引言
据国家癌症中心统计数据显示,2022年我国新发肝癌病率居恶性肿瘤第4位,死亡率居恶性肿瘤第2位[1].在全球范围内,中国肝癌的发病率和死亡率也不容乐观[2,3].硬化结节(Cirrhotic Nodules,CN)-异型增生结节(Dysplastic Nodules,DN)-肝细胞癌(Hepatocellular Carcinoma,HCC)是如今最常见的肝癌演变过程,对肝结节所处时期的判断,不仅能够帮助临床医生给予患者相应的治疗,同时也能降低肝癌患者死亡率[4,5].动态增强磁共振成像(Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging,DCE-MRI)在肝癌诊断中占据重要地位,相比超声、计算机断层扫描(Computerized Tomography,CT),DCE-MRI可进行多参数成像,具有优越的软组织分辨率,能够评估正常组织与病灶的血流动力学,有助于肝细胞癌早期症状的观测[6,7].
近年来,相关学者针对肝癌的早期诊断提出了许多解决方案,大致可分为基于传统机器学习和基于卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)的分类方法.在基于传统机器学习的分类方法中,支持向量机、随机森林、逻辑回归等分类模型得到了广泛应用[8⇓-10].不过,随着人工智能的快速发展,使用深度学习对医学图像进行分类的应用也越来越多[11⇓⇓⇓-15],且表现性能较好.在基于CNN的分类方法中,使用卷积自动提取肝结节特征,代替传统的手工设计特征,并以有监督的学习方式端到端地训练模型,节省人力.根据卷积维度可将CNN分为两类,即基于2D CNN和3D CNN的深度学习算法.目前,基于2D CNN的分类模型使用较多,例如,Saha等[11]设计基于混合2D CNN的深度学习模型,用于将肝脏肿瘤分为三类:HCC、恶性肿瘤(HCC除外)和良性肿瘤或囊肿.Cheng等[12]使用了四个深度神经网络(ResNet50、InceptionV3、Xception和Ensemble)对硬化结节、异性增生结节、肝细胞癌进行组织病理学诊断,实现人工智能技术在肝结节病理诊断中的临床应用.但传统2D CNN只能捕捉二维特征信息,无法有效提取时间序列特征.而3D CNN可以提取3D图像或视频中的空间和时间维度特征,获得相邻平面间的相关性,使得网络的分类性能得到进一步提高.在医学影像领域,如MRI和CT等,图像数据往往是3D的,因此使用3D CNN可以直接将3D图像作为输入,充分学习多维特征.Trivizakis等[13]提出将2D CNN扩展到3D,以推进深度学习癌症分类,并应用于磁共振成像(MRI)肝肿瘤检测中.Zhang等[14]提出了一种多输入密集卷积网络对肝细胞癌和肝内胆管癌进行分类,考虑到医学图像的空间特征,在实验过程中使用3D卷积网络以达到更好的分类效果.此外,Zhou等[15]提出一种多尺度、多模态3D CNN模型,利用其结构对恶性病变(肝细胞癌、肝内胆管癌和肝转移瘤)和良性病变(血管瘤、局灶性结节性增生和囊肿)进行鉴别,分别构建二分类和六分类模型,平均准确率可达82.5%和73.4%,优于3DVGG16、Faster R-CNN和ResNet18.
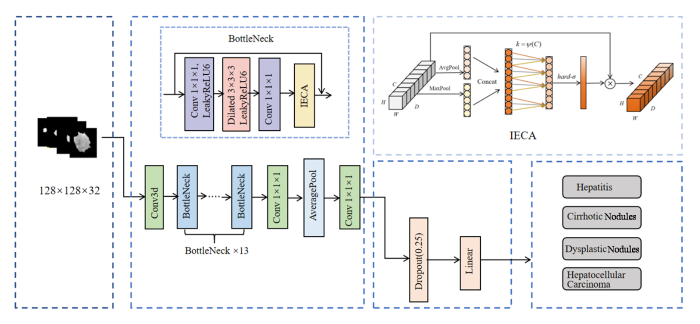
上述研究大多为肝癌的良恶性鉴别或肝细胞癌与肝内胆管癌的鉴别诊断,针对具体的肝硬化肝癌的进展研究还较少且具有挑战.因此,对基于DCE-MRI的肝炎肝实质(Hepatitis)、硬化结节、异型增生结节和肝细胞癌进行分类是本次研究的重点.为了充分利用DCE-MRI的图像信息,提高模型的分类精度,本文构建了基于MobileNetV2改进的分类网络模型(3D ELD_MobileNetV2),该网络包含融合局部特征和全局特征的高效通道注意力模块(Improved Efficient Channel Attention,IECA)、空洞(Dilated)卷积以及新型Leaky ReLU6激活函数以提升网络的特征提取能力,实现肝结节四分类,为后续肝硬化肝癌的鉴别诊断提供研究思路.
