
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 20-32.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212912
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yan-yan LI1,Lv LI2,Xue-song LI1,*( ),Hua GUO2
),Hua GUO2
Received:2021-04-26
Published:2022-03-05
Online:2021-05-17
Contact:
Xue-song LI
E-mail:lixuesong@bit.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yan-yan LI,Lv LI,Xue-song LI,Hua GUO. 3D Dynamic MRI with Homotopic l0 Minimization Reconstruction[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 20-32.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
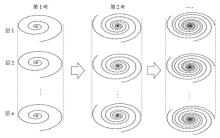
Fig.1
The acquisition strategy of stack of golden angle variable density spiral. The acquisition loop is in slice direction first. After spiral interleaves with a fixed angle being sampled in all the slices, in the time dimension, the next spiral interleaves which are rotated by a golden angle will be sampled

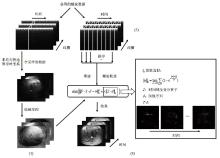
Fig.2
The reconstruction process of the proposed method with l0 minimization. In part (1), sensitivity maps are acquired from the full-sampled spiral data through time. In part (2), the acquired k-space data is sorted into several undersampled groups. In part (3), the sorted data is reconstructed to dynamic image series with the minimization problem in the middle. In the right black box, the approximation of l0 norm is expressed with a limitation, and the image series after the sparse transform (temporal total variation) are shown
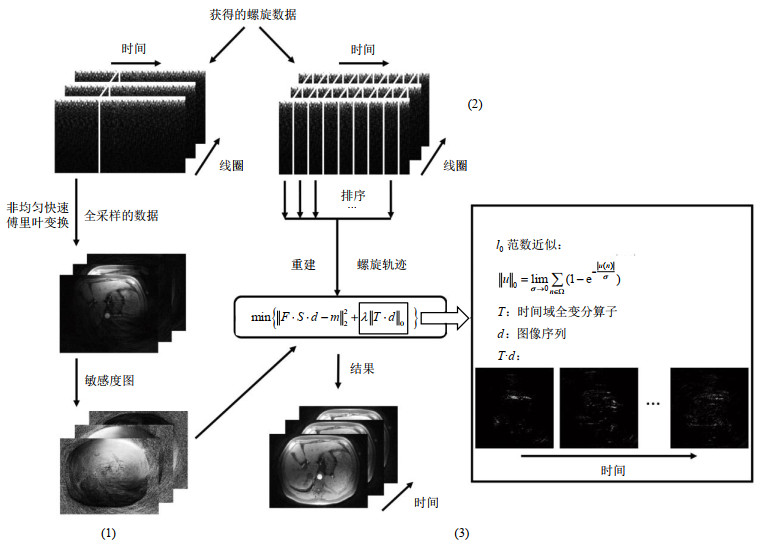
Table 1
Algorithm for homotopic l0 minimization
| 目标函数: |
| 输入:F –非均匀快速傅里叶变换算子 S –线圈敏感度图 m – k空间测量数据 |
| 输出:d –目标函数的数值近似解 |
| 初始化: |
| 迭代:while |
| while |
使用共轭梯度法求解 end |
| end |
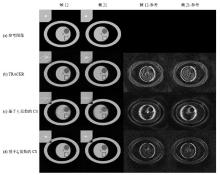
Fig.3
Reconstruction results of simulated image (Grouping 4 interleaves for 1 frame, corresponding to 48 interleaves of full sampled track, undersampling rate = 12) and their difference maps (7×) with reference. The four columns show frame 12, frame 21, the difference map of frame 12 and the difference map of frame 21, respectively. Figure (a) shows the reference images of the simulation phantom. Figures (b)~(d) show the reconstruction results using TRACER, CS with l1 minimization and l0 minimization respectively. The boxes indicate the regions of the detailed structure in the phantom, and the regions are zoomed in and placed on the top left side of each image

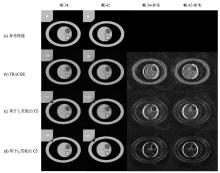
Fig.4
