
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2023, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 410-422.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20233053
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
REN Hongjin,MA Yan,XIAO Liang*( )
)
Received:2023-01-15
Published:2023-12-05
Online:2023-06-25
CLC Number:
REN Hongjin, MA Yan, XIAO Liang. Knee Joint Model Construction and Local Specific Absorption Rate Estimation Based on Generative Adversarial Networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 410-422.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
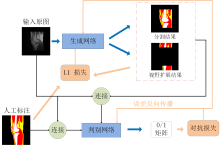
Fig. 2
The architecture of the proposed CGAN. The countermeasure loss is calculated according to the 0/1 matrix of the output of the discriminator network. The error is propagated back to the generator network and the discriminator network, and the L1 loss is calculated by using the artificially labeled image and the generating result of the generator network, transmitting back to the generator network, and the network parameters are continuously adjusted according to the gradient descent principle
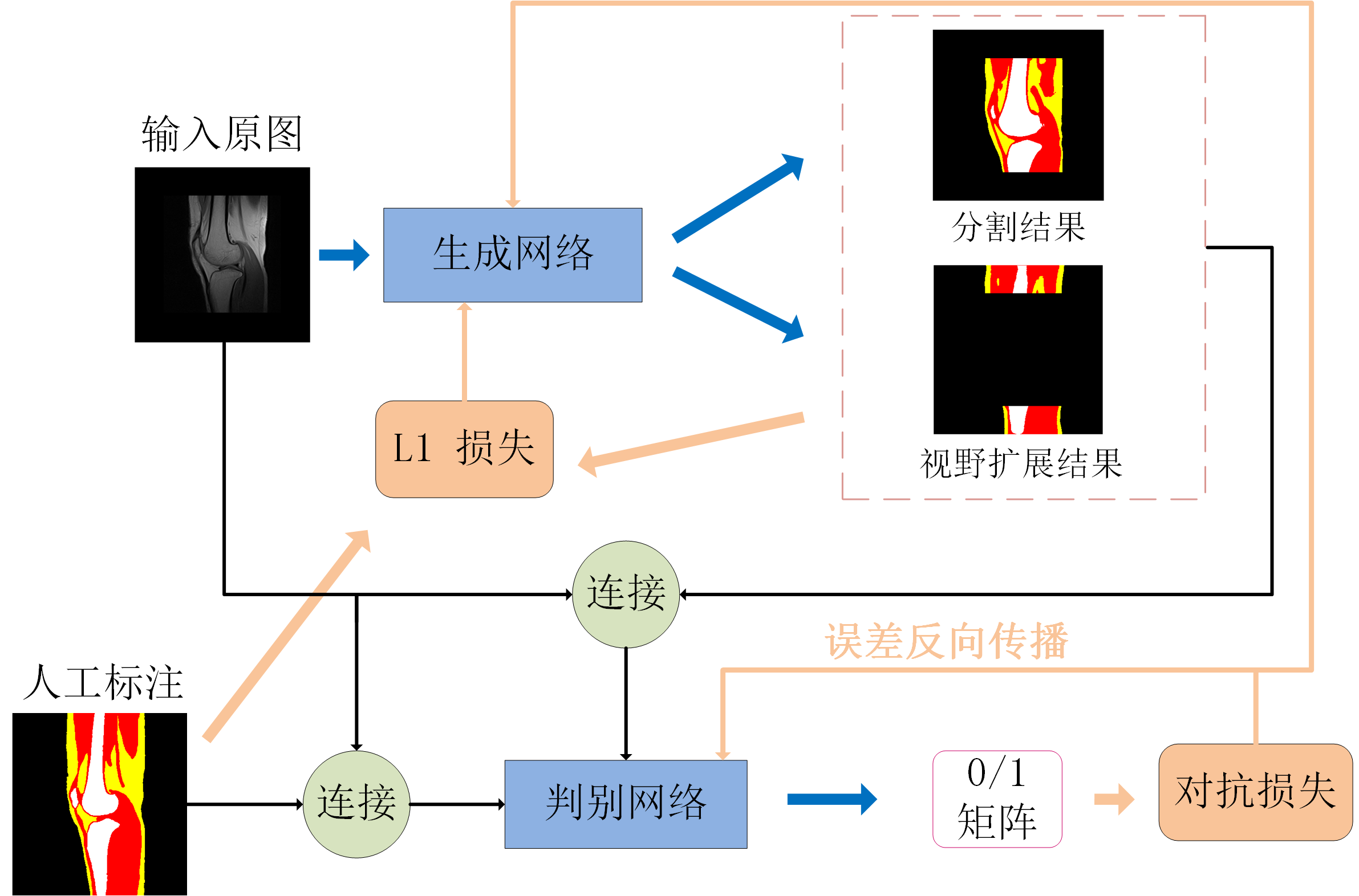

Fig. 4
The attention modules used in generator network. The attention coefficient matrix α is calculated by using the decoded partial characteristic graph dl and the coded partial characteristic graph el-1 as the input, el-1 multiplies the attention coefficient matrix α pixel by pixel to select the focus region
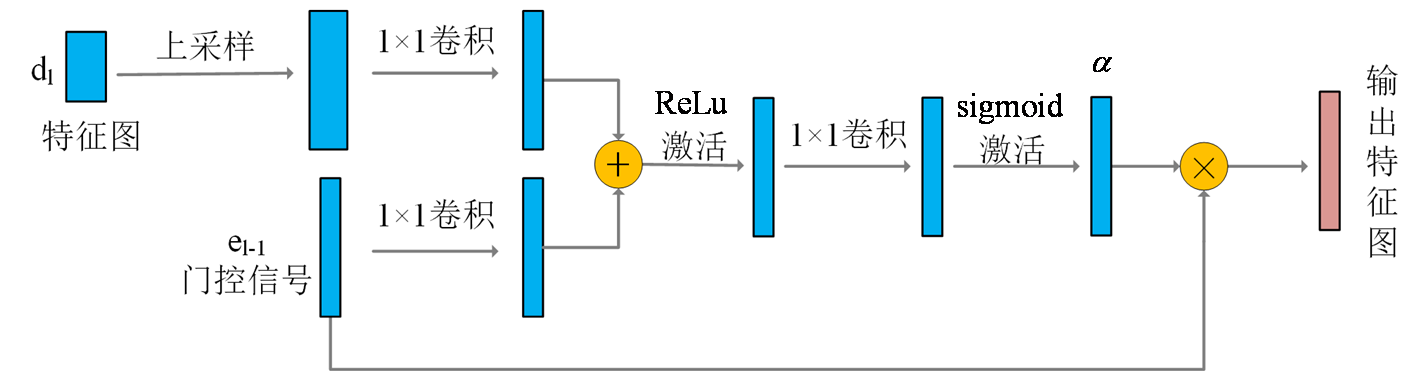
Table 1
Evaluation indexes of the segmentation results of various methods (the proposed method, U-Net, Attention U-Net compared with the manual labeling results)
| 分割方法 | 评价指标 | 肌肉 | 脂肪 | 骨骼 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 所提方法 | DCC | 0.8798 | 0.9135 | 0.9022 |
| TPR | 0.8915 | 0.9198 | 0.9114 | |
| U-Net | DCC | 0.8472 | 0.9040 | 0.9006 |
| TPR | 0.8841 | 0.8785 | 0.8921 | |
| Attention U-Net | DCC | 0.8578 | 0.9022 | 0.9058 |
| TPR | 0.9059 | 0.8611 | 0.8991 |
