
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2025, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 205-220.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20243126cstr: 32225.14.cjmr20243126
• Review Article • Previous Articles
Received:2024-08-06
Published:2025-06-05
Online:2024-10-21
Contact:
*Tel: 13761603606, E-mail: CLC Number:
MENG Jingxin, WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress on Tractography of Superficial White Matter Based on Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 205-220.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
SWM fiber tract segmentation method studies
| 第一作者 | 研究区域 | 分割方法 | 主要连接和发现 | 定量评价 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分割数量 | 准确率% | ||||
| Catani[ | 枕叶、颞叶 | ROI/手动选择 | 枕颞外侧区相邻回的下纵束 | 1 | / |
| Wu[ | 颞叶、顶叶、枕叶 | ROI/手动选择 | 上纵束后段连接颞中回和颞下回的后部与角回和缘上回;垂直枕束连接下顶叶、颞叶和枕叶;新的颞顶叶连接,将颞下回、颞中回、枕颞外侧回以及枕叶下部与顶叶上部互连 | 3 | / |
| Wakana[ | 全脑 | ROI/手动选择 | 上纵束的一部分;枕叶束 | 2 | / |
| Catani[ | 额叶、中央沟、中央前沟、岛沟、额缘沟 | ROI/手动选择 | PrCG-PoCG,PrCG-MFG,SFG-IFG,SFG-MFG,FOP,FMT,FSL,FIL,Ins-Or/Tr/Op/PrCG/SuCG | 13 | / |
| Rojkova[ | 额叶 | ROI/手动选择 | 连接中央前回和中央后回的U型纤维;额叶斜束;连接额叶和岛叶的五个U型纤维;额叶上纵束和下纵束;额哐束和额边缘束 | 30 | / |
| Burks[ | 顶下小叶 | ROI/手动选择 | 连接缘上回和角回的U型纤维;连接颞上沟边缘正下方和颞叶的U型纤维;连接侧裂末端和额叶的U型纤维 | 3 | / |
| Catani[ | 顶叶 | ROI/手动选择 | SMG-SPL,AG-SPL,PoCG-AG,PoCG-SMG,PoCG-SPL,AG-SMG,SMG-SMG,aPrCu-pPrCu,SPL的前后连接和内外侧连接 | 9 | / |
| Shinohara[ | 全脑 | ROI/手动选择 | 脑回内和脑回间U型纤维从各个方向汇聚到白质脊的交界处,构成了“金字塔形交叉” | / | / |
| Oishi[ | 全脑 | ROI/自动选择 | SFG-IFG,MFG-PrCG,PrCG-PoCG,psaf | 4 | / |
| Zhang[ | 全脑 | ROI/自动选择 | SFG-IFG,MFG-PrCG,PrCG-PoCG,SPG-SMG,SPG-PoCG,SPG-AG,SPG-PrCu,SPG-SOG,SPG-MOG,CG-SFG,CG-PrCu,SFG-MFG,SFG-PrCG,MFG-IFG,IFG-PrCG,PoCG-SMG,AG-MOG,AG-SMG,Cu-LG,Cu-SOG,Cu-MOG,FuG-IOG,FuG-MOG,SOG-MOG,IOG-MOG,STG-MTG,STG-SMG,ITG-MTG,LFOG-MFOG | 29 | / |
| Pardo[ | 全脑 | ROI/自动选择 | 研究其SWM束的变异性 | 80 | / |
| Ouyang[ | 全脑 | ROI/自动选择 | 没有特定的束,短关联纤维根据它们连接的两个相邻回进行分组 | / | / |