1 实验部分
1.1 实验方法
本文提出一种基于深度学习的3D ELD_MobileNetV2肝结节分类方法,该方法的主要实验流程如图1所示.首先对图像进行归一化处理,接着通过寻找由临床专家勾画出的感兴趣区域(Region of Interest,ROI)连通域的中心,对结节图像进行裁剪;然后对处理后的图像按照8:2的比例划分训练集和测试集,并对训练集做数据增强处理,扩大数据量,所有病人的图像均只存在于训练集或测试集其中一类;接着使用3D ELD_MobileNetV2模型对训练集进行训练,在训练过程中采用五折交叉验证,以确保实验的可靠性,并且动态调整学习率,保存最优参数;最后,使用准确率、精确率、召回率、F1_Score等对实验结果进行评估,并与AlexNet[16]、VggNet16[17]、ResNet50[18]、ConvNeXt[19]等模型结果进行对比分析.
图1
1.2 基于MobileNetV2改进的深度学习模型
1.2.1 MobileNetV2
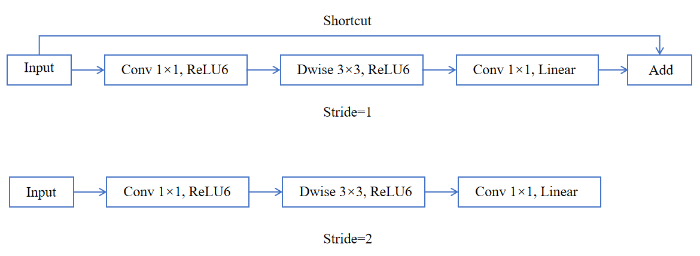
MobileNetV2[20]沿袭了MobileNetV1的优点并在此基础上进行改进,保留深度可分离卷积结构,降低计算成本和模型参数量.MobileNetV2主要特点表现为瓶颈(Bottleneck)中的反向残差结构和线性瓶颈结构.反向残差结构与传统的残差块[21]在维度升降顺序方面完全相反,反向残差结构通过先升维再降维的特征提取方式,来实现轻量化和模型复杂度降低的目的,其结构如图2所示[20].其中,Shortcut表示跨层连接,Dwise为深度卷积层,Stride表示步幅.线性瓶颈结构设计是将瓶颈层中最后一个卷积层中ReLU激活函数替换为线性(Linear)激活函数,以避免ReLU激活函数导致低维特征丢失的问题.
图2
由于MobileNetV2出色的表现及其极高的轻量级和计算效率,目前被广泛应用于医学图像分类任务中.Tripathi等[22]提出一种改进的MobileNetV2L2 模型对肺部疾病进行检测,在两个公开数据集上的分类准确率分别达到95.51%和99.26%.Wang 等[23]提出基于MobileNetV2的轻量级模型用于皮肤病变分类,在HAM10000数据集上达到了87.07%的分类准确率.Xu等[24]将MobileNetV2与元启发式算法结合,用于脑肿瘤诊断,结果表明,所提出的模型分类精度达到97.68%,优于其他网络.以上研究证明MobileNetV2在医学图像分类任务中表现出了良好的性能,拥有较强的特征提取能力.因此,本文选用MobileNetV2作为基础框架进行改进,进一步提高模型在肝结节分类中的表现性能.
1.2.2 3D IECA
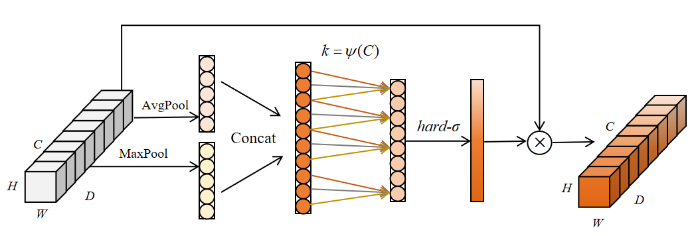
为了提高从MRI图像中提取有效信息的能力,本文在MobileNetV2的瓶颈结构之间引入了融合全局特征和局部特征的高效通道注意力机制(IECA),该机制在ECA[25]的基础上进行改进,由一维卷积层、批归一化(BN)层、最大池化(MaxPool)、平均池化(AvgPool)和Hard-sigmoid(hard-σ)激活函数组成,其模块结构如图3所示.其中,H、W、D和C分别代表特征图的高、宽、深和通道数;Concat表示拼接(Concatenate)操作.IECA通过聚合平均池化和最大池化结果来丰富特征信息的提取,平均池化能够反映特征图的全局信息,最大池化反映了最突出特征的信息,通过结合两种池化,可以更好地捕获重要特征通道.通过动态地学习通道特征之间的相关性,可以有效提高关键特征通道的权重,增强关键信息的表达,避免了降维带来的通道信息损失,提高模型的性能.
图3
IECA模块使用核大小为k的一维卷积来实现通道权重的学习,一维卷积的卷积核大小与通道数之间的映射关系对捕获通道信息交互至关重要.当通道数C确定时,卷积核的大小k可根据(1)式计算得到:
其中,γ和b用于改变通道数C和卷积核大小之间的比例,在实验中一般设置为2和1,|X|odd表示选择最接近X的奇数.