| [1] | LIU X, XU H W, JIANG T, et al. MRI and 18F-FDG PET/CT findings of a giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath of the knee joint (pigmented villonodular synovitis): a case report and literature review[J]. Hell J Nucl Med, 2021, 24(2): 149-154. |
| [2] | YANG W H. The development of ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Physics, 2019, 48(4): 227-236. |
| 杨文晖. 磁共振成像发展与超高场磁共振成像技术[J]. 物理, 2019, 48(4): 227-236. | |
| [3] | WANG Y S, DENG A Q, MAO J L, et al. Automatic segmentation of knee joint synovial magnetic resonance images based on 3D VNetTrans[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(3): 303-315. |
| 王颖珊, 邓奥琦, 毛瑾玲, 等. 基于3D VNetTrans的膝关节滑膜磁共振图像自动分割[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(3): 303-315. | |
| [4] |
PADORMO F, BEQIRI A, HAJNAL J V, et al. Parallel transmission for ultrahigh-field imaging[J]. NMR Biomed, 2016, 29(9): 1145-1161.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.3313 pmid: 25989904 |
| [5] |
YETISIR F, ABACI TURK E, GUERIN B, et al. Safety and imaging performance of two-channel RF shimming for fetal MRI at 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 86(5): 2810-2821.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.28895 |
| [6] | ZENG Q, GUO R, ZHENG J, et al. Impacts of RF shimming on local SAR caused by MRI 3 T birdcage coil near femoral plate implants[C]// IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA: IEEE, 2017: 1005-1006. |
| [7] | GAGLIARDI V, RETICO A, BIAGI L, et al. Subject-specific knee SAR prediction using a degenerate birdcage at 7 T[C]// IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Rome, Italy: IEEE, 2018: 1-5. |
| [8] |
LIU W, WANG H, ZHANG P, et al. Statistical evaluation of radiofrequency exposure during magnetic resonant imaging: Application of whole-body individual human model and body motion in the coil[J]. Int J Env Res Pub He, 2019, 16(6): 1069.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph16061069 |
| [9] |
STEENSMA B R, MELIADÒ E F, LUIJTEN P, et al. SAR and temperature distributions in a database of realistic human models for 7 T cardiac imaging[J]. NMR Biomed, 2021, 34(7): e4525.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.4525 pmid: 33955061 |
| [10] |
