引言
超极化129Xe磁共振成像(Hyperpolarized 129Xe Magnetic Resonance Imaging,129Xe MRI)是一种新兴的高灵敏度肺部成像技术,该技术利用超极化的129Xe核作为成像对比剂,以提高肺部及其他组织的磁共振信号强度,检测和定量分析肺部的局部通气和气体交换功能,实现对肺部通气功能的可视化测量[1-
目前,针对MRI的去噪算法可以分为传统去噪算法和深度学习去噪算法.其中,传统去噪算法又可分为空间域滤波方法、变换域方法以及基于偏微分方程的方法等.Manjón等[8]在传统的非局部均值滤波方法(Non-Local Means,NLM)中,利用MRI的稀疏性和自相似性,对带有莱斯噪声的MRI进行去噪,实现了无偏非局部均值滤波(Unbiased Non-Local Means,UNLM).Manjón等[9]使用新的局部噪声估计方法,将有关局部图像噪声水平的信息用于调整滤波器的去噪强度,并通过将空间图像变换到其他域(如傅里叶域、小波域和曲波域)进行去噪.在针对超极化磁共振图像去噪上,Soderlund等[10]改进了基于全局-局部补丁的高阶奇异值分解方法(Higher-Order Singular Value Decomposition,HOSVD),用于提高图像的信噪比,并利用动力学气体理论和物理自由扩散模型检查去噪结果.尽管传统的MRI去噪算法在先前的去噪工作中具有一定的效果,但依旧存在一些难以解决的问题[11].例如,这些方法过于依赖对图像和噪声类型的建模,同时计算量大,复杂度高,需要手动调整参数等,限制了传统去噪方法在临床应用中的有效性[12]. 相比之下,基于深度学习的MRI去噪技术能够自动提取图像特征,学习从有噪图像到无噪图像的非线性映射关系,从而减少了对噪声的依赖,同时表现出了优秀的去噪结果.
近年来,随着深度学习方法的发展,MRI去噪方法得到了进一步的扩充.卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)[13]通过使用受噪声影响的图像和真实图像对进行训练,学习恢复无噪声图像.Zhang等[14]提出了一种利用批量归一化和残差学习构建的前馈去噪卷积神经网络(Denoising Convolutional Neural Network,DnCNN)不仅可以加快网络训练速度,还可以更好地消除高斯噪声.Wang等[15]在此基础上提出了一种非盲去噪卷积神经网络,利用复值构建块和噪声水平信息来提高各种环境中的去噪性能.虽然基于CNN的网络在一定程度上改善了捕获噪声的范围,但由于CNN架构本身所固有的局限性,对于噪声信息的利用仍然不是最优的[16,17].Shi等[11]提出了一种混合Transformer-CNN的去噪模型(Hybrid Transformer-CNN network,HTC-net)用于超极化129Xe MRI去噪.然而这种更深层的CNN编码器和更多层次的特征聚合增加了过拟合的风险,可能导致模型泛化能力下降.Tian等[18,19]提出了一种使用条件生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks,GAN)的新型MRI去噪方法,使用卷积神经网络作为判别器,以区分从条件GAN获得的图像.而GAN网络不可避免地会受到训练过程不稳定和模式崩溃等问题的影响.为了解决这些限制,人们提出了去噪扩散概率模型(Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model,DDPM)作为GAN的替代方案,期望能够生成更好质量和更多样化的合成图像[20].DDPM模型通常是使用U形卷积神经网络来学习降噪,以输出具有良好视觉效果的医学图像.同时可以避免GAN网络中通常需要的对抗性训练,从而提高了训练的稳定性和生成图像的真实性,但现阶段所提出的DDPM模型还未用于超极化129Xe MRI的去噪工作中.我们通过前期预实验发现,凭借单一的模态生成会使模型陷入某一种特定的模式中,导致无法准确反映训练数据的多样性和复杂性,造成去噪结果的真实性缺失,还会因为DDPM模型自身的前向加噪过程,导致图像轮廓和细节区域的保留效果较差[21],降低了129Xe MRI临床应用的可靠性.
为了解决上述问题,提升对肺部129Xe MRI的去噪性能,本文提出了一种基于多模态信息增强的条件扩散模型(DDPM-HXe).由于1H MRI是在屏气采集129Xe MRI的时候进行采集的,所以我们利用1H MRI数据明确的边缘信息作为约束条件,提高模型在去噪过程中对129Xe MRI边缘的判断能力.此外,为了解决噪声对肺部129Xe MRI细节区域的影响,我们改进了内嵌的卷积神经网络结构,设计了一种多模态特征增强模块,用于提高模型对多模态信息的利用和对微小局部变换的敏感程度.