1.2.3 三维空洞卷积
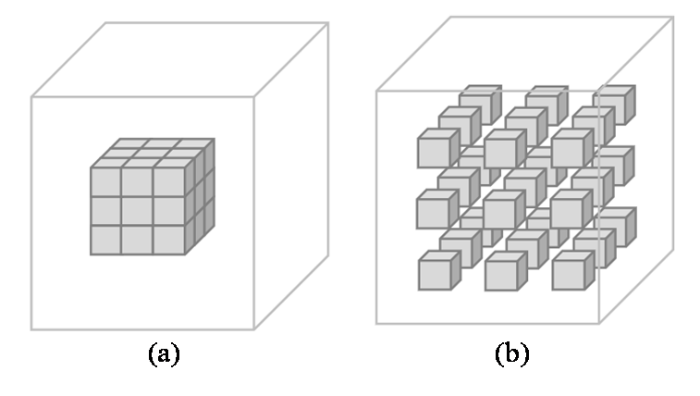
图4
图4
不同空洞率r下的空洞卷积,(a) r = 1; (b) r = 2
Fig. 4
Dilated convolution with different dilation rate r, (a) r = 1; (b) r = 2
1.2.4 Leaky ReLU6
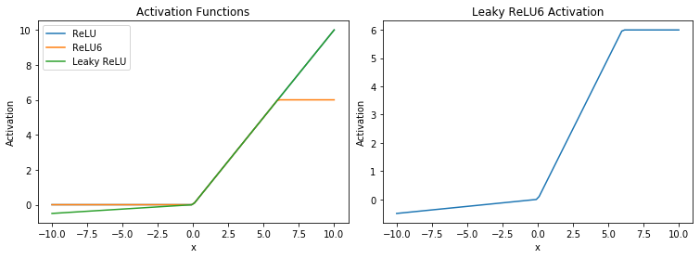
本文将Leaky ReLU与ReLU6的优点结合,形成了一个新的激活函数Leaky ReLU6,如(5)式所示,实验过程中将α设置为0.01.从图5中可以更直观的看出不同激活函数的特点,改进的Leaky ReLU6激活函数不仅保留了ReLU6的优点,还解决了ReLU6中x < 0时神经元可能“死亡”的问题,从而更有效地提取低级网络中的图像特征.
图5
1.2.5 3D ELD_MobileNetV2分类模型
本文基于MobileNetV2模型的改进如下:首先,将MobileNetV2中的二维卷积和池化操作扩展为三维操作,避免对磁共振图像进行特征提取时出现空间特征损失的现象;其次,将逐点卷积后的特征输入到IECA模块中,经过平均池化和最大池化融合之后,与相邻k个通道信息交互,调整重要特征权重,将交互后的特征信息与输入特征相乘,生成输出特征;同时,在步长为1的深度卷积中引入空洞率为2的空洞结构,不仅可以增大感受野,还可以保留数据的空间信息,充分获取肝结节的相关特征;最后,使用Leaky ReLU6取代原来的激活函数,加快神经网络的收敛.由于MobileNetV2中较大的膨胀系数会产生大量冗余特征,导致过拟合问题,通过降低原始网络中的扩展因子,可以减少网络参数和运算浮点的数量.通过实验分析,当扩展因子减小到4时,可以保证网络的分类精度更高、速度更快.
本文提出的3D ELD_MobileNetV2整体结构如图6所示,首先,肝结节数据在输入层内被统一调整为128×128×32×1;随后进入特征提取网络,调整输入数据的维度和通道数,得到大小为64×64×16×32的特征图;然后经过添加IECA模块和空洞卷积的Bottleneck结构,提取丰富、有效的病灶特征;最后,进入分类网络,由Softmax函数得出每种结节对应的概率值,并将最高概率值的类别作为预测结果返回至输出层,实现肝结节的分类.
图6
1.3 实验数据与预处理
本文回顾性收集了上海某三甲医院120例患者的DCE-MRI图像,包含30个肝炎病例(男性15例,女性15例,平均年龄46.7±12.1岁)、30个CN病例(男性24例,女性6例,平均年龄57.1±10.2岁)、30个DN病例(男性24例,女性6例,平均年龄58.9±9.3岁)以及30个HCC病例(男性25例,女性5例,平均年龄58.1±9.9岁).所有患者均已提供书面知情同意书.动脉期、门脉期和延迟期图像均使用GE 1.5T磁共振扫描仪(型号:Signa Infinity Twin Speed),通过肝脏加速容积采集成像(Liver Acquisition with Volume Acceleration,LAVA)序列获得.其中,重复时间为3.712 ms,回波时间为1.724 ms,反转时间为7 ms,翻转角为15˚,图像矩阵为512*512,层厚为2.5 mm,层间距为2.5 mm.
为了实现卷积神经网络对病灶的分类任务,病灶需要预先勾画.经验丰富的临床专家通过ITK-SNAP手动勾画每个病人三期图像所有层面的病灶区域,以上被分割出的病灶区域均被概述为ROI.随后将ROI点乘原始图像作为深度学习网络的输入.由于ROI只占整个肝脏较小的区域,而大幅图像尺寸会增加网络的计算,使得训练时间过长,因此需要对这些勾画后的病灶进行处理.通过寻找ROI连通域的中心,使用128×128×32长方体覆盖病灶区域来缩小图像尺寸,长方体内病灶部位的体素保持不变,其余非病灶部位体素为0.
