
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2025, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 378-389.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20253155cstr: 32225.14.cjmr20253155
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Yinghao1,2, WANG Lihui3, WANG Sucheng1, ZHU Zhongqi1, HUANG Changdong1, LI Renfeng3, CAO Kaiming3, HU Haiyang3, JIA Yiming3, LIANG Songtao3, YANG Guang1,2,§( ), LU Qing3,#(
), LU Qing3,#( ), WANG Hongzhi1,2,*(
), WANG Hongzhi1,2,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-27
Published:2025-12-05
Online:2025-04-23
Contact:
§ Tel: 18521510757, E-mail: gyang@phy.ecnu.edu.cn; # Tel: 021-38804518, E-mail: Drluqingsjtu@163.com; * Tel: 13916346546, E-mail: hzwang@phy.ecnu.edu.cn.
CLC Number:
LI Yinghao, WANG Lihui, WANG Sucheng, ZHU Zhongqi, HUANG Changdong, LI Renfeng, CAO Kaiming, HU Haiyang, JIA Yiming, LIANG Songtao, YANG Guang, LU Qing, WANG Hongzhi. Study on Pancreas Automatic Segmentation, Regional Quantification, and Diabetes Assessment[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(4): 378-389.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
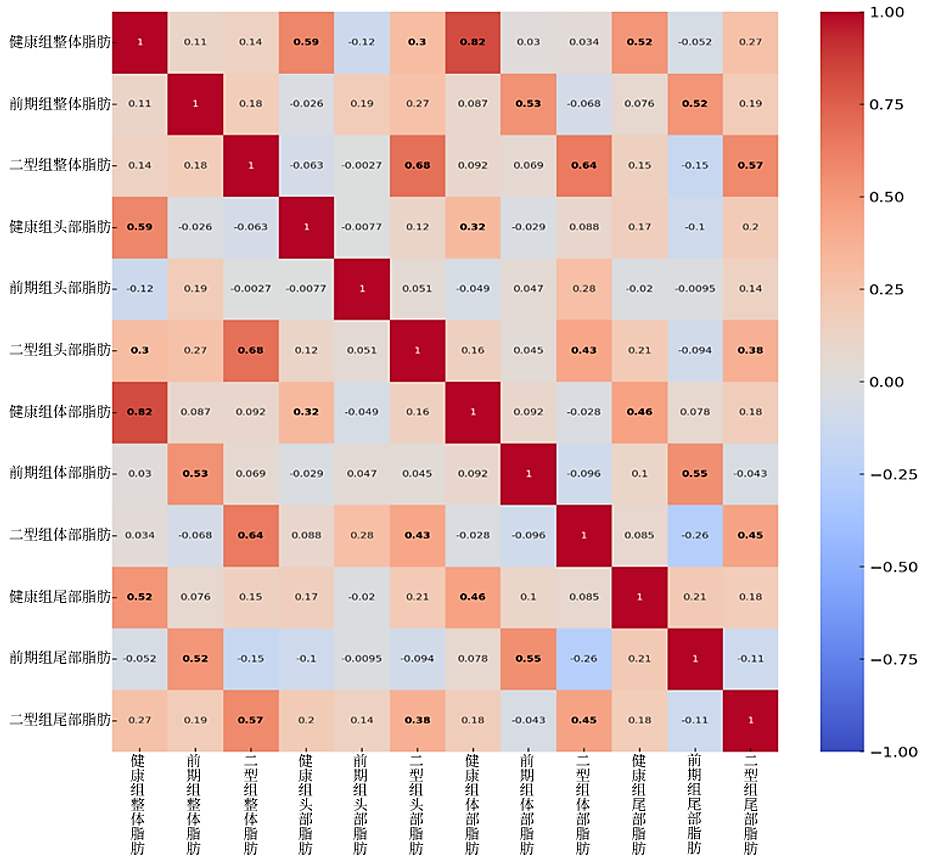
Fig. 7
Correlation analysis map of fat content in different pancreatic regions across the three patient groups, with color ranging from blue to red representing correlation values from 0 to 1. The Healthy, Pre-diabetic, and Type 2 groups represent healthy individuals, pre-diabetic patients, and T2DM patients, respectively
| [1] |
ONG K L, STAFFORD L K, MCLAUGHLIN S A, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet, 2023, 402(10397): 203-234.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6 pmid: 37356446 |
| [2] | TURNER C D, BAGNARA J T. General endocrinology[M]. 6th ed. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company, 1976. |
| [3] |
TAYLOR R. Understanding the cause of type 2 diabetes[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2024, 12(9): 664-673.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(24)00157-8 |
| [4] |
WANG X, MISAWA R, ZIELINSKI M C, et al. Regional differences in islet distribution in the human pancreas-preferential beta-cell loss in the head region in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. PloS one, 2013, 8(6): e67454.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067454 |
| [5] |
SARMA M K, SAUCEDO A, DARWIN C H, et al. Noninvasive assessment of abdominal adipose tissues and quantification of hepatic and pancreatic fat fractions in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2020, 72: 95-102.