1 实验部分
1.1 噪声问题描述
在进行129Xe MRI数据采集时,主要噪声来源为扫描对象自身的热噪声,产生的这种噪声特征可以理解为身体、线圈和电子扫描设备等相关的独立随机噪声的特征组合.由于采集到的原始K空间数据为复值形式,因此,采集的实部和虚部数据会受到独立同分布的高斯噪声污染.在进行傅里叶变换时,由于傅里叶变换的线性与正交性质,从K空间变换到图像数据的实部和虚部噪声仍然满足高斯分布.因此,磁共振成像的幅度图噪声满足莱斯分布,如(1)式所示:
其中
在本文中,我们主要进行129Xe MRI幅度图去噪,通过我们设计的去噪网络来确定最优的结果
1.2 总体模型
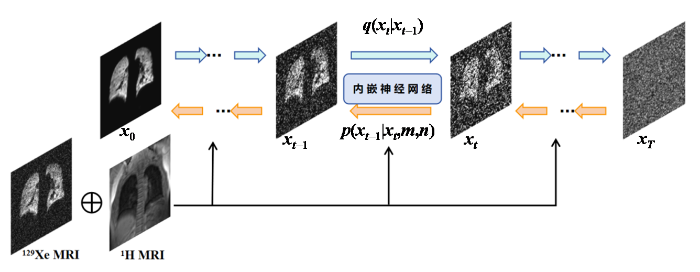
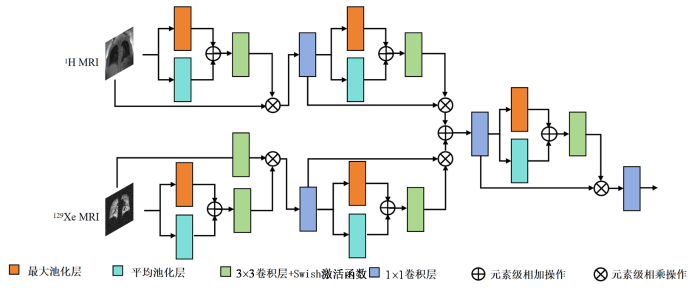
本文提出的去噪模型总体架构如图1所示.该模型包括条件扩散过程和内嵌的卷积神经网络.初始时输入高质量数据
图1
1.2.1 扩散模型原理
图2
图2
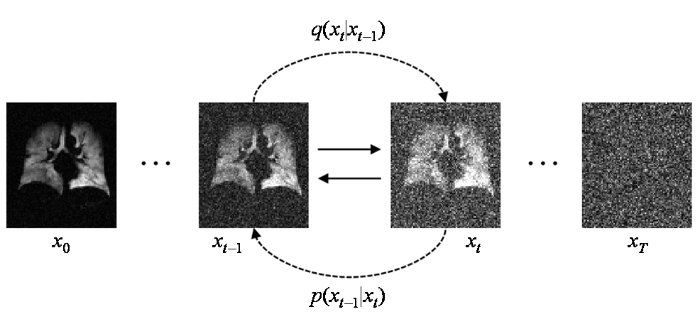
前向扩散逐步添加高斯噪声与逆向扩散逐步去除噪声恢复图像过程
Fig. 2
Forward diffusion progressive addition of gaussian noise and backward diffusion progressive removal of noise recovery image processes
模型的前向扩散加噪过程可以看作是将上一时刻输入的图像与一个高斯分布采样进行加权融合,如(2)式和(3)式所示,N表示高斯分布,I是单位矩阵,
其中,
逆向去噪过程仍然是一个逐步进行的过程,它可以利用贝叶斯公式进行推导[24].如果我们的目标是从目标数据分布
其中,μ 表示噪声均值.在扩散模型中利用神经网络来拟合出噪声预测模型,得到均值
由于方差由扩散过程的参数决定,通常是固定的,所以无需通过神经网络拟合,而参数
1.2.2 内嵌神经网络架构
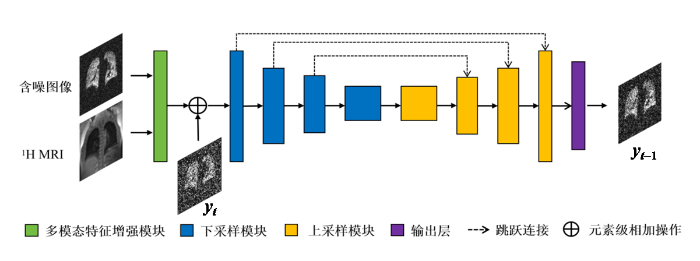
本文在扩散模型的内嵌神经网络是一个编码-解码结构,具体架构如下图3所示.在这个神经网络架构中,包括了我们为增强多模态信息利用效果而设计的专属模块,以及下采样模块,上采样模块和输出层.通过跳跃连接的方式将下采样模块和上采样模块进行连接,来提升模型中信息的流动和利用效率,改善去噪效果和模型训练的稳定性.
图3
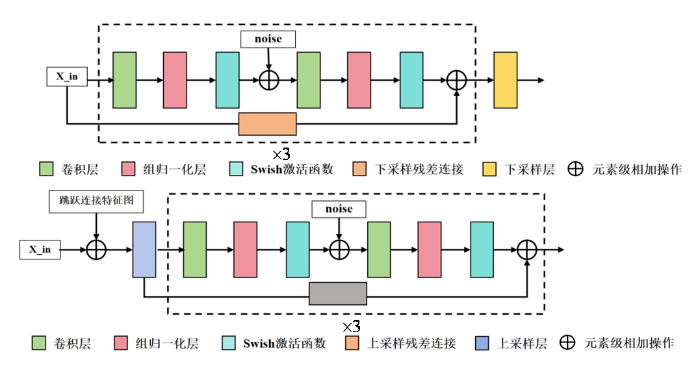
在每个上采样和下采样模块中,分别包括了三个残差块,并在图4中举例描述了上采样和下采样时经过一个残差块的过程.数据在每个残差块中依次进行卷积、组归一化、Swish激活函数、正则化和卷积处理.在进行残差块设计的时候,考虑到提升网络应对不同噪声级别的处理能力,以及提升网络的稳定性和灵活性,我们选用了组归一化和Swish激活函数,如(9)式所示.此外,我们在上下采样过程中根据时间t的取值添加了一个噪声noise,当t > 0时该噪声的特征与前向扩散t时刻添加的噪声特征一致,因此该噪声可以视为一种额外的信息源.最后将残差块的输入与输出进行对应的残差连接,以允许低级别的特征通过.