CARLUCCIO G, AKGUN C, VAUGHAN J T, et al. Temperature-based MRI safety simulations with a limited number of tissues[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 86(1): 543-550.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.28693 pmid: 33547673 |
| [11] |
VAN DEN BERGEN B, VAN DEN BERG C A, BARTELS L W, et al. 7 T body MRI: B-1 shimming with simultaneous SAR reduction[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2007, 52(17): 5429.
doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/52/17/022 |
| [12] |
DE BUCK M H, JEZZARD P, JEONG H, et al. An investigation into the minimum number of tissue groups required for 7 T in-silico parallel transmit electromagnetic safety simulations in the human head[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(2): 1114-1122.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.v85.2 |
| [13] |
WOLF S, DIEHL D, GEBHARDT M, et al. SAR simulations for high-field MRI: how much detail, effort, and accuracy is needed?[J] Magn Reson Med, 2013, 69(4): 1157-1168.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24329 pmid: 22611018 |
| [14] |
SENGAR S S, MEULENGRACHT C, BOESEN M P, et al. Multi-planar 3D knee MRI segmentation via UNet inspired architectures[J]. Int J Imag Syst Tech, 2023, 33(3): 985-998.
doi: 10.1002/ima.v33.3 |
| [15] |
GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J]. Commun Acm, 2020, 63(11): 139-144.
doi: 10.1145/3422622 |
| [16] | CHANG X, CAI X, YANG G, et al. Applications of generative adversarial networks in medical image processing[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(3): 366-380. |
| 常晓, 蔡昕, 杨光, 等. 生成对抗网络在医学图像转换领域的应用[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(3): 366-380. | |
| [17] | CHEN Y, SHI F, CHRISTODOULOU A G, et al. Efficient and accurate MRI super-resolution using a generative adversarial network and 3D multi-level densely connected network[C]// Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2018: 21st International Conference, Granada, Spain:Springer, 2018: 91-99. |
| [18] |
KANG E, KOO H J, YANG D H, et al. Cycle-consistent adversarial denoising network for multiphase coronary CT angiography[J]. Med Phys, 2019, 46(2): 550-562.
