈癌病灶的诊断价值显著,可有效查漏补缺,确保诊断准确性,值得临床推广应用.
利益冲突
无
参考文献
Cervical cancer screening and predictors of screening by diabetes status
[J].
Potential role of microRNAs in the treatment and diagnosis of cervical cancer
[J].
Worldwide trends in cervical cancer incidence and mortality, with predictions for the next 15 years
[J].
DOI:10.1002/cncr.33795
PMID:34368955
[本文引用: 1]

Cervical cancer is 1 of the most common cancers in females worldwide. Understanding the most recent global patterns and temporal trends of cervical cancer burden might be helpful for its prevention and control.Data on cervical cancer (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, code C53) incidence and mortality in 2018 were extracted from the GLOBOCAN 2018 database and further analyzed for their correlations with the Human Development Index. Temporal trends were analyzed using the annual percent change with joinpoint analysis among 31 countries with highly qualified data from the Cancer Incidence in Five Continents Plus and World Health Organization mortality databases. Future trends for the next 15 years were predicted using an open-source age-period-cohort model.Cervical cancer incidence and mortality rates were both negatively correlated with the Human Development Index (r = -0.56 for incidence, r = -0.69 for mortality; P <.001) in cross-sectional analysis, and both remained stable in 12 countries or even decreased in 14 and 18 countries for incidence and mortality, respectively, during the most recent 10 data years. Similar findings were observed for the next 15 years.Cervical cancer burden was correlated with socioeconomic development. An overwhelming majority of countries had stable or decreasing trends in incidence and mortality rates, especially in those with effective cervical cancer screening programs and human papillomavirus vaccination.The authors investigated the most up-to-date data from official databases released by the International Agency for Research on Cancer and found that cervical cancer incidence and mortality were negatively correlated with socioeconomic development. Among the 31 countries analyzed, most (26 countries were analyzed for incidence, and 30 were analyzed for mortality) had stable or even decreasing temporal trends over the most recent 10 years, especially in those with effective cervical cancer screening programs. In addition, the predicted trends for the next 15 years were basically consistent with the observed trends among most of the analyzed countries (19 countries for incidence and 26 countries for mortality).© 2021 American Cancer Society.
Desmocollin 3 mediates follicle stimulating hormone-induced ovarian epithelial cancer cell proliferation by activating the EGFR/Akt signaling pathway
[J].
Study on the relationship between serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D and estradiol levels and the occurrence of cervical cancer
[J].
血清25-羟-维生素D及雌二醇水平与宫颈癌发生的关系研究
[J].
Expression of immune cell markers and tumor markers in patients with cervical cancer
[J].
DOI:10.1136/ijgc-2020-001254
PMID:32518078
[本文引用: 1]

Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide, and immune function may impact disease progression. Serum markers may also be associated with diagnosis and progression. The aim of this study was to explore the clinical usefulness of determining the levels of peripheral blood immune cells and serum tumor markers in predicting diagnosis and prognosis of patients with cervical cancer.82 patients with cervical cancer (early stage group: IA-IB1 and IIA1; locally advanced group: IB2 and IIA2), 54 patients with cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia (CIN), and 54 healthy women (control group) were recruited. Inclusion criteria were: (1) patients whose cervical lesions were determined based on biopsy; and (2) patients who had not undergone immunotherapy, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients with a history of other malignant tumors; (2) patients with heart, kidney, and other organ failure; (3) patients with immune diseases; and (4) pregnant or lactating women. The levels of immunocytes and tumor markers were assayed. The relationships among histopathologic factors were analyzed. The correlation between the levels of immunocytes and tumor markers in patients with different degrees of cervical lesions (pre-invasive or cancer) and healthy women was evaluated.The squamous cell carcinoma antigen and carcinoembryonic antigen levels in the control group and the CIN group were significantly lower than those in the cervical cancer groups (p<0.01). The incidence of lymph node metastasis in the early stage and locally advanced groups were 22.9% (11/48) and 46.2% (12/26), respectively, and 58.8% (20/34) and 7.5% (3/37) in the positive and negative lymphovascular invasion groups, respectively (p<0.05). The levels of CD8 and CD8 CD28 T cells in the early stage group were markedly lower than those in the CIN group and the control group (p=0.014, p=0.008, respectively). The ratio of CD4CD25/CD4 in the cervical cancer groups was significantly higher than in the control group (p<0.01). The increased serum squamous cell carcinoma and carcinoembryonic antigen levels and CD4CD25/CD4 ratio were risk factors for cervical cancer by logistic regression analysis (p<0.05).In patients with cervical cancer, immune function was impaired compared with that in healthy women and patients with CIN, while squamous cell carcinoma and carcinoembryonic antigen levels were increased. Combined detection of the levels of peripheral blood immune cells and serum tumor markers may be helpful for early detection, diagnosis, and prognosis evaluation of patients with cervical cancer.© IGCS and ESGO 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Segmentation of breast tumors based on fully convolutional network and dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance image
[J].
基于全卷积网络的乳腺肿瘤动态增强磁共振图像分割
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20212921
[本文引用: 1]