图4
图4
上采样和下采时经过残差块的过程
Fig. 4
Up-sampling and down-sampling go through a residual block process
整个网络的具体流程是:数据先经过设计的多模态特征增强模块进行多模态信息提取与融合,然后经过4个下采样模块,每个下采模样块中都包括三个残差块以及下采样层.然后再经过4个上采样模块.在每个上采样模块中,输入数据会与跳跃连接得到的下采样阶段的特征拼接,并依次经过三个残差块和上采样层后输出到下一阶段.最后在输出层通过1×1卷积转换为最终输出通道数,输出估计的噪声结果,并利用(7)式计算得到最终输出,即前一时刻的图像yt-1.
1.2.3 多模态特征增强模块
在进行129Xe MRI去噪中,很多细节和轮廓区域因为噪声的影响而变得模糊不清,而在相同屏气状态下采集的1H MRI却可以提供明确的边缘信息.因此,在本文方法中,我们设计了一种多模态特征增强模块,用于提取与融合1H MRI和有噪声的129Xe MRI的全局和局部信息.该模块由最大池化层,平均池化层,卷积层和Swish激活函数组成,相关模块计算如(10)~(13)式所示.当数据输入后,通过最大池化层提取最大值,并在反向传播时向特征图中响应最大的地方提供反馈.通过平均池化层提取平均值,并在反向传播时为特征图上的每个像素提供反馈.该模块具体结构如图5所示.以1H MRI输入到该模块为例,分别经过一个最大池化层和一个平均池化层,得到对应的特征图
图5
图5
多模态特征增强模块结构图
Fig. 5
Structure of the multi-modal feature enhancement module
将生成的特征注意力图
1.3 实验设计
1.3.1 数据集
本研究获取了85名受试者的肺部1H和129Xe MRI.其中健康受试者为43人,炎症相关的肺部疾病受试者为22人,结构性病变疾病为18人,感染性肺部疾病受试者为2人.所有实验均在1.5 T全身MRI扫描仪(Avanto, Siemens Medical Solutions)上进行,并经当地机构审查委员会批准(批准号:2013079). 129Xe MRI采集时基于自旋交换光抽运(Spin-Exchange Optical Pumping,SEOP)技术[25],使用商用的超极化气体发生器(verImagin Healthcare,中国)对浓缩的129Xe气体进行极化[26,27].将功能残气量吸入气体混合后,屏住呼吸进行数据采集.129Xe MRI的参数为:矩阵大小= 96 × 84,重复时间/回波时间 (TR/TE) = 4.2/1.9 ms,视野大小= 384 × 336 mm2,切片厚度= 8 mm,带宽= 38.4 kHz,切片数= 24,采用3D bSSFP 序列,翻转角= 10˚,扫描时间= 8.4 s.在相同的屏气状态下也进行了1H MRI采集:重复时间/回波时间 (TR/TE) =2.4/0.7 ms,矩阵大小= 96 × 84,视野大小= 384 × 336 mm2,切片厚度= 8 mm,带宽= 48 kHz,切片数= 24,翻转角= 5˚,扫描时间= 2 s.
1.3.2 数据预处理
我们从获取的129Xe MRI数据中选择了信噪比(SNR)大于16的图像,最终获得了1 059张129Xe MRI用于实验,并把这些图像填充为96 × 96.从该数据集中,我们随机选择了850张图像用于训练,并保留了209张图像用于测试.训练图像通过水平翻转,90˚、180˚和270˚旋转操作进行训练集增强,并在这些图像中添加了莱斯噪声,以获得不同SNR范围内的含噪图像.
1.3.3 实验环境和评估指标
本文提出的方法使用PyTorch框架实现.训练和测试在一台配备24 GB内存的NVIDIA RTX 3090和Intel Xeon(R) W-2245 CPU的工作站上进行.采用AdamW优化器,
在训练参数设置中,初始学习率为0.000 1,批次大小为32,损失函数为L2损失,训练迭代2 000次.此外,在扩散过程中我们选择线性调度的方式进行,初始噪声调度的值为1 × 10-4,结束值为2 × 10-2,扩散步数为2 000步.
对于去噪后的评价指标,使用峰值信噪比(Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio,PSNR)和结构相似度(Structure Similarity Index Measure,SSIM)作为评价标准.以下是使用的评价指标介绍.
PSNR是一种广泛用于图像评价的客观指标[21].它主要用于衡量图像的噪声水平和图像质量,以此来评估图像处理算法的相关性能.它是通过图像像素点的最大值和图像之间的均方误差来定义的,计算公式如(15)式所示.其中,
SSIM是用于评估两幅图像相似度的指标,常用于衡量图像去噪前与去噪后的相似性,包括对比度、亮度、结构三个方面之间的关系函数[28].当SSIM值越低,代表图像中的失真程度越高,质量越差.其计算公式如(16)式所示.其中,μ 表示图像像素平均值,
其中
我们使用Dice相似系数(Dice similarity coefficient,Dice)对去噪后图像中通气缺陷区域进行了分割比较,以进一步评估去噪结果的准确性.其计算公式如(18)式所示.其中,A、B分别表示两张对比图像中的像素数.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 实验结果
2.1.1 去噪结果分析
我们对比了几种传统去噪方法和基于深度学习的去噪方法,分别从评价指标和视觉结果上进行对比分析.在对比模型中,我们选择了NLM、UNLM两种传统去噪方法和三种基于深度学习的医学图像去噪方法(DnCNN、HTC-net、DDPM).在遵循不同方法原始设计初衷的情况下,对能够修改输入模态的网络进行了输入改变,尽可能的保持与本文所提方法输入模态一致.其中,DnCNN[14]为现阶段常用的深度学习去噪对比方法,并将DnCNN方法修改为多模态输入,HTC-net[11]为最新的用于129Xe MRI去噪的方法,而DDPM方法是对相关文献[31]中扩散概率模型的训练参数、损失函数进行修改,使其在只保留基础扩散概率模型的情况下适用于MRI去噪任务.通过对多种方法去噪结果的对比验证本文所提出的扩散模型(DDPM-HXe)在设计上的优势.