Reconstruction results of simulated image (Grouping 2 interleaves for 1 frame, corresponding to 48 interleaves of full sampled track, undersampling rate=24) and their difference maps (7×) with reference. The four columns show frame 24, frame 42, the difference map of frame 24 and the difference map (7×) of frame 42 respectively. Figure (a) shows the reference images of the simulation phantom. Figures (b)~(d) show the reconstruction results using TRACER, CS with l1 minimization and l0 minimization respectively. The boxes indicate the regions of the detailed structure in the phantom, and the regions are zoomed in and placed on the top left side of each image
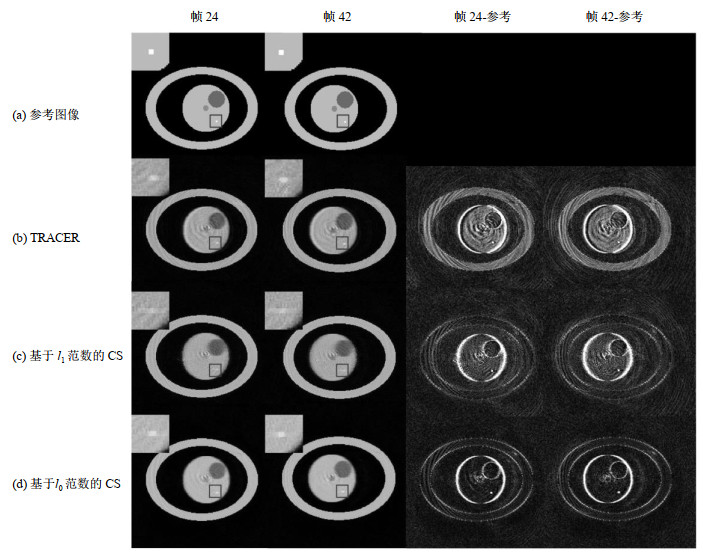
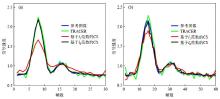
Fig.5
The simulated signal intensity curves in the small discs. These figures show the performance of different algorithms in a fixed undersampling rate (temporal resolution). (a) and (b) show the results with 12-fold undersampling rate and 24-fold undersampling rate respectively. The blue curve represents the reference of the signal intensity curve. The green, red, black curves represent the signal intensity curves resulting from TRACER, CS with l1 minimization and l0 minimization respectively
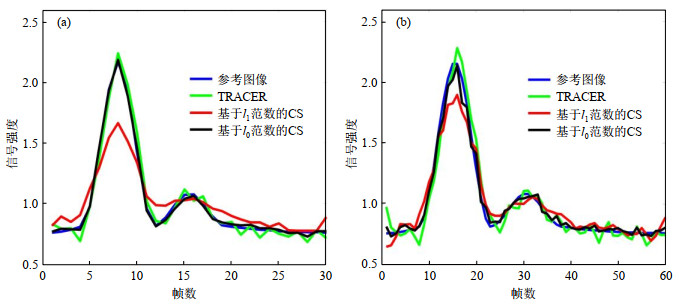
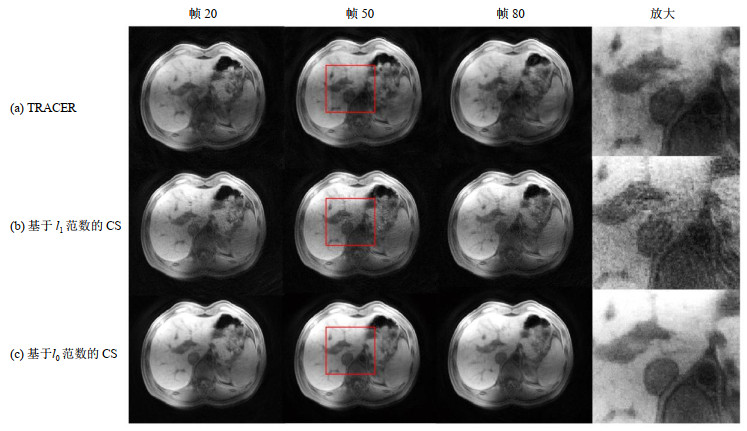
Fig.7
Reconstruction results of the non-contrast-enhanced liver image series (undersampling rate = 24). The first three columns show frame 20, frame 50, frame 80 and the fourth column shows the regions in the red boxes in frame 50 which are zoomed in. Rows (a), (b), (c) show the reconstruction results using TRACER, CS with l1 minimization and l0 minimization respectively
| 1 |
LIU J , SPINCEMAILLE P , CODELLA N C , et al. Respiratory and cardiac self-gated free-breathing cardiac CINE imaging with multiecho 3D hybrid radial SSFP acquisition[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2010, 63 (5): 1230- 1237.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.22306 |
| 2 |
OTAZO R . Combination of compressed sensing and parallel imaging for highly accelerated first-pass cardiac perfusion MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2010, 64 (3): 767- 776.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.22463 |
| 3 |
WRIGHT K L , CHEN Y , SAYBASILI H , et al. Quantitative high-resolution renal perfusion imaging using 3-dimensional through-time radial generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisition[J]. Invest Radiol, 2014, 49 (10): 666- 674.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000070 |
| 4 |
BO X , SPINCEMAILLE P , CHEN G , et al. Fast 3D contrast enhanced MRI of the liver using temporal resolution acceleration with constrained evolution reconstruction[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 69 (2): 370- 381.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24253 |
| 5 |