| Movahedian[ | 初级和次级视觉皮层区域 | ROI/自动选择 | 初级和次级视觉皮层区域的短关联纤维束连接 | / | / |
| Vergani[ | 辅助运动区 | ROI/半自动选择 | SMA-PrCG,SMA-CG | 2 | / |
| Magro[ | 中央前回和中央后回 | ROI/半自动选择 | 中央前回和中央后回9条纤维束 | 9 | / |
| Guevara[ | 全脑 | 流线标记/几何距离 | 在中央沟和颞上沟发现了不同人群的纤维组织的变异性 | / | / |
| Vindas[ | 全脑 | 流线标记/几何距离 | 所提出的方法在两个数据集中都发现了更多的SWM纤维束 | / | / |
| Zhang[ | 中央沟、中央前沟、中央后沟、颞上沟、额下沟和顶内沟 | 流线标记/聚类 | 三种数据类型共有:SFG-MFG,MFG-IFG,PrCG-PoCG,SPG-IFG,PoCG-SPG;DSI:MFG-IPL,SFG-IPL,MFG-SMG,IFG-MTG,PoCG-IPL,SPG-SMG,SMG-MTG,MTG-ITG,IPL-MOG,SFG-SPG,MFG-MTG,IFG-SPG,PrCG-SPG,SPG-IPL,SPG-SOG,SPG-MTG,STG-MTG; HARDI:SPG-SMG,MFG-MTG,SFG-IFG,SOG-MOG,MFG-PrCG,PoCG-SMG,SPG-MTG,STG-MTG,SPG-IPL,SMG-PrCG,IPL-SMG,IPL-MTG; DTI:SFG-IFG,MFG-PrCG,IFG-PrCG,SMG-MTG,PrCG-SPG,SFG-PrCG,SFG-PoCG,SFG-SPG,PrCG-MTG,SPG-SOG,IPL-MTG,IFG-STG,PoCG-IPL,PrCG-IPL,PoCG-IPL,IPL-MOG,SMG-MOG,STG-SMG | / | / |
| Guevara[ | 全脑 | 流线标记/聚类 | 左半球与右半球一致:SFG-IFG(ant,mid,post),SFG-MFG(ant,mid,post),MFG-IFG,MFG(mid,mid2,post,post2),IFG-Ins,IFG(post,inf),LFOG(inf,sup),MFOG,MFOG-CG,SFG-CG(mid),MFG-PrCG(sup,mid),PrCG-PoCG(sup,inf),PrCG-Ins,PrCG-SMG,PaCG-PrCu,PoCG-SMG,SMG,SPG,AG(sup,inf),STG-AG,MTG-AG,STG(post),MTG-Ins,STG-Ins,ITG-MOG,Cu,Cu-Li,LG,FuG(ant,mid,post),PrCu-CG,PrCu-SFG,CG(ant,mid,post) | 94 | / |
| Román[ | 全脑 | 流线标记/聚类 | 两半球共有:SPL_SPL_0i,PrCG_SFG_0i,PoCG_PrCG_0-3i,Op_SFG_0i,CMFG_PrCG_0-1i,MTG_MTG_0-1i,PrCG_SMG_0-1i,CMFG_CMFG_0i,FuG_ITG_0i,IPL_SPL_0i,MTG_STG_0i,LorFG_LorFG_0i,CMFG_Op_0i,RMFG_SFG_0-1i,Tr_SFG_0i,SMG_SMG_0-2i,RMFG_RMFG_0-1i,PoCG_SMG_0i,FuG_FuG_0i,STG_STG_0i,Tr_RMFG_0i,LOG_LOG_0-1i, 左半球:ITG_ITG_0-1l,SFG_SFG_0l,FuG_FuG_1l,PrCG_PrCG_0l,STG_STG_1l,Cu_LG_0l,PrCu_PrCu_0l,MTG_MTG_1l,LOG_LOG_2l,PrCG_Ins_0l 右半球:Tr_Tr_0r,Tr_Ins_0r,MTG_MTG_0r,SFG_SFG_1-2r,RMFG_SFG_0r,RMFG_RMFG_0-1r,PoCG_PoCG_1r,PoCG_PrCG_1r,SPL_SPL_0r,PrCu_PrCu_0r,IPL_LOG_0r,IPL_IPL_0r,LoFG_LoFG_1r,Tr_SFG_1r | 左:44; 右:49 | / |
| Zhang[ | 全脑 | 流线标记/聚类 | 198短纤维簇连接:颞叶、顶叶-颞叶、顶叶-枕叶、顶叶、枕颞叶、枕叶、额叶-顶叶和额叶区域 | 198 | / |