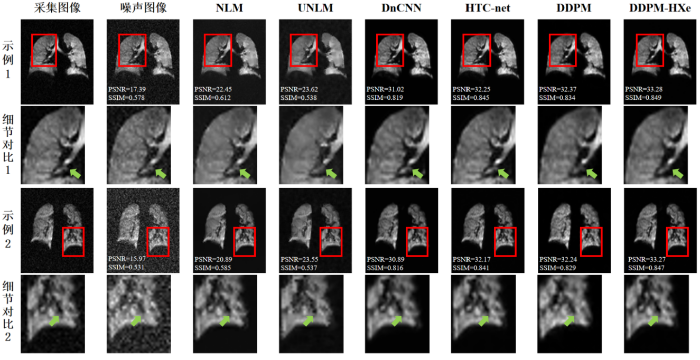
在去噪结果中,我们选取了两张示例结果进行了视觉对比分析.图6为不同方法的去噪结果和放大后的细节图.从这些结果图中可以看出,传统的去噪方法往往会导致图像过度平滑,从而导致细节区域缺失,这一结果与评价指标上的表现相对应.相反,深度学习方法在保留细节方面表现更好,尤其是在肺部轮廓边缘区域和气管交界区域.其中,我们提出的方法在恢复129Xe MRI的低信号区域方面表现更好,能够有效地降低背景噪声,实验结果优于其他方法.
图6
图6
不同模型与本文模型去噪效果对比图
Fig. 6
Comparison of denoising effect between different models and the model in this paper
表1 不同模型和本文模型在评价指标上的对比
Table 1
| 方法 | PSNR | SSIM |
|---|---|---|
| 噪声图像 | 17.973±3.237** | 0.512±0.163** |
| NLM | 20.862±3.481** | 0.584±0.079** |
| UNLM | 24.319±3.125** | 0.431±0.153** |
| DnCNN | 30.758±2.739** | 0.814±0.053** |
| HTC-net | 31.915±2.452** | 0.843±0.057** |
| DDPM | 32.116±2.283* | 0.827±0.055** |
| DDPM-HXe | 33.264±2.594 | 0.847±0.058 |
注:*为p 值 < 0.05;**为p 值 < 0.001
2.1.2 不同噪声等级图像去噪结果分析
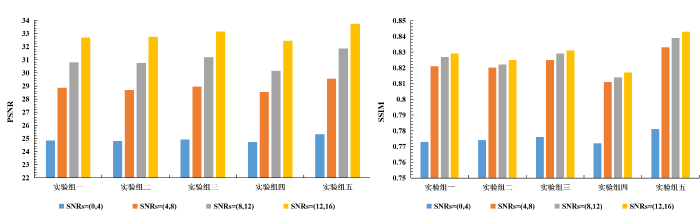
为了更全面地评估本文所提方法在129Xe MRI去噪工作上的可靠性,我们分别对采集数据进行了不同程度的噪声添加.与数据预处理操作相似,我们选择了信噪比大于16的图像,并在这些图像中添加了不同程度的莱斯噪声,使其SNR分别控制在(0,4)、(4,8)、(8,12)和(12,16)这四个区间之内,通过构建不同噪声等级的模拟噪声数据,验证模型在不同噪声等级情况下对129Xe MRI去噪和细节保持的性能.结果如图7所示.从结果上可以看到,本文所提方法在不同噪声等级的数据中均取得了最优的评价指标,同时我们发现当噪声影响逐渐增大时,所有方法去噪性能均有不同程度的下降,但本文方法相对于其他方法表现更加稳定,这一特征主要原因在于本文模型对多模态数据特征的利用效果更好.
图7
图7
不同方法在各级噪声图像上的去噪结果对比
Fig. 7
Comparison of denoising results of different methods on noisy images at all levels
2.1.3 消融实验分析
本文所提模型是一种基于多模态信息的条件扩散模型,设计了一种多模态特征增强模块以提高对多模态信息的利用效果.为进一步验证模型设计的有效性和可靠性,我们设计了五组消融实验,并在模拟的不同噪声等级的数据上验证了不同方案的去噪效果.五组实验中,实验组一以1H MRI单模态输入作为约束条件,实验组二以129Xe MRI单模态输入作为约束条件,实验组三以1H MRI和129Xe MRI同时输入作为约束条件,实验组四以在完整模型上使用3×3卷积块和ReLU激活函数代替残差块设计的多模态输入,实验组五为本文所提出的完整模型,即使用多模态输入,并使用多模态特征增强模块和残差块设计.实验结果如表2和图8所示.对比实验组一、二和三结果,我们发现同时输入1H MRI和129Xe MRI数据对模型的去噪能力具有一定的提升作用.对比实验组三和五结果,证明了本文设计的多模态特征增强模块可以有效提升模型对多模态数据的利用效果.对比实验组四和实验组五结果,证明了本文在残差块设计上对提升网络去噪性能和应对不同噪声强度的优势.