doi: S0730-725X(20)30326-X pmid: 32668273 |
| [6] |
NADARAJAH C, FANANAPAZIR G, CUI E, et al. Association of pancreatic fat content with type II diabetes mellitus[J]. Clin Radiol, 2020, 75(1): 51-56.
doi: S0009-9260(19)30269-7 pmid: 31711639 |
| [7] | GO VLW, DIMAGNO E P, GARDNER J D, et al. The Pancreas: An Integrated Textbook of Basic Science, Medicine, and Surgery[M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken: Blackwell Publishing, 2004. |
| [8] |
SHEN J, BAUM T, CORDES C, et al. Automatic segmentation of abdominal organs and adipose tissue compartments in water-fat MRI: application to weight-loss in obesity[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2016, 85(9): 1613-1621.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.06.006 pmid: 27501897 |
| [9] |
WOLZ R, CHU C, MISAWA K, et al. Automated abdominal multi-organ segmentation with subject-specific atlas generation[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2013, 32(9): 1723-1730.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2013.2265805 |
| [10] | CHU C, ODA M, KITASAKAI T, et al. Multi-organ segmentation based on spatially-divided probabilistic atlas from 3D abdominal CT images[C]// Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2013: 16th International Conference, Nagoya, Japan, September 22-26, 2013, Proceedings, Part II 16. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2013: 165-172. |
| [11] |
SAITO A, NAWANO S, SHIMIZU A. Joint optimization of segmentation and shape prior from level-set-based statistical shape model, and its application to the automated segmentation of abdominal organs[J]. Med Image Anal, 2016, 28: 46-65.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.11.003 pmid: 26716720 |
| [12] | 王鑫. 基于统计模型的胰腺分割算法的研究与实现[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2013. |
| [13] | DAI J L, HE C, WU J, et al. Pancreatic cystic neoplasms segmentation network combining dual decoding and global attention upsampling modules[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2024, 41(2): 151-161. |
|
戴俊龙, 何聪, 武杰, 等. 融合双解码和全局注意力上采样模块的胰腺囊性肿瘤分割网络[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2024, 41(2): 151-161.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20233073 |
|
| [14] |
CHEN L, WAN L. CTUNet: automatic pancreas segmentation using a channel-wise transformer and 3D U-Net[J]. Vis Comput, 2023, 39(11): 5229-5243.
doi: 10.1007/s00371-022-02656-2 |
| [15] |
PAITHANE P, KAKARWA S. LMNS-Net: Lightweight multiscale novel semantic-net deep learning approach used for automatic pancreas image segmentation in CT scan images[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2023, 234: 121064.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121064 |
| [16] |
GHORPADE H, JAGTA J, PATIL S, et al. Automatic segmentation of pancreas and pancreatic tumor: a review of a decade of research[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 108727-108745.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3320570 |
| [17] |
ISENSEE F, JAEGER P F, KOHL S A A, et al. nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation[J]. Nat Methods, 2021, 18(2): 203-211.
doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-01008-z pmid: 33288961 |
| [18] |
SULOCHANA S, SIVAKAMI T. A gross morphological study of the pancreas in human cadavers[J]. Natl J Clin Anat, 2012, 1(2): 55-60.