每个病人的三期图像作为独立样本用于网络训练和测试,因此实验数据集为360组MRI样本数据,训练集和独立测试集按8 : 2的比例随机划分(288例用于训练,72例用于测试).考虑到实验所使用的数据量较少,可能导致过拟合现象的产生,影响模型的性能和泛化能力.因此,本文对数据进行扩增处理,数据扩增[30]通过从现有数据中生成新的数据来人为地增加样本量和数据多样性,使模型具有更好的泛化能力.本文采用随机上下翻转、随机旋转方法对数据进行处理.最终,训练集样本量由288扩充到864.
1.4 模型训练策略和参数设置
实验操作系统为 Windows10,主要开发环境为 Python3.7,使用 Tensorflow下的keras构建网络框架.在五折交叉训练过程中,训练集被随机分成5个子集,交叉验证每轮选择其中1组作为验证集,剩余子集用于模型训练.在推理(inference)阶段,五折交叉验证独立训练的模型被融合,并采用多数投票策略来确定最终的分类,即当存在四个模型对某一类达成一致时,将其分为该类.
在实验过程中,使用Adam优化器和交叉熵损失函数、批尺寸(batch_size)设置为16,丢弃(Dropout)率为0.25.设置不同的学习率,通过评估模型结果确定最优学习率,在最优学习率下训练3D ELD_MobileNetV2模型,获得预测结果.
1.5 模型评价指标
ROC曲线(Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve)[31]作为机器学习模型的评估指标之一,是研究二分类问题的主流工具.ROC曲线下面积(Area Under Curve,AUC)处于0~1之间,曲线越靠近左上角,模型的分类性能越好.为了从多方面评估模型的性能,本文除使用ROC曲线和AUC值外,还将采用召回率(Recall)、精确率(Precision)、准确率(Accuracy)和F1分数(F1_Score)等分类模型评价指标,其表达式如下:
其中,公式中指标的含义如表1所示.
表1 混淆矩阵
Table 1
| 实际表现 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | ||
| 预测表现 | 1 | 真阳性 (True Positive,TP) | 假阳性 (False Positive,FP) |
| 0 | 假阴性 (False Negative,FN) | 真阴性 (True Negative,TN) | |
2 结果与讨论
2.1 不同学习率分类效果对比
表2 不同学习率下分类性能比较
Table 2
| 初始学习率 | 准确率 | 损失率 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0001 | 0.734 | 0.8187 |
| 0.00005 | 0.792 | 0.6895 |
| 0.00001 | 0.764 | 0.7596 |
2.2 消融实验
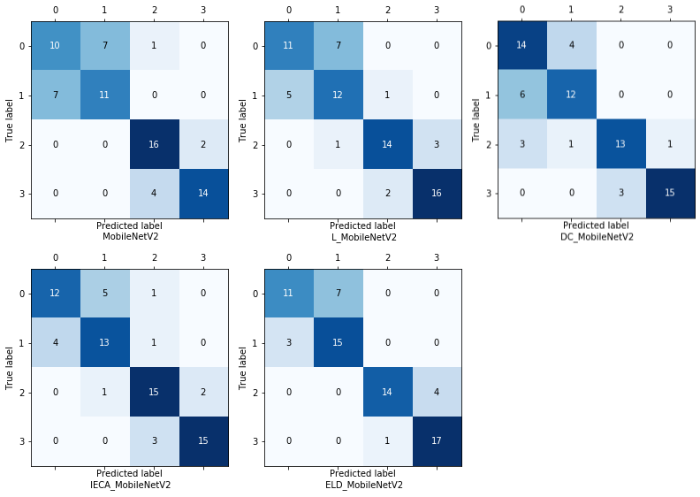
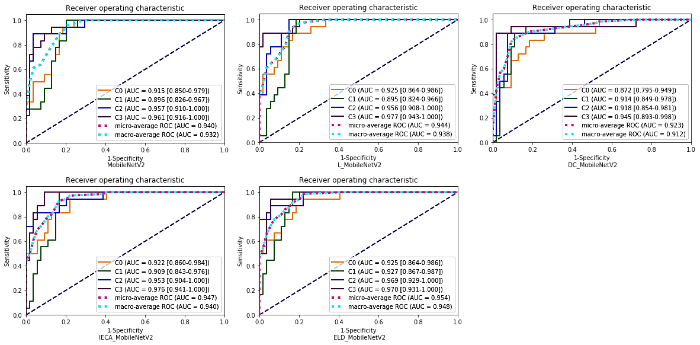
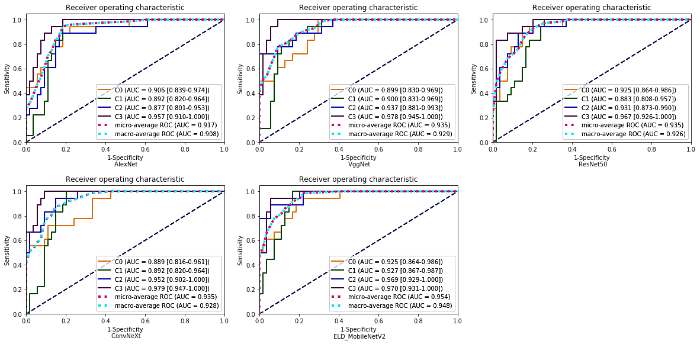
为了验证改进策略的有效性,使用消融实验分析所提改进策略对实验结果的影响.MobileNetV2、L_MobileNetV2、IECA_MobileNetV2、DC_MobileNetV2、ELD_MobileNetV2模型的分类准确率分别为 0.708、0.736、0.764、0.750、0.792.其中,MobileNetV2为原始模型,L_MobileNetV2、IECA_MobileNetV2、DC_MobileNetV2分别为架构调整后添加Leaky ReLU6模块、IECA模块、空洞卷积的改进模型,ELD_MobileNetV2为本文所提模型.相较于MobileNetV2,改进模型的准确率均有所提高,说明改进策略具有一定的有效性.表3为不同改进策略的精确率、召回率和F1_Score,其中,C0~C3分别代表肝炎肝实质、CN、DN、HCC.从表3可见,激活函数的改变,注意力模块以及空洞卷积的添加均在一定程度上提高了原始模型的性能.由于原始模型结构、膨胀系数的更改以及新模块的添加,可能会导致模型针对某一类病灶的查准率和查全率有所降低.因此,深度学习多分类模型的评估需要利用不同的评估指标来判断模型的性能,整体而言,改进后的模型性能是要优于原始模型的.图7为不同改进策略的混淆矩阵图,每一行表示真实类别(True label),每一列表示预测类别(Predicted label),对角线上的数字表示每类病灶被准确预测的个数.从混淆矩阵中可以更直观地看出改进模型针对某一类别的分类能力,对于肝炎肝实质、CN、HCC的预测正确个数较原始模型均有所增加,由于DN的MRI表现多样,信号强度与CN和早期HCC有部分重叠,可能导致模型对DN的查全率较低.图8为不同改进策略的ROC曲线和AUC值,ELD_MobileNetV2模型的微平均(micro-average)ROC的AUC值为0.954,宏平均(macro-average)ROC的AUC值为0.948,均高于原始模型和其他改进模型.