表2 消融实验在评价指标上的对比
Table 2
| 方法 | PSNR | SSIM |
|---|---|---|
| 噪声图像 | 17.973±3.237** | 0.512±0.163** |
| 实验组一 | 32.032±2.174** | 0.831±0.052** |
| 实验组二 | 32.116±2.283** | 0.827±0.055** |
| 实验组三 | 32.694±2.272* | 0.835±0.053** |
| 实验组四 | 31.972±2.189** | 0.819±0.052** |
| 实验组五 | 33.264±2.594 | 0.847±0.058 |
注:*为p 值 < 0.05;**为p 值 < 0.001
图8
图8
不同组合模型在各级噪声图像上的去噪结果对比
Fig. 8
Comparison of denoising results of different combination models on images with various noise levels
2.1.4 通气缺陷区域分割结果分析
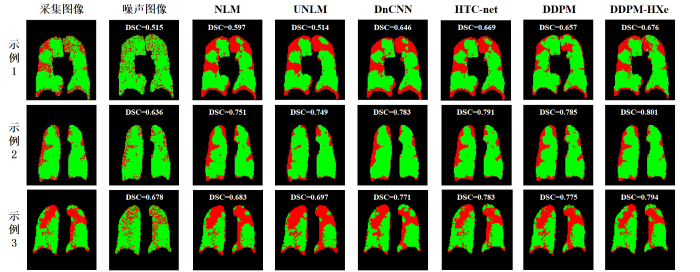
为了验证不同方法去噪结果在临床诊疗中的可靠性,我们使用K-means聚类方法对去噪结果进行了通气缺陷区域分割(图9).从结果来看,使用NLM和UNLM方法去噪的图像在准确分割通气缺陷区域方面表现较差,传统去噪方法在对129Xe MRI的细节恢复上还存在一定的局限.相比之下,基于我们方法的分割结果最接近真实通气缺陷情况,获得了最高的Dice系数,比其他深度学习方法高出1%~4%.
图9
图9
不同方法去噪结果的通气缺陷区域分割对比
Fig. 9
Comparison of ventilation defect area segmentation results of denoising results of different methods
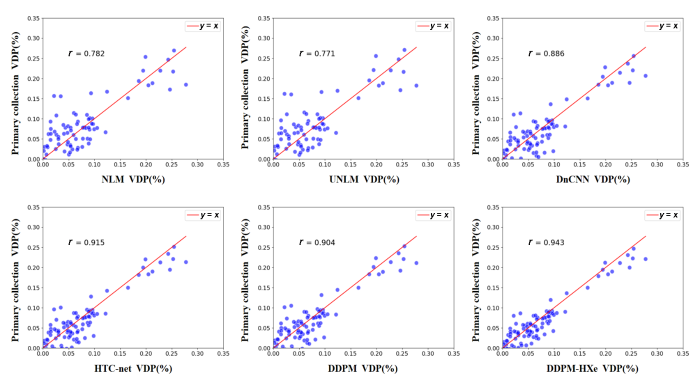
此外,我们还将不同方法的去噪结果进行了VDP的计算,并与实际划分得到的VDP进行了比较.如图10所示,我们通过散点图的形式展示了不同去噪方法的比较结果,以评估在实际应用中的效果.由结果可知,本文所提方法计算的VDP与实际划分得到的VDP具有更高的皮尔逊相关系数r = 0.943,高于其他方法结果.
图10
图10
不同方法去噪结果的VDP比较
Fig. 10
VDP comparison of denoising results of different methods
2.2 讨论
为了增强129Xe MRI质量,提升129Xe MRI在肺部疾病诊疗中的作用,通过图像去噪增强工作,得到准确清晰的129Xe MRI数据具有重要的意义.本文提出了一种基于多模态信息增强的条件扩散模型,用于去除噪声,提升图像质量.我们在前期的预实验中发现,只使用129Xe MRI数据的扩散模型在去噪工作中会过于依赖单一模态信息而缺乏生成多样性,导致模型在处理多样化噪声时去噪效果差、去噪结果真实度低.因此,我们在模型中加入了同一屏气状态下采集的1H MRI数据,利用1H MRI数据明确的边缘信息作为约束条件,提高模型对129Xe MRI数据中肺部边缘的判断能力.此外,为了解决模型加噪扩散过程和图像本身噪声对129Xe MRI肺部细节区域的影响,我们通过改进扩散模型中卷积神经网络的结构,设计了一种多模态特征增强模块,提高模型对多模态信息的利用效果和对图像细节区域变化的敏感程度.
在本文中,我们通过实验证明了所提方法能够有效利用多模态信息,提升模型对129Xe MRI数据的去噪性能.首先,在多模型方法对比中,我们分别与多种传统去噪方法和深度学习去噪方法进行了对比.在评价指标上,本文所提方法的PSNR为33.264,SSIM为0.847,为多模型对比结果中评价指标提升最高的一种.在视觉对比分析中,我们选取了两张示例结果进行了对比分析,从结果图中可以直观地看到,传统的去噪方法会导致图像过度平滑,肺部细节区域缺失严重,很难将去噪结果作为临床疾病的诊断依据,这一结论在评价指标上得到了进一步证明.相反,深度学习方法在保留细节方面表现更好,尤其是在肺部边缘区域和气管交界区域.在实验结果中,我们提出的方法在恢复129Xe MRI的低信号区域方面表现最好,能够有效地降低背景噪声.此外,为了更全面地评估本文所提方法在129Xe MRI去噪工作上的稳定性,我们对采集的数据分别进行不同程度的噪声添加,通过构建不同噪声等级的模拟数据,验证模型在不同噪声强度下对129Xe MRI去噪和细节保留的能力.我们发现,当噪声等级逐渐增大时,所有方法的去噪性能均有不同程度的降低,但本文方法相对于其他方法表现更加稳定,这一结果的主要是因为本文模型能更好地利用多模态数据特征,对噪声等级变化的适应能力更强.其次,我们通过消融实验进行了单模态扩散模型、多模态扩散模型和本文所提出的条件扩散模型在129Xe MRI去噪性能上的比较,实验结果证明了我们所提方法在多模态选择、多模态特征增强模块设计上的有效性.最后,为了验证不同方法去噪结果在临床诊疗中的可靠性,我们使用K-means聚类方法对去噪结果进行了通气缺陷区域分割.从分割结果来看,传统去噪方法对129Xe MRI的细节恢复能力存在一定的局限性,通气缺陷分割结果与真实情况差距较大.在深度学习的去噪方法中,基于本文方法的分割结果最接近真实通气缺陷情况,获得了最高的Dice分数和皮尔逊相关系数,比其他深度学习方法高出1%~4%,该分割结果进一步证明了本文方法在提升129Xe MRI临床应用可靠性上的作用.