准确可靠的乳腺肿瘤分割是乳腺癌诊断、治疗、预后评估的关键.针对现有的基于动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)的乳腺肿瘤分割方法易遗漏小目标肿瘤等不足,本文提出了一种基于全卷积网络的可靠高效的乳腺肿瘤DCE-MRI图像分割方法.首先,对乳腺DCE-MRI数据进行预处理后,截取128*128大小的图像块,并以肿瘤区域像素数为依据将数据分为两个子数据集;其次,利用数据集训练CBP5-Net得到分类模型;然后,利用两个子数据集分别训练RAU-Net得到两个分割模型;最后,将测试集数据送到网络输入端,并对网络输出结果进行后处理,得到最终的乳腺肿瘤分割结果.利用本文提出的方法得到的Dice系数、敏感性、特异性和交并比(IoU)分别达到了0.938 8、0.952 3、0.998 5和0.876 8,说明利用本文方法能够有效、精确地分割乳腺肿瘤DCE-MRI图像.
Diagnosis of cervical squamous cell carcinoma and cervical adenocarcinoma based on Raman spectroscopy and support vector machine
[J].
DOI:S1572-1000(19)30062-6
PMID:31136828
[本文引用: 1]

In this report, we collected the Raman spectrum of cervical adenocarcinoma and cervical squamous cell carcinoma tissues by a micro-Raman spectroscopy system. We analysed, compared and summarized the characteristics and differences of the normalized mean Raman spectra of the two tissues and pointed out the major differences in the biochemical composition between the two tissues. The PCA-SVM model that was used to distinguish the two types of cervical cancer tissues was established. The accuracy of the model in differentiating cervical adenocarcinoma from cervical squamous cell carcinoma was 93.125%. The results of this study indicate that Raman spectroscopy of cervical adenocarcinoma and cervical squamous cell carcinoma tissue in combination with SVM (support vector analysis) and PCA (principal component analysis) can be useful for the classification of cervical adenocarcinoma and cervical squamous cell carcinoma tissues and for the exploration of the differences in biochemical compositions between the two types of cervical tissue. This study lays a foundation to further study Raman spectroscopy as a clinical diagnostic method for cervical cancer.Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Relationship between serum SCC-Ag and tissue ATF3 and clinical stage and tumor diameter in patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma
[J].
子宫颈鳞癌患者血清SCC-Ag及组织ATF3与临床分期及肿瘤直径的关系
[J].
Application value of dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance imaging combined with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
[J].
动态增强磁共振成像联合磁共振弥散加权成像在宫颈癌患者分期诊断中的应用价值
[J].
Detection rates and factors affecting thereof in endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial carcinoma, and cervical glandular lesions on cervical smear
[J].
Evaluating the ovarian cancer gonadotropin hypothesis: a candidate gene study
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.12.017
PMID:25528498
[本文引用: 1]

Ovarian cancer is a hormone-related disease with a strong genetic basis. However, none of its high-penetrance susceptibility genes and GWAS-identified variants to date are known to be involved in hormonal pathways. Given the hypothesized etiologic role of gonadotropins, an assessment of how variability in genes involved in the gonadotropin signaling pathway impacts disease risk is warranted.Genetic data from 41 ovarian cancer study sites were pooled and unconditional logistic regression was used to evaluate whether any of the 2185 SNPs from 11 gonadotropin signaling pathway genes was associated with ovarian cancer risk. A burden test using the admixture likelihood (AML) method was also used to evaluate gene-level associations.We did not find any genome-wide significant associations between individual SNPs and ovarian cancer risk. However, there was some suggestion of gene-level associations for four gonadotropin signaling pathway genes: INHBB (p=0.045, mucinous), LHCGR (p=0.046, high-grade serous), GNRH (p=0.041, high-grade serous), and FSHB (p=0.036, overall invasive). There was also suggestive evidence for INHA (p=0.060, overall invasive).Ovarian cancer studies have limited sample numbers, thus fewer genome-wide susceptibility alleles, with only modest associations, have been identified relative to breast and prostate cancers. We have evaluated the majority of ovarian cancer studies with biological samples, to our knowledge, leaving no opportunity for replication. Using both our understanding of biology and powerful gene-level tests, we have identified four putative ovarian cancer loci near INHBB, LHCGR, GNRH, and FSHB that warrant a second look if larger sample sizes and denser genotype chips become available.Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Analysis of diagnostic accuracy of pancreatic cancer by enhanced magnetic resonance imaging combined with serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9, carbohydrate antigen 125 and carcinoembryonic antigen detection
[J].
增强磁共振成像联合血清糖类抗原19-9、糖类抗原125、癌胚抗原检测对胰腺癌诊断准确性的分析
[J].
Identification of benign and malignant breast lesions based on multimodal MRI and deep learning
[J].
基于多模态MRI与深度学习的乳腺病变良恶性鉴别
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20222969
[本文引用: 1]