| Pron[ | 中央沟 | 流线标记/聚类 | 左半球五条U型纤维连接中央前回和中央后回 | 左:5 | / |
| Pron[ | 中央沟 | 流线标记/聚类 | 左右半球各有五条U型纤维连接中央前回和中央后回 | 左:5;右:5 | / |
| Zhang[ | 全脑 | 流线标记/深度 学习 | 198短纤维簇连接:颞叶、顶叶-颞叶、顶叶-枕叶、顶叶、枕颞叶、枕叶、额叶-顶叶和额叶区域 | 198 | 98.42 |
| Xue[ | 全脑 | 流线标记/深度 学习 | 198短纤维簇连接:颞叶、顶叶-颞叶、顶叶-枕叶、顶叶、枕颞叶、枕叶、额叶-顶叶和额叶区域 | 198 | 96.79 |
| Guevara[ | 全脑 | ROI选择和聚 类相结合 | 两半球共有:CACG-PrCu_0,CMFG-PrCG_0-1,CMFG-RMFG_0,CMFG-SFG_0,IC-PrCu_0,IPL-ITG_0,IPL-MTG_0,IPL-SMG_0,IPL-SPL_0,LOFG-RMFG_0-1,LOFG-STG_0,MOFG-STG_0,MTG-SMG_0,MTG-STG_0,Op-Ins_0,Op-PrCG_0,Op-SFG_0,Or-Ins_0,PoCiG-PrCu_1,PoCiG-RACG_0,PoCG-PrCG_0-2,PoCG-SMG_0,PrCG-Ins_0,PrCG-SMG_0,RMFG-SFG_0-1,SMG-Ins_0,SPL-SMG_0,STG-TTG_0,Tr-Ins_0,Tr-SFG_0 左半球:CMFG-Op_0,CMFG-PoCG_0,Fu-LOG_0,IPL-LOG_1,IPL-SPL_1,ITG-MTG_0,LOFG-Or_0,PoCG-Ins_0,PoCiG-PrCu_0,PoCiG-SFG_0,PoCG-PrCG_3,PoCG-SMG_1,PrCG-SFG_0,RACG-SFG_1,STG-Ins_0 右半球:CACG-PoCiG_0,CMFG-SFG_1,Cu-LG_0,Fu-LOG_1,IPL-LOG_0,ITG-MTG_1-2,LOFG-MOFG_0,LOG-SPL_0,Op-Tr_0,PoCiG-PrCu_2,PoCG-SPL_0,PrCG-SPL_0,RACG-SFG_0 | 100 | / |
| Román[ | 全脑 | ROI选择和聚 类相结合 | 图谱由整个大脑的525束短关联纤维组成,其中384束连接不同ROI部分,141束连接相同ROI部分 | 525 | / |
Fig. 3
SWM fiber tract atlas construction process. (a) Preprocessing: denoising and removal of Gibbs ring artifacts, head motion correction and eddy current correction, bias field correction, alignment to standard space; (b) whole brain tractography: deterministic tractography algorithm or probabilistic tractography algorithm; (c) whole brain fiber tract filtering: fiber tract length filtering, fiber tract smoothing filtering, DWM tract filtering; (d) SWM fiber tract clustering: SWM fiber tract clustering using different clustering methods, labeling by different cortical partitions; (e) SWM fiber tract atlas
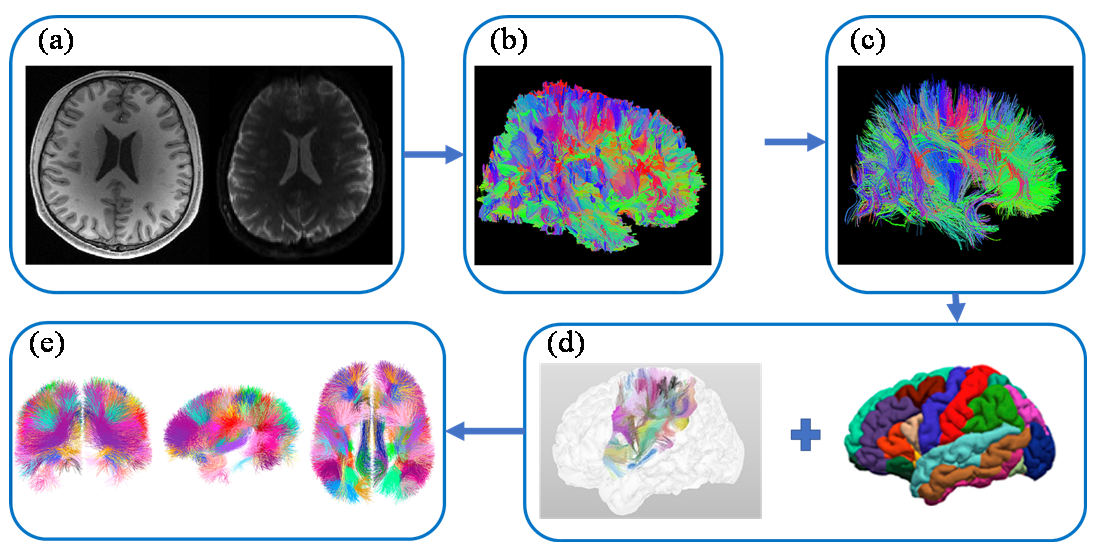
Table 2
Comparison of SWM fiber tract atlas construction methods
| 第一作者 | 图谱构成 | 构建数据 | 测试数据 | 纤维束追踪方法 | 概率性/确定性追踪 | 构建方法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guevara[ | 36个DWM束,94个SWM束 | 12 NMR | 20 HARDI | Q-ball+正则化 粒子轨迹 | 确定性 | 层次聚类 |