本研究还存在一定局限性.我们在分析多模态数据时发现,由于测试者个体肺活量或采集过程中存在的一些误差,导致部分数据在相同屏气状态下采集的1H MRI和129Xe MRI在轮廓上存在一定的差异,这可能会导致我们在使用1H MRI数据作为条件约束时对去噪结果产生不利的影响.后续我们将尝试在预处理阶段对多模态数据进行轮廓配准,通过联合图像配准的方式减少上述局限对去噪结果产生的影响.此外,在训练和计算不同方法计算复杂度的比较中,本文方法依旧存在着扩散模型计算复杂度大,运行时间长的问题,后续我们将在扩散方式和扩散步数上进行优化,以减少计算复杂度和时间.
3 结论
在提升超极化129Xe MRI质量和临床诊疗可靠性的研究中,本文提出了一种利用多模态信息作为约束的条件扩散模型.我们首次将去噪扩散概率模型应用到129Xe MRI的去噪工作中,并通过设计的多模态特征增强模块,实现了模型对1H MRI和129Xe MRI数据的高效利用,提高了模型对图像中微小局部变换的敏感性.实验结果表明,在与多种传统去噪方法和深度学习去噪方法对比时,本文方法的去噪结果能够保留更准确的肺部边缘和内部结构信息,获得了最高的评价指标.在通气缺陷分割任务中,本文方法得到的通气缺陷结果更接近真实情况,分割结果进一步证明了本文方法对提升129Xe MRI临床可靠性的作用.
利益冲突
无
参考文献
Hyperpolarized gas MRI in pulmonology
[J].
Hyperpolarized gas magnetic resonance imaging of the lung
[J].
超极化气体肺部磁共振成像
[J].

磁共振成像(MRI)技术具有非侵入、无放射性的特点,在临床疾病诊断中具有独特的优势,但是肺部空腔的特殊结构使传统质子MRI 无法对其直接成像.自旋交换光抽运(SEOP)方法可以使惰性气体原子的极化度增强4 个量级以上,从而使肺部的气体MRI 成为可能.该文介绍了超极化惰性气体肺部MRI 的最新研究进展,包括超极化气体磁共振相关参数的测量方法、肺部通气结构成像、肺部气体交换功能成像,同时比较了常用于肺部MRI气体的优点和缺点.
Overview and progress of X-nuclei magnetic resonance imaging in biomedical studies
[J].
Damaged lung gas exchange function of discharged COVID-19 patients detected by hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI
[J].
Evaluation of injuries caused by coronavirus disease 2019 using multi-nuclei magnetic resonance imaging
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.mrl.2021.100009
PMID:35673615
[本文引用: 1]

The ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been a great burden for the healthcare system in many countries because of its high transmissibility, severity, and fatality. Chest radiography and computed tomography (CT) play a vital role in the diagnosis, detection of complications, and prognostication of COVID-19. Additionally, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), especially multi-nuclei MRI, is another important imaging technique for disease diagnosis because of its good soft tissue contrast and the ability to conduct structural and functional imaging, which has also been used to evaluate COVID-19-related organ injuries in previous studies. Herein, we briefly reviewed the recent research on multi-nuclei MRI for evaluating injuries caused by COVID-19 and the clinical H MRI techniques and their applications for assessing injuries in lungs, brain, and heart. Moreover, the emerging hyperpolarized Xe gas MRI and its applications in the evaluation of pulmonary structures and functional abnormalities caused by COVID-19 were also reviewed.© 2021 The Authors.
Noise in MRI
[J].This study analyzes the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in magnetic resonance imaging. The factors that determine the SNR are derived starting from basic principles. The SNR, for a given object, is shown to be proportional to the voxel volume and the square root of the acquisition time. The noise generated by the body is derived using a cylindrical model and is shown to be proportional to the square of the radius and the square root of the length.
A survey on the magnetic resonance image denoising methods
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.bspc.2013.10.007 URL [本文引用: 1]
MRI denoising using Non-Local Means
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.media.2008.02.004
PMID:18381247
[本文引用: 1]

Magnetic Resonance (MR) images are affected by random noise which limits the accuracy of any quantitative measurements from the data. In the present work, a recently proposed filter for random noise removal is analyzed and adapted to reduce this noise in MR magnitude images. This parametric filter, named Non-Local Means (NLM), is highly dependent on the setting of its parameters. The aim of this paper is to find the optimal parameter selection for MR magnitude image denoising. For this purpose, experiments have been conducted to find the optimum parameters for different noise levels. Besides, the filter has been adapted to fit with specific characteristics of the noise in MR image magnitude images (i.e. Rician noise). From the results over synthetic and real images we can conclude that this filter can be successfully used for automatic MR denoising.