表3 消融实验结果
Table 3
| MobileNetV2 | L_MobileNetV2 | IECA_MobileNetV2 | DC_MobileNetV2 | ELD_MobileNetV2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | Precision | 0.588 | 0.688 | 0.750 | 0.609 | 0.786 | ||
| Recall | 0.556 | 0.611 | 0.667 | 0.778 | 0.611 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.571 | 0.647 | 0.706 | 0.683 | 0.688 | |||
| C1 | Precision | 0.611 | 0.600 | 0.684 | 0.706 | 0.682 | ||
| Recall | 0.611 | 0.667 | 0.722 | 0.667 | 0.833 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.611 | 0.632 | 0.703 | 0.686 | 0.750 | |||
| C2 | Precision | 0.762 | 0.824 | 0.750 | 0.812 | 0.933 | ||
| Recall | 0.889 | 0.778 | 0.833 | 0.722 | 0.778 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.821 | 0.800 | 0.789 | 0.765 | 0.848 | |||
| C3 | Precision | 0.875 | 0.842 | 0.882 | 0.938 | 0.810 | ||
| Recall | 0.778 | 0.889 | 0.833 | 0.833 | 0.944 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.824 | 0.865 | 0.857 | 0.882 | 0.872 | |||
| 总体 | Precision | 0.709 | 0.739 | 0.767 | 0.766 | 0.803 | ||
| Recall | 0.709 | 0.736 | 0.764 | 0.750 | 0.792 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.709 | 0.737 | 0.765 | 0.758 | 0.797 | |||
| Accuracy | 0.708 | 0.736 | 0.764 | 0.750 | 0.792 | |||
图7
图8
2.3 不同网络模型的分类性能对比
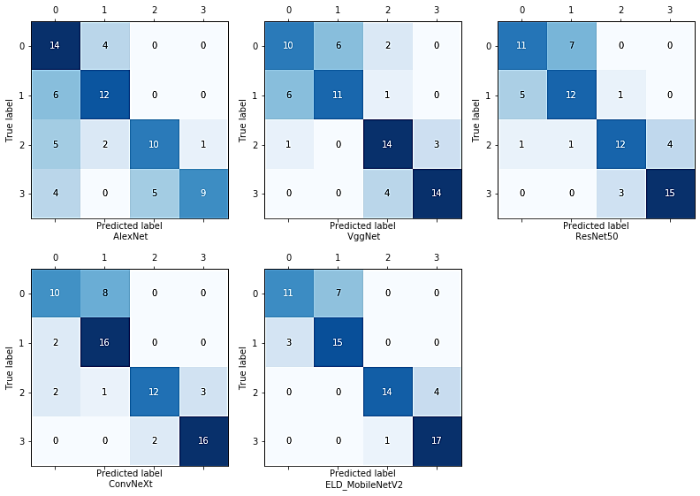
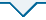
为了更全面的评估所提模型的优越性,选用一些具有代表性且常用于医学图像分类任务中的网络模型与本文模型进行比较,分别为AlexNet、VggNet16、ResNet50以及新型网络ConvNeXt.在实验过程中,将学习率设置为0.000 05,比较不同网络模型的分类效果.3D AlexNet、3D VggNet16、3D ResNet50、3D ConvNeXt和3D ELD_MobileNetV2的准确率分别为0.625、0.681、0.694、0.750和0.792,本文所提模型的分类准确率最高.表4为不同模型的精确率、召回率以及F1_Score,其中F1_Score为精确率和召回率的调和平均值,更好地兼顾查准率和查全率.从表4可以看出,虽然,在HCC的鉴别中,VggNet(0.824)和ConvNeXt(0.842)的精确率略高于本文模型(0.810),但从另一角度来看,本文模型召回率(0.944)要远高于这两种模型,说明模型有更好的查全率.本文模型的F1_Score在四种病灶的分类中均达到最高,为0.688、0.750、0.848、0.872.图9为不同分类模型的混淆矩阵图,从图中可以看出3D ELD_MobileNetV2的总正确预测个数是最多的,且有效提高了对HCC的鉴别能力,说明本文模型对HCC有更好的识别能力,并保证了其他病灶的识别准确率.为更好的评价所有对比模型,根据灵敏度和特异度计算出AUC值做定量分析,并绘制ROC曲线,如图10所示.从图中可以看出,3D ELD_MobileNetV2的micro-average AUC值和macro-average AUC值最高.因此,经过综合比较,说明本文模型的改进具有一定的优越性,可有效提高四分类的准确性,具有良好的诊断性能.