doi: 10.1002/mp.13284 pmid: 30449055 |
| [19] | LAHIRI A, AYUSH K, KUMAR BISWAS P, et al. Generative adversarial learning for reducing manual annotation in semantic segmentation on large scale miscroscopy images: Automated vessel segmentation in retinal fundus image as test case[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017: 42-48. |
| [20] |
GAJ S, YANG M, NAKAMURA K, et al. Automated cartilage and meniscus segmentation of knee MRI with conditional generative adversarial networks[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2020, 84(1): 437-449.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.28111 pmid: 31793071 |
| [21] | ZHANG L, GOOYA A, FRANGI A F. Semi-supervised assessment of incomplete LV coverage in cardiac MRI using generative adversarial nets[C]// International Workshop on Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging. Cham: Springer, 2017: 61-68. |
| [22] | MIRZA M, OSINDERO S. Conditional generative adversarial nets[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.1784, 2014. |
| [23] | MA Y, XING C J, XIAO L. Knee joint image segmentation and model construction based on cascaded network[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2022, 39(2): 184-195. |
| 马岩, 邢藏菊, 肖亮. 基于级联网络的膝关节图像分割与模型构建[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2022, 39(2): 184-195. | |
| [24] | SCHLEMPER J, OKTAY O, SCHAAP M, et al. Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images[J]. Med Image Anal, 2019, 53197-207. |
| [25] |
LEE J, GEBHARDT M, WALD L L, et al. Local SAR in parallel transmission pulse design[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2012, 67(6): 1566-1578.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.23140 pmid: 22083594 |
| [26] |
MILSHTEYN E, GURYEV G, TORRADO-CARVAJAL A, et al. Individualized SAR calculations using computer vision-based MR segmentation and a fast electromagnetic solver[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2021, 85(1): 429-443
doi: 10.1002/mrm.v85.1 |
| [27] |
HARDY B M, BANIK R, YAN X Q, et al. Bench to bore ramifications of inter-subject head differences on RF shimming and specific absorption rates at 7 T[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2022, 92: 187-196.
doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2022.07.009 |
| [28] |
CHRIST A, KAINZ W, HAHN E G, et al. The Virtual Family—development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2009, 55(2): N23.
doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/2/N01 |
| [1] | MA Yingxue, ZHAO Yanqiang, YANG Xiaodong, JIANG Bin, TAO Cheng. Opportunities and Challenges of High-field and Ultra-high-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 334-344. |
| [2] | SHU Wei. Diagnostic Efficacy Comparison of B-scan Ultrasonography and MRI in Fetal Skeletal Abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 265-274. |
| [3] | SUI Meiju, ZHANG Lei, WANG Ruifang, LUO Yingying, LI Sha, QIU Maosong, XU Qiuyi, CHEN Daiqin, CHEN Shizhen, ZHOU Xin. MRI-traceable Nanoenzyme for Cascade Catalysis-enhanced Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 231-248. |
| [4] | MENG Jingxin, WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress on Tractography of Superficial White Matter Based on Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 205-220. |
| [5] | CHEN Qun, YANG Zijian, CHENG Xinyi, JIA Siyi, DU Xiaoxia, WANG Mengxing. Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technology in Pediatric Exercise Intervention Research [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 195-204. |
| [6] | ZUO Bingyu, SHI Lili, SONG Jia, ZHAO Yang, LI Qian. Application of Estrogen and Tumor Markers Combined with DCE-MRI in Diagnosis and Clinical Staging of Cervical Cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 164-173. |
| [7] | YANG Jiacheng, WANG Yuanjun. Improved Constrained Spherical Deconvolution for Microstructural Imaging of Brain Gray Matter [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 67-79. |
| [8] | PANG Qifan, WANG Zhichao, WU Yupeng, LI Jianqi. The Impact of K-Space Filling Strategy on Fat Artifacts in APT Imaging Based on FLASH Sequence [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 443-453. |
| [9] | HUANG Min, ZHU Junlin, KAO Yuchen, ZHOU Dao, TANG Qiling. Multi-Coil MRI Image Reconstruction Based on ISTAVS-Net of Physical Model [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 418-429. |
| [10] | Dai Junlong, He Cong, Wu Jie, Bian Yun. Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms Segmentation Network Combining Dual Decoding and Global Attention Upsampling Modules [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 151-161. |
| [11] | CHANG Bo, SUN Haoyun, GAO Qingyu, WANG Lijia. Research Progress on Cardiac Segmentation in Different Modal Medical Images by Traditional Methods and Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 224-244. |
| [12] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [13] | LIU Ying, LIN Ling, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Research Progress of MRI Gradient Waveform Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 99-115. |
| [14] | ZHOU Tianli, ZHANG Dian, WU Jizhi, JIA Huihui, CHANG Yan, SHENG Mao, YANG Xiaodong. Application of MRI-based Finite Element Modeling and Analysis in Periacetabular Osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 397-409. |
| [15] | CHEN Mengying, WU Yupeng, PANG Qifan, ZHONG Haodong, LI Gaiying, LI Jianqi. Simultaneously Neuromelanin-sensitive Imaging and Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping in the Whole Brain [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 385-396. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||