CHENG J Y , TAO Z , RUANGWATTANAPAISARN N , et al. Free-breathing pediatric MRI with nonrigid motion correction and acceleration[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2015, 42 (2): 407- 420.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.24785 |
| 6 |
FENG L , GRIMM R , BLOCK K T , et al. Golden-angle radial sparse parallel MRI: combination of compressed sensing, parallel imaging, and golden-angle radial sampling for fast and flexible dynamic volumetric MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2014, 72 (3): 707- 717.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24980 |
| 7 |
FENG L , AXEL L , CHANDARANA H , et al. XD-GRASP: Golden-angle radial MRI with reconstruction of extra motion-state dimensions using compressed sensing[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2016, 75 (2): 775- 788.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.25665 |
| 8 |
PRINCE M R , YUCEL E K , KAUFMAN J A , et al. Dynamic gadolinium-enhanced 3DFT abdominal MR arteriography[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 1993, 3 (6): 877- 881.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880030614 |
| 9 |
ROFSKY N M , LEE V S , LAUB G , et al. Abdominal MR imaging with a volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination[J]. Radiology, 1999, 212 (3): 876- 884.
doi: 10.1148/radiology.212.3.r99se34876 |
| 10 |
HAGIWARA M , RUSINEK H , LEE V S , et al. Advanced liver fibrosis: diagnosis with 3D whole-liver perfusion MR imaging-initial experience[J]. Radiology, 2008, 246 (3): 926- 934.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2463070077 |
| 11 |
LEE V S , LAVELLE M T , ROFSKY N M , et al. Hepatic MR imaging with a dynamic contrast-enhanced isotropic volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination: feasibility, reproducibility, and technical quality[J]. Radiology, 2000, 215 (2): 365- 372.
doi: 10.1148/radiology.215.2.r00ma16365 |
| 12 |
MATERNE R , SMITH A M , PEETERS F , et al. Assessment of hepatic perfusion parameters with dynamic MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2002, 47 (1): 135- 142.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.10045 |
| 13 | BAXTER S , ZHEN J W , JOE B N , et al. Timing bolus dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI assessment of hepatic perfusion: Initial experience[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2010, 29 (6): 1317- 1322. |
| 14 | HAIDER C R , HU H H , CAMPEAU N G , et al. 3D high temporal and spatial resolution contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the whole brain[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2010, 60 (3): 749- 760. |
| 15 |
PRUESSMANN K P , WEIGER M , SCHEIDEGGER M B , et al. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1999, 42 (5): 952- 962.