doi: 10.4103/2277-4025.298007 |
| [19] |
KUKU G M, HITTATIYA K, SPRINKART A M, et al. Comparison between modified Dixon MRI techniques, MR spectroscopic relaxometry, and different histologic quantification methods in the assessment of hepatic steatosis[J]. Eur Radiol, 2015, 25: 2869-2879.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3703-6 pmid: 25903702 |
| [20] |
FEDOROV A, BEICHEL R, KALPATHY-CRAMER J, et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2012, 30(9): 1323-1341.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.05.001 pmid: 22770690 |
| [21] | BI X L, LU M, XIAO B, et al. Pancreas segmentation based on dual-decoder U-Net convolutional neural network[J]. J Softw, 2022, 33(5): 1947-1958. |
| 毕秀丽, 陆猛, 肖斌, 等. 基于双解码U型卷积神经网络的胰腺分割[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33(5): 1947-1958. | |
| [22] |
ZHANG Z, KELES E, DURAK G, et al. Large-scale multi-center CT and MRI segmentation of pancreas with deep learning[J]. Med Image Anal, 2025, 99: 103382.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2024.103382 |
| [23] |
QU T, LI X, WANG X, et al. Transformer guided progressive fusion network for 3D pancreas and pancreatic mass segmentation[J]. Med Image Anal, 2023, 86: 102801.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2023.102801 |
| [24] | CHEN J, CHEN W, ZHU Z, et al. MAFE-Net: A multi-level attention feature extraction network for pancreas segmentation[J]. J Mach Learn, 2024,10: 1-19. |
| [25] |
SKUDDE-HILL L, SEQUEIRA I R, CHO J, et al. Fat distribution within the pancreas according to diabetes status and insulin traits[J]. Diabetes, 2022, 71(6): 1182-1192.
doi: 10.2337/db21-0976 |
| [1] | CHEN Xi, LIU Sijie, CAI Yue, CHENG Linlin, WANG Xuxia, KANG Yan, LIN Fuchun, LEI Hao. Effects of Seizure-inducing Doses Nicotine on Hippocampal Structure in Adolescent Female Rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(4): 345-354. |
| [2] | GAO Zhaoyao, ZHANG Zhan, HU Liangliang, XU Guangyu, ZHOU Sheng, HU Yuxin, LIN Zijie, ZHOU Chao. PMRI Image Reconstruction Method Based on Virtual Coils and GRAPPA-enhanced Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(4): 390-401. |
| [3] | ZHANG Mingyu, XIAO Sa, SHI Shengjie, ZHANG Xuecheng, ZHOU Xin. Research on a Multi-modal Enhanced Denoising Diffusion Model for Hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(4): 364-377. |
| [4] | MA Yingxue, ZHAO Yanqiang, YANG Xiaodong, JIANG Bin, TAO Cheng. Opportunities and Challenges of High-field and Ultra-high-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 334-344. |
| [5] | SUI Meiju, ZHANG Lei, WANG Ruifang, LUO Yingying, LI Sha, QIU Maosong, XU Qiuyi, CHEN Daiqin, CHEN Shizhen, ZHOU Xin. MRI-traceable Nanoenzyme for Cascade Catalysis-enhanced Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 231-248. |
| [6] | CAO Fei, XU Qianqian, CHEN Hao, ZU Jie, LI Xiaowen, TIAN Jin, BAO Lei. An Intelligent Diagnosis Method for NIID Based on Cross Self-supervision and DWI [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 154-163. |
| [7] | CHEN Qun, YANG Zijian, CHENG Xinyi, JIA Siyi, DU Xiaoxia, WANG Mengxing. Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technology in Pediatric Exercise Intervention Research [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 195-204. |
| [8] | XUE Peiyang, GENG Chen, LI Yuxin, BAO Yifang, LU Yucheng, DAI Yakang. A Classification Method for Cerebral Aneurysms in TOF-MRA Based on Improved 3D ResNet50 Model [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 56-66. |
| [9] | NING Xinzhou, HUANG Zhen, CHEN Xiqu, LIU Xinjie, CHEN Gang, ZHANG Zhi, BAO Qingjia, LIU Chaoyang. Research on Transformer Super-Resolution Reconstruction Algorithm for Ultrafast Spatiotemporal Encoding Magnetic Resonance Imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 454-468. |
| [10] | PANG Qifan, WANG Zhichao, WU Yupeng, LI Jianqi. The Impact of K-Space Filling Strategy on Fat Artifacts in APT Imaging Based on FLASH Sequence [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 443-453. |
| [11] | YANG Liming, WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress of Denoising Algorithms for Diffusion Tensor Images [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(3): 341-361. |
| [12] | Dai Junlong, He Cong, Wu Jie, Bian Yun. Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms Segmentation Network Combining Dual Decoding and Global Attention Upsampling Modules [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 151-161. |
| [13] | YANG Yu, CHEN Bo, WU Liubin, LIN Enping, HUANG Yuqing, CHEN Zhong. Spectrum Reconstruction for Laplace NMR: From Handcraft Regularization to Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 191-208. |
| [14] | CHANG Bo, SUN Haoyun, GAO Qingyu, WANG Lijia. Research Progress on Cardiac Segmentation in Different Modal Medical Images by Traditional Methods and Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 224-244. |
| [15] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||