表4 不同网络模型的分类性能比较
Table 4
| AlexNet | VggNet16 | ResNet50 | ConvNeXt | ELD_MobileNetV2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 | Precision | 0.483 | 0.588 | 0.647 | 0.714 | 0.786 | ||
| Recall | 0.778 | 0.556 | 0.611 | 0.556 | 0.611 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.596 | 0.571 | 0.629 | 0.625 | 0.688 | |||
| C1 | Precision | 0.667 | 0.647 | 0.600 | 0.640 | 0.682 | ||
| Recall | 0.667 | 0.611 | 0.667 | 0.889 | 0.833 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.667 | 0.629 | 0.632 | 0.744 | 0.750 | |||
| C2 | Precision | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.750 | 0.857 | 0.933 | ||
| Recall | 0.556 | 0.778 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.778 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.606 | 0.718 | 0.706 | 0.750 | 0.848 | |||
| C3 | Precision | 0.900 | 0.824 | 0.789 | 0.842 | 0.810 | ||
| Recall | 0.500 | 0.778 | 0.833 | 0.889 | 0.944 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.643 | 0.800 | 0.811 | 0.865 | 0.872 | |||
| 总体 | Precision | 0.679 | 0.682 | 0.697 | 0.763 | 0.803 | ||
| Recall | 0.625 | 0.681 | 0.695 | 0.750 | 0.792 | |||
| F1_Score | 0.651 | 0.681 | 0.695 | 0.757 | 0.797 | |||
| Accuracy | 0.625 | 0.681 | 0.694 | 0.750 | 0.792 | |||
图9
图10
3 结论
本文基于腹部DCE-MRI图像,建立3D ELD_MobileNetV2分类模型,实现了对肝炎肝实质、CN、DN和HCC的有效判断,可为肝癌早期诊断提供有效帮助.实验在MobileNetV2的基础上扩展了卷积操作,使其在特征提取的过程中可以捕捉到更加丰富的信息.与原始MobileNetV2相比,主要优点是考虑了通道间的信息交互,扩大了感受野,提高了模型的鲁棒性和收敛能力.通过消融实验结果可以看出IECA模块、空洞卷积结构的添加以及激活函数的创新均在一定程度上提高了模型的分类性能.结果表明,3D ELD_MobileNetV2模型的分类准确率要高于原始模型,而且在与常用的深度学习模型的对比中,也表现最好.本研究还存在一定局限性:首先,本实验所使用的临床数据集有限,而深度学习模型的有效表达需要大数据的支撑;此外,医疗数据大多是不均衡的,而本文不同类型病灶之间的数据量较为均衡,可能会对实验结果造成影响,后续将进一步扩充原始数据量以提高模型的稳定性和准确性;其次,本文未将具有统计学意义的临床指标纳入模型,后续将收集这些参数,构建临床-深度学习模型与单纯的深度学习模型进行比较;最后,为了更好的评估模型的鲁棒性及其适用性,未来可能需要继续收集不同医学中心数据对该模型进行验证.综上所述,本研究构建的3D ELD_MobileNetV2模型对肝结节有较好的诊断性能,有助于区分肝硬化肝癌进展中的结节类型,可在一定程度上提高早期肝癌的诊断率.
利益冲突
无
参考文献
Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022
[J].
Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.021
PMID:36208844
[本文引用: 1]

The burden of liver cancer varies across the world. Herein, we present updated estimates of the current global burden of liver cancer (incidence and mortality) and provide predictions of the number of cases/deaths to 2040.We extracted data on primary liver cancer cases and deaths from the GLOBOCAN 2020 database, which includes 185 countries. Age-standardised incidence and mortality rates (ASRs) per 100,000 person-years were calculated. Cases and deaths up to the year 2040 were predicted based on incidence and mortality rates for 2020 and global demographic projections to 2040.In 2020, an estimated 905,700 people were diagnosed with, and 830,200 people died from, liver cancer globally. Global ASRs for liver cancer were 9.5 and 8.7 for new cases and deaths, respectively, per 100,000 people and were highest in Eastern Asia (17.8 new cases, 16.1 deaths), Northern Africa (15.2 new cases, 14.5 deaths), and South-Eastern Asia (13.7 new cases, 13.2 deaths). Liver cancer was among the top three causes of cancer death in 46 countries and was among the top five causes of cancer death in 90 countries. ASRs of both incidence and mortality were higher among males than females in all world regions (male:female ASR ratio ranged between 1.2-3.6). The number of new cases of liver cancer per year is predicted to increase by 55.0% between 2020 and 2040, with a possible 1.4 million people diagnosed in 2040. A predicted 1.3 million people could die from liver cancer in 2040 (56.4% more than in 2020).Liver cancer is a major cause of death in many countries, and the number of people diagnosed with liver cancer is predicted to rise. Efforts to reduce the incidence of preventable liver cancer should be prioritised.The burden of liver cancer varies across the world. Liver cancer was among the top three causes of cancer death in 46 countries and was among the top five causes of cancer death in 90 countries worldwide. We predict the number of cases and deaths will rise over the next 20 years as the world population grows. Primary liver cancer due to some causes is preventable if control efforts are prioritised and the predicted rise in cases may increase the need for resources to manage care of patients with liver cancer.Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries
[J].
Hepatocellular carcinoma
[J].
DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01200-4
PMID:36084663
[本文引用: 1]

Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most common cancers worldwide and represents a major global health-care challenge. Although viral hepatitis and alcohol remain important risk factors, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is rapidly becoming a dominant cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. A broad range of treatment options are available for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, including liver transplantation, surgical resection, percutaneous ablation, and radiation, as well as transarterial and systemic therapies. As such, clinical decision making requires a multidisciplinary team that longitudinally adapts the individual treatment strategy according to the patient's tumour stage, liver function, and performance status. With the approval of new first-line agents and second-line agents, as well as the establishment of immune checkpoint inhibitor-based therapies as standard of care, the treatment landscape of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma is more diversified than ever. Consequently, the outlook for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma has improved. However, the optimal sequencing of drugs remains to be defined, and predictive biomarkers are urgently needed to inform treatment selection. In this Seminar, we present an update on the causes, diagnosis, molecular classification, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
State-of-the-art review on the correlations between pathological and magnetic resonance features of cirrhotic nodules
[J].
Multicenter validation of abbreviated MRI for detecting early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma
[J].
Performance of contrast-enhanced sonography versus MRI with a liver-specific contrast agent for diagnosis of hepatocellular adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia
[J].
Performance analysis of liver tumor classification using machine learning algorithms
[J].
Application of radiomics based on new support vector machine in the classification of hepatic nodules
[J].
基于新型支持向量LIDI机的影像组学在肝脏结节分类中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20212916
[本文引用: 1]

肝癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,亚洲地区最为常见的肝癌演变过程为肝炎-肝硬化结节-异型增生结节-肝细胞性肝癌.判断肝脏结节在演变过程所处分期,并采取干预措施,对降低肝癌的发生率非常关键.本文针对影像组学提出了更精确的支持向量机(SVM)分类算法——LFOA-F-SVM,用于对120名患者的腹部动态增强磁共振图像的肝脏结节进行四分类.该算法利用了考虑半径与几何间距的F-SVM,并结合莱维飞行策略(LF)的果蝇优化算法(FOA)寻求超参.为了验证方法的有效性,本文另外添加了5个UCI分类数据集(心脏、帕金森疾病、虹膜、葡萄酒和动物园),并与SVM、PSO-SVM、FOA-SVM、F-SVM进行比较.结果表明,在6个分类数据集(包括肝脏结节数据集和5个UCI分类数据集)中,相对于其他分类算法,LFOA-F-SVM的分类准确率最高,在肝脏结节数据集中的四分类精确率和查全率也较高.
Application of enhanced CT-based radiomics in differentiating small hepatocellular carcinoma from hepatic dysplastic nodules
[J].
基于增强CT影像组学鉴别小肝癌与肝不典型增生结节的应用研究
[J].
An automated liver tumour segmentation and classification model by deep learning based approaches
[J].
Deep learning-based classification of hepatocellular nodular lesions on whole-slide histopathologic images
[J].