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199911)42:5<952::AID-MRM16>3.0.CO;2-S |
| 16 |
GRISWOLD M A , JAKOB P M , HEIDEMANN R M , et al. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA)[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2002, 47 (6): 1202- 1210.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.10171 |
| 17 |
TSAO J , BOESIGER P , PRUESSMANN K P . k-t BLAST and k-t SENSE: Dynamic MRI with high frame rate exploiting spatiotemporal correlations[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2003, 50 (5): 1031- 1042.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.10611 |
| 18 |
HUANG F , AKAO J , VIJAYAKUMAR S , et al. k-t GRAPPA: A k-space implementation for dynamic MRI with high reduction factor[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2005, 54 (5): 1172- 1184.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.20641 |
| 19 |
LUSTIG M , DONOHO D L , SANTOS J M , et al. Compressed sensing MRI[J]. IEEE Signal Proc Mag, 2008, 25 (2): 72- 82.
doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914728 |
| 20 |
LUSTIG M , DONOHO D L , PAULY J M . Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2007, 58 (6): 1182- 1195.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.21391 |
| 21 |
KIM Y C , NARAYANAN S S , NAYAK K S . Flexible retrospective selection of temporal resolution in real-time speech MRI using a golden-ratio spiral view order[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2011, 65 (5): 1365- 1371.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.22714 |
| 22 |
TRZASKO J , MANDUCA A . Highly undersampled magnetic resonance image reconstruction via homotopic l0-minimization[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2009, 28 (1): 106- 121.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2008.927346 |
| 23 |
WONG A , MISHRA A , FIEGUTH P , et al. Sparse reconstruction of breast MRI using homotopic l0 minimization in a regional sparsified domain[J]. IEEE T Biomed Eng, 2013, 60 (3): 743- 752.
doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2089456 |
| 24 |
MEYER C H , HU B S , NISHIMURA D G , et al. Fast spiral coronary artery imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1992, 28 (2): 202- 213.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910280204 |
| 25 | PRUESSMANN K P, WEIGER M, BORNERT P, et al. A gridding approach for sensitivity encoding with arbitrary trajectories[C]. In: Proc ISMRM 8th Annual Meeting, Denver, 2000, 276. |
| 26 |
WINKELMANN S , SCHAEFFTER T , KOEHLER T , et al. An optimal radial profile order based on the golden ratio for time-resolved MRI[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2007, 26 (1): 68- 76.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2006.885337 |
| 27 |
LIU Q G , WANG S S , YANG K , et al. Highly undersampled magnetic resonance image reconstruction using two-level Bregman method with dictionary updating[J]. IEEE T Med Imaging, 2013, 32 (7): 1290- 301.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2013.2256464 |
| 28 |
LIU Q G , WANG S S , YING L , et al. Adaptive dictionary learning in sparse gradient domain for image recovery[J]. IEEE T mage Procss, 2013, 22 (12): 4652- 4663.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2277798 |
| 29 |
ZHANG Z Y , QU X B , LIN Y Q , et al. A sparse reconstruction algorithm for NMR spectroscopy based on approximate l0 norm minimization[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2013, 30 (4): 528- 540.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4556.2013.04.006 |
|
张正炎, 屈小波, 林雁勤, 等. 基于近似l0范数最小化的NMR波谱稀疏重建算法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2013, 30 (4): 528- 540.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4556.2013.04.006 |
|
| 30 | HUBER P J. Robust Statistics[M]. Wiley-Interscience, 1981. |
| 31 | LI L , ZHOU Z C , YUAN C , et al. Imaging lenticulostriate arteries at 3 Tesla using optimized flow-sensitive black-blood technique[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2016, 33 (4): 528- 538. |
| 李律, 周赜辰, 苑纯, 等. 基于优化后流动敏感黑血序列的豆纹动脉3 T磁共振成像[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2016, 33 (4): 528- 538. | |