为提高基于动态增强磁共振成像(DCE-MRI)的计算机辅助(CAD)方法对乳腺病变良恶性鉴别的精度,本文基于多模态特征融合,提出一种联合非对称卷积和超轻子空间注意模块的卷积神经网络AC_Ulsam_CNN.首先,采用迁移学习方法预训练模型,筛选出对乳腺病变良恶性鉴别最为有效的DCE-MRI扫描时序.而后,基于最优扫描时序图像,搭建基于AC_Ulsam_CNN网络的模型,以增强分类模型的特征表达能力和鲁棒性.最后,将影像特征与乳腺影像数据报告和数据系统(BI-RADS)分级、表观扩散系数(ADC)和时间-信号强度曲线(TIC)类型等多模态信息进行特征融合,以进一步提高模型对病灶的预测性能.采用五折交叉验证方法进行模型验证,本文方法获得了0.826的准确率(ACC)和0.877的受试者工作曲线下面积(AUC).这表明该算法在小样本量数据下可较好区分乳腺病变的良恶性,而基于多模态数据的融合模型也进一步丰富了特征信息,从而提高病灶的检出精度,为乳腺病灶良恶性的自动鉴别诊断提供了新方法.
Estrogen receptors promote migration, invasion and colony formation of the androgen-independent prostate cancer cells PC-3 through β-catenin pathway
[J].
Human papillomavirus molecular biology and disease association
[J].
Analysis of relevant test indicators in differential diagnosis of prostate cancer
[J].
前列腺癌鉴别诊断的相关检验指标分析
[J].
Correlation between Galectin-3, CA19-9 levels and clinicopathological characteristics of cervical cancer
[J].
宫颈癌组织中Galectin-3、CA19-9水平与临床病理特征的相关性
[J].
Clinical value of combined detection of serum tumor marker CA125 and CEA in diagnosis of cervical cancer
[J].
血清肿瘤标志物CA125、CEA联合检测在宫颈癌诊断中的临床价值
[J].
Automatic segmentation of breast and gland in breast DCE-MR images based on nnU-Net
[J].
基于nnU-Net的乳腺DCE-MR图像中乳房和腺体自动分割
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20212883
[本文引用: 1]

在乳腺动态增强磁共振(DCE-MR)图像中,乳房分割和腺体分割是进行乳腺癌风险评估的关键步骤.为实现在三维脂肪抑制乳腺DCE-MR图像中乳房和腺体的自动分割,本文提出一种基于nnU-Net的自动分割模型,利用U-Net分层学习图像特征的优势,融合深层特征与浅层特征,得到乳房分割和腺体分割结果.同时,基于nnU-Net策略,所使用的模型能根据图像参数自动进行预处理和数据扩增,并动态调整网络结构和参数配置.实验结果表明,在具有多样化参数的三维脂肪抑制乳腺DCE-MR图像数据集上,该模型能准确、有效地实现乳房和腺体分割,平均Dice相似系数分别达到0.969±0.007和0.893±0.054.
Application of image omics based on novel support vector machine to liver nodule classification
[J].
基于新型支持向量机的影像组学在肝脏结节分类中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20212916
[本文引用: 1]

肝癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,亚洲地区最为常见的肝癌演变过程为肝炎-肝硬化结节-异型增生结节-肝细胞性肝癌.判断肝脏结节在演变过程所处分期,并采取干预措施,对降低肝癌的发生率非常关键.本文针对影像组学提出了更精确的支持向量机(SVM)分类算法——LFOA-F-SVM,用于对120名患者的腹部动态增强磁共振图像的肝脏结节进行四分类.该算法利用了考虑半径与几何间距的F-SVM,并结合莱维飞行策略(LF)的果蝇优化算法(FOA)寻求超参.为了验证方法的有效性,本文另外添加了5个UCI分类数据集(心脏、帕金森疾病、虹膜、葡萄酒和动物园),并与SVM、PSO-SVM、FOA-SVM、F-SVM进行比较.结果表明,在6个分类数据集(包括肝脏结节数据集和5个UCI分类数据集)中,相对于其他分类算法,LFOA-F-SVM的分类准确率最高,在肝脏结节数据集中的四分类精确率和查全率也较高.
Significance of MRI combined with serum SCCA and CA125 in the diagnosis of cervical cancer
[J].
MRI联合血清SCCA、CA125对宫颈癌的诊断意义
[J].
Multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics analysis of cervical cancer for preoperative prediction of lymphovascular space invasion
[J].
The value of detection of FT_4, FT_3, E_2 and progesterone levels in the diagnosis of breast cancer
[J].
FT_4、FT_3、E_2、孕酮水平检测在乳腺癌诊断中的价值
[J].