DOI:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.025
PMID:35202643
[本文引用: 2]

Hepatocellular nodular lesions (HNLs) constitute a heterogeneous group of disorders. Differential diagnosis among these lesions, especially high-grade dysplastic nodule (HGDN) and well differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma (WD-HCC), can be challenging, let alone biopsy specimens. We aimed to develop a deep learning system to solve these puzzles, improving the histopathologic diagnosis of HNLs (WD-HCC, HGDN, low-grade DN, focal nodular hyperplasia, hepatocellular adenoma) and background tissues (nodular cirrhosis, normal liver tissue).The samples consisting of surgical specimens and biopsies were collected from six hospitals. Each specimen was reviewed by 2-3 subspecialists. Four deep neural networks (ResNet50, InceptionV3, Xception and the Ensemble) were employed. The performances were evaluated by confusion matrix, ROC curve, classification map and heatmap. Furthermore, the predictive efficiency of the optimal model was verified by comparing with that of nine pathologists.A total of 213,280 patches from 1115 WSIs of 738 cases were obtained. An optimal model was finally chosen based on F1 score and AUC value, named hepatocellular-nodular artificial intelligence model (HnAIM), with the overall seven-category AUC of 0.935 in the independent external validation cohort. For biopsy specimens, the agreement rate with subspecialists' majority opinion was higher for HnAIM than nine pathologists on both patch-level and WSI-level.We first developed a deep learning diagnostic model for HNLs, which performed well and contributed to enhancing the diagnosis rate of early HCC and risk stratification of HNLs patients. Furthermore, HnAIM had significant advantages in patch-level recognition, with important diagnostic implications for fragmentary or scarce biopsy specimens.Copyright © 2022 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Extending 2-D convolutional neural networks to 3-D for advancing deep learning cancer classification with application to MRI liver tumor differentiation
[J].
Multi-input dense convolutional network for classification of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
[J].
Automatic detection and classification of focal liver lesions based on deep convolutional neural networks: a preliminary study
[J].
ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks
[J].
Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition
[J].
A transfer learning approach for the classification of liver cancer
[J].
A convnet for the 2020s
[C]//
Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks
[C]//
Deep residual learning for image recognition
[C]//
Improving early detection and classification of lung diseases with innovative MobileNetV2 framework
[J].
Classification of skin lesions with generative adversarial networks and improved MobileNetV2
[J].
Brain tumor diagnosis from MRI based on Mobilenetv2 optimized by contracted fox optimization algorithm
[J].
ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks
[C]//
Hyperspectral image classification based on residual dense and dilated convolution
[J].
Nonlinear approximation and (deep) ReLU networks
[J].
Establishment and validation of an artificial intelligence-based model for real-time detection and classification of colorectal adenoma
[J].
DOI:10.1038/s41598-024-61342-6
PMID:38729988
[本文引用: 1]

Colorectal cancer (CRC) prevention requires early detection and removal of adenomas. We aimed to develop a computational model for real-time detection and classification of colorectal adenoma. Computationally constrained background based on real-time detection, we propose an improved adaptive lightweight ensemble model for real-time detection and classification of adenomas and other polyps. Firstly, we devised an adaptive lightweight network modification and effective training strategy to diminish the computational requirements for real-time detection. Secondly, by integrating the adaptive lightweight YOLOv4 with the single shot multibox detector network, we established the adaptive small object detection ensemble (ASODE) model, which enhances the precision of detecting target polyps without significantly increasing the model's memory footprint. We conducted simulated training using clinical colonoscopy images and videos to validate the method's performance, extracting features from 1148 polyps and employing a confidence threshold of 0.5 to filter out low-confidence sample predictions. Finally, compared to state-of-the-art models, our ASODE model demonstrated superior performance. In the test set, the sensitivity of images and videos reached 87.96% and 92.31%, respectively. Additionally, the ASODE model achieved an accuracy of 92.70% for adenoma detection with a false positive rate of 8.18%. Training results indicate the effectiveness of our method in classifying small polyps. Our model exhibits remarkable performance in real-time detection of colorectal adenomas, serving as a reliable tool for assisting endoscopists.© 2024. The Author(s).
Reluplex made more practical: Leaky ReLU
[C]//
Data augmentation for medical imaging: A systematic literature review
[J].
ROC-ing along: Evaluation and interpretation of receiver operating characteristic curves
[J].
Classification of pancreatic cystic tumors based on DenseNet and transfer learning
[J].
基于DenseNet结合迁移学习的胰腺囊性肿瘤分类方法
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20223047
[本文引用: 1]

本文采用了DenseNet结合迁移学习的分类模型,对胰腺黏液性囊性肿瘤(MCN)和浆液性囊性肿瘤(SCN)进行分类. 首先对来自长海医院的65例MCN和107例SCN数据进行扩增和预处理,其次构建DenseNet结合迁移学习的分类模型并进行微调,实验过程采用五折交叉验证,对MCN和SCN进行识别分类,并将该模型与AlexNet、VGG16、ResNet50等其他深度学习模型进行对比. 结果显示本文的分类模型识别效果最好,在测试集上ROC曲线下面积(AUC值)达到0.989,准确率为0.943,召回率为0.949,精确率为0.938. 由此可见基于DenseNet结合迁移学习的分类模型对MCN和SCN具有较高的识别准确率,优于其他深度学习模型,并具有较强的学习能力,可以辅助医生在临床上的诊断,在一定程度上节省人力物力. 该模型对于胰腺囊性肿瘤识别分类的潜在价值和临床意义.