| 32 |
STONE S S , HALDAR J P , TSAO S C , et al. Accelerating advanced MRI Reconstructions on GPUs[J]. J Parallel Distr Com, 2008, 68 (10): 1307- 1318.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2008.05.013 |
| 33 | CHENG H T , WANG S S , KE Z W , et al. A deep recursive cascaded convolutional network for parallel MRI[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2019, 36 (4): 437- 445. |
| 程慧涛, 王珊珊, 柯子文, 等. 基于深度递归级联卷积神经网络的并行磁共振成像方法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2019, 36 (4): 437- 445. | |
| 34 | WANG W T , SU S , JIA S , et al. Reconstruction of simultaneous multi-slice MRI data by combining virtual conjugate coil technology and convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37 (4): 8- 22. |
| 王婉婷, 苏适, 贾森, 等. 基于虚拟线圈和卷积神经网络的多层同时激发图像重建[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37 (4): 8- 22. |
| [1] | LIU Ying, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Design of a Portable Magnetic Resonance Multi-source RF Pulse Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 285-298. |
| [2] | KOU Xinhui, ZHANG Yubing. Study on the Enantiomeric Recognition of Chiral Ureas Containing Amino Acid Units [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 221-230. |
| [3] | MA Yingxue, ZHAO Yanqiang, YANG Xiaodong, JIANG Bin, TAO Cheng. Opportunities and Challenges of High-field and Ultra-high-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 334-344. |
| [4] | JIANG Chaochao, YAO Shouquan, XU Juncheng, JIANG Yu. Design of the Broadband Magnetic Resonance Microcoil [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 299-307. |
| [5] | SHU Wei. Diagnostic Efficacy Comparison of B-scan Ultrasonography and MRI in Fetal Skeletal Abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 265-274. |
| [6] | SUI Meiju, ZHANG Lei, WANG Ruifang, LUO Yingying, LI Sha, QIU Maosong, XU Qiuyi, CHEN Daiqin, CHEN Shizhen, ZHOU Xin. MRI-traceable Nanoenzyme for Cascade Catalysis-enhanced Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 231-248. |
| [7] | LI Keyan, CHENG Xin, CHEN Junfei, CAO Li, HUANG Zhen, LIU Chaoyang. Development of Low-noise Preamplifier for Low-field NMR [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 321-333. |
| [8] | TANG Shihao, YANG Jinyu, XU Yajie, WANG Ya, PENG Bowen, GAO Yuhao, YANG Xiaodong. A Design of Circularly Polarized Coil for Low-field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometers [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 308-320. |
| [9] | HE Fengcheng, LI Mingdao, LV Xinglong, YAO Shouquan, JIANG Yu. Software Design of the Handheld NMR Spectrometer Console [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 0, (): 0-0. |
| [10] | . Structural Identification and Complete NMR Spectral Assignments of 4-Isopropoxy-1-(trifluoroacetyl)naphthalene [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 0, (): 0-0. |
| [11] | CAO Fei, XU Qianqian, CHEN Hao, ZU Jie, LI Xiaowen, TIAN Jin, BAO Lei. An Intelligent Diagnosis Method for NIID Based on Cross Self-supervision and DWI [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 154-163. |
| [12] | SUN Haoyun, WANG Lijia. Application of 3D ELD_MobileNetV2 Incorporating Attention Mechanism and Dilated Convolution in Hepatic Nodules Classification [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 130-142. |
| [13] | WEI Zhihong, KONG Xudong, KONG Yan, YAN Shiju, DING Yang, WEI Xianding, KONG Dong, YANG Bo. Application of Generative Adversarial Networks Based on Global and Local Feature Information in Hippocampus Segmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 143-153. |
| [14] | CHEN Bo, LIU Quan, MA Lei, CHEN Shunian, JIA Yaqi, ZHU Bin, GUO Junwang. Simulink-based Simulation Study of Continuous Wave Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Signal Processing and Detection [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 174-183. |
| [15] | GU Jiajia, WANG Yuanjun. Hybrid Attention and Multiscale Module for Alzheimer's Disease Classification [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 103-116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||