New methods for MRI denoising based on sparseness and self-similarity
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.media.2011.04.003
PMID:21570894
[本文引用: 1]

This paper proposes two new methods for the three-dimensional denoising of magnetic resonance images that exploit the sparseness and self-similarity properties of the images. The proposed methods are based on a three-dimensional moving-window discrete cosine transform hard thresholding and a three-dimensional rotationally invariant version of the well-known nonlocal means filter. The proposed approaches were compared with related state-of-the-art methods and produced very competitive results. Both methods run in less than a minute, making them usable in most clinical and research settings.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Improved diffusion-weighted hyperpolarized 129Xe lung MRI with patch-based higher-order, singular value decomposition denoising
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.acra.2024.06.029 URL [本文引用: 1]
Magnetic resonance image denoising for Rician noise using a novel hybrid transformer-CNN network (HTC-net) and self-supervised pretraining
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mp.17562
PMID:39641989
[本文引用: 4]

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a crucial technique for both scientific research and clinical diagnosis. However, noise generated during MR data acquisition degrades image quality, particularly in hyperpolarized (HP) gas MRI. While deep learning (DL) methods have shown promise for MR image denoising, most of them fail to adequately utilize the long-range information which is important to improve denoising performance. Furthermore, the sample size of paired noisy and noise-free MR images also limits denoising performance.To develop an effective DL method that enhances denoising performance and reduces the requirement of paired MR images by utilizing the long-range information and pretraining.In this work, a hybrid Transformer-convolutional neural network (CNN) network (HTC-net) and a self-supervised pretraining strategy are proposed, which effectively enhance the denoising performance. In HTC-net, a CNN branch is exploited to extract the local features. Then a Transformer-CNN branch with two parallel encoders is designed to capture the long-range information. Within this branch, a residual fusion block (RFB) with a residual feature processing module and a feature fusion module is proposed to aggregate features at different resolutions extracted by two parallel encoders. After that, HTC-net exploits the comprehensive features from the CNN branch and the Transformer-CNN branch to accurately predict noise-free MR images through a reconstruction module. To further enhance the performance on limited MRI datasets, a self-supervised pretraining strategy is proposed. This strategy employs self-supervised denoising to equip the HTC-net with denoising capabilities during pretraining, and then the pre-trained parameters are transferred to facilitate subsequent supervised training.Experimental results on the pulmonary HP Xe MRI dataset (1059 images) and IXI dataset (5000 images) all demonstrate the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods, exhibiting superior preservation of edges and structures. Quantitatively, on the pulmonary HP Xe MRI dataset, the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by 0.254-0.597 dB in PSNR and 0.007-0.013 in SSIM. On the IXI dataset, the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by 0.3-0.927 dB in PSNR and 0.003-0.016 in SSIM.The proposed method can effectively enhance the quality of MR images, which helps improve the diagnosis accuracy in clinical.© 2024 American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Deep adaptive blending network for 3D magnetic resonance image denoising
[J].DOI:10.1109/JBHI.2021.3087407 URL [本文引用: 1]
HyperDense-Net: a hyper-densely connected CNN for multi-modal image segmentation
[J].DOI:10.1109/TMI.42 URL [本文引用: 1]
Beyond a gaussian denoiser: residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIP.83 URL [本文引用: 2]
MRI denoising with a non-blind deep complex-valued convolutional neural network
[J].DOI:10.1002/nbm.v38.1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Resolution enhancement processing on low quality images using swin transformer based on interval dense connection strategy
[J].DOI:10.1007/s11042-023-16088-0 [本文引用: 1]
A review of convolutional neural network architectures and their optimizations
[J].DOI:10.1007/s10462-022-10213-5 [本文引用: 1]
Boosting magnetic resonance image denoising with generative adversarial networks
[J].
Denoising of 3D magnetic resonance images with multi-channel residual learning of convolutional neural network
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s11604-018-0758-8
PMID:29982919
[本文引用: 1]

To test if the proposed deep learning based denoising method denoising convolutional neural networks (DnCNN) with residual learning and multi-channel strategy can denoise three dimensional MR images with Rician noise robustly.Multi-channel DnCNN (MCDnCNN) method with two training strategies was developed to denoise MR images with and without a specific noise level, respectively. To evaluate our method, three datasets from two public data sources of IXI dataset and Brainweb, including T1 weighted MR images acquired at 1.5 and 3 T as well as MR images simulated with a widely used MR simulator, were randomly selected and artificially added with different noise levels ranging from 1 to 15%. For comparison, four other state-of-the-art denoising methods were also tested using these datasets.In terms of the highest peak-signal-to-noise-ratio and global of structure similarity index, our proposed MCDnCNN model for a specific noise level showed the most robust denoising performance in all three datasets. Next to that, our general noise-applicable model also performed better than the rest four methods in two datasets. Furthermore, our training model showed good general applicability.Our proposed MCDnCNN model has been demonstrated to robustly denoise three dimensional MR images with Rician noise.
Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models
[C]//
Diffusion models in vision: a survey
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3261988 URL [本文引用: 2]
DiffCharge: Generating EV charging scenarios via a denoising diffusion model
[J].DOI:10.1109/TSG.2024.3360874 URL [本文引用: 1]
Convergent-diffusion denoising model for multi-scenario CT image reconstruction
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.compmedimag.2024.102491 URL [本文引用: 1]
PET image denoising based on denoising diffusion probabilistic model
[J].DOI:10.1007/s00259-023-06417-8 [本文引用: 1]
Study on the automatic accumulation-thawing device of hyperpolarized 129Xe
[J].
超极化 129Xe自动收集-升华装置研究
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20222998
[本文引用: 1]

因其较高的核自旋极化度所提供的探测灵敏度,超极化129Xe气体已被成功应用于动物和人体磁共振成像(MRI).但是,在超极化129Xe的收集-升华过程中,多种因素会导致129Xe核自旋弛豫,进而限制其应用范围.本文通过理论模型分析和实验测量,验证了温度、磁场、螺旋冷阱材质等对冷冻恢复过程中超极化129Xe弛豫的影响;同时,测量了自动收集-升华装置的稳定性.研究结果表明,升华方式和冷阱材质对129Xe极化度损耗的影响显著;自制收集-升华装置的自动化程度高、长时间稳定,129Xe极化度的恢复率可达到85.6% ± 4.7%.本研究非常有助于提升超极化129Xe在动物和人体MRI中的使用效率.
Association of 129Xe ventilation functional MRI with pulmonary lesion types
[J].
129Xe通气功能MRI与肺部病灶类型关联研究
[J].
DOI:10.11938/cjmr20243103
[本文引用: 1]

本研究旨在探索129Xe通气功能MRI与肺部病灶类型之间的关联.我们对143例患者进行129Xe通气功能MRI和肺部CT扫描,并分析了肺叶水平的通气功能与肺部病灶类型之间的关系.结果显示,大部分肺叶(74.6%)129Xe肺通气功能MRI和CT结果一致.通气功能损伤与CT病灶类型相关,且混合疾病和肺气肿/肺大疱更易引起肺通气功能障碍.此外,我们的研究显示不同肺部病灶类型会呈现出不同的通气模式.即129Xe通气功能MRI和肺部CT能够提供互补信息.本研究的初步结果将为肺部病灶引起的通气功能损伤评估提供数据支持,为临床影像学诊断提供更多的参考依据,有助于优化肺部疾病的诊断和治疗.
Complementation-reinforced network for integrated reconstruction and segmentation of pulmonary gas MRI with high acceleration
[J].
DOI:10.1002/mp.16591
PMID:37401205
[本文引用: 1]

Hyperpolarized (HP) gas MRI enables the clear visualization of lung structure and function. Clinically relevant biomarkers, such as ventilated defect percentage (VDP) derived from this modality can quantify lung ventilation function. However, long imaging time leads to image quality degradation and causes discomfort to the patients. Although accelerating MRI by undersampling k-space data is available, accurate reconstruction and segmentation of lung images are quite challenging at high acceleration factors.To simultaneously improve the performance of reconstruction and segmentation of pulmonary gas MRI at high acceleration factors by effectively utilizing the complementary information in different tasks.A complementation-reinforced network is proposed, which takes the undersampled images as input and outputs both the reconstructed images and the segmentation results of lung ventilation defects. The proposed network comprises a reconstruction branch and a segmentation branch. To effectively exploit the complementary information, several strategies are designed in the proposed network. Firstly, both branches adopt the encoder-decoder architecture, and their encoders are designed to share convolutional weights for facilitating knowledge transfer. Secondly, a designed feature-selecting block discriminately feeds shared features into decoders of both branches, which can adaptively pick suitable features for each task. Thirdly, the segmentation branch incorporates the lung mask obtained from the reconstructed images to enhance the accuracy of the segmentation results. Lastly, the proposed network is optimized by a tailored loss function that efficiently combines and balances these two tasks, in order to achieve mutual benefits.Experimental results on the pulmonary HP Xe MRI dataset (including 43 healthy subjects and 42 patients) show that the proposed network outperforms state-of-the-art methods at high acceleration factors (4, 5, and 6). The peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity (SSIM), and Dice score of the proposed network are enhanced to 30.89, 0.875, and 0.892, respectively. Additionally, the VDP obtained from the proposed network has good correlations with that obtained from fully sampled images (r = 0.984). At the highest acceleration factor of 6, the proposed network promotes PSNR, SSIM, and Dice score by 7.79%, 5.39%, and 9.52%, respectively, in comparison to the single-task models.The proposed method effectively enhances the reconstruction and segmentation performance at high acceleration factors up to 6. It facilitates fast and high-quality lung imaging and segmentation, and provides valuable support in the clinical diagnosis of lung diseases.© 2023 American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 URL [本文引用: 1]
Encoding enhanced complex CNN for accurate and highly accelerated MRI
[J].DOI:10.1109/TMI.2024.3351211 URL [本文引用: 1]
Impact of field number and beam angle on functional image-guided lung cancer radiotherapy planning
[J].
DOI:10.1088/1361-6560/aa8074
PMID:28800298
[本文引用: 1]

To investigate the effect of beam angles and field number on functionally-guided intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) normal lung avoidance treatment plans that incorporate hyperpolarised helium-3 magnetic resonance imaging (He MRI) ventilation data. Eight non-small cell lung cancer patients had pre-treatment He MRI that was registered to inspiration breath-hold radiotherapy planning computed tomography. IMRT plans that minimised the volume of total lung receiving ⩾20 Gy (V) were compared with plans that minimised He MRI defined functional lung receiving ⩾20 Gy (fV). Coplanar IMRT plans using 5-field manually optimised beam angles and 9-field equidistant plans were also evaluated. For each pair of plans, the Wilcoxon signed ranks test was used to compare fV and the percentage of planning target volume (PTV) receiving 90% of the prescription dose (PTV). Incorporation of He MRI led to median reductions in fV of 1.3% (range: 0.2-9.3%; p = 0.04) and 0.2% (range: 0 to 4.1%; p = 0.012) for 5- and 9-field arrangements, respectively. There was no clinically significant difference in target coverage. Functionally-guided IMRT plans incorporating hyperpolarised He MRI information can reduce the dose received by ventilated lung without comprising PTV coverage. The effect was greater for optimised beam angles rather than uniformly spaced fields.
Image super-resolution via iterative refinement
[J].