| Román[ | 93个SWM束 | 74 CONNECT/Archi | 78 HARDI | Q-ball+正则化 粒子轨迹 | 确定性 | 层次聚类 |
| Zhang[ | 58 DWM束,198个SWM束 | 100名健康受试者 | 584名患有多 种健康状况的 受试者 | 双张量无迹 卡尔曼滤波 | 确定性 | 谱聚类 |
| Guevara[ | 100个SWM束 | 79 CONNECT/Archi | 26 HARDI | Q-ball+正则化 粒子轨迹 | 确定性 | 自动ROI选择+层次聚类 |
| Román[ | 525个SWM束 | 100 HCP | 79 HARDI | CSD+iFOD2 | 概率性 | 自动ROI选择+FFClust聚类+层次聚类 |
Table A1
Chinese and English full names for corresponding abbreviations
| 缩写 | 英文全称 | 中文全称 |
|---|---|---|
| PrCG | precentral gyrus | 中央前回 |
| PoCG | postcentral gyrus | 中央后回 |
| SFG | superior frontal gyrus | 额上回 |
| MFG | middle frontal gyrus | 额中回 |
| IFG | inferior frontal gyrus | 额下回 |
| FOP | fronto-orbitopolar tract | 额眶极束 |
| FMT | fronto-marginal tract | 额叶边缘束 |
| FSL | frontal superior longitudinal tract | 额叶上纵束 |
| FIL | frontal inferior longitudinal tract | 额叶下纵束 |
| Ins | insular | 脑岛 |
| Or | orbital | 眶部 |
| Tr | triangular | 三角部 |
| Op | opercular | 岛盖部 |
| SuCG | sub-central gyrus | 亚中央回 |
| SMG | supramarginal gyrus | 缘上回 |
| SPL | superior parietal lobule | 顶上小叶 |
| IPL | inferior parietal lobule | 顶下小叶 |
| AG | angular gyrus | 角回 |
| PrCu | precuneus | 楔前叶 |
| psaf | parietal short association fibers | 顶叶短关联纤维 |
| SPG | superior parietal gyrus | 顶上回 |
| SOG | superior occipital gyrus | 枕上回 |
| MOG | medial occipital gyrus | 枕中回 |
| CG | cingulate gyrus | 扣带回 |
| SFG | superior frontal gyrus | 额上回 |
| MFG | medial frontal gyrus | 额中回 |
| IFG | inferior frontal gyrus | 额下回 |
| Cu | cuneus | 楔叶 |
| LG | lingual gyrus | 舌回 |
| FuG | fusigorm gyrus | 枕颞外侧回 |
| IOG | inferior occipital gyrus | 枕下回 |
| STG | superior temporal gyrus | 颞上回 |
| MTG | middle temporal gyrus | 颞中回 |
| ITG | inferior temporal gyrus | 额下回 |
| LFOG | lateral fronto-orbital gyrus | 内侧眶额回 |
| MFOG | medial fronto-orbital gyrus | 外侧眶额回 |
| SMA | supplementary motor area | 辅助运动区 |
| CMFG | caudal middle frontal gyrus | 额中回尾部 |
| LoFG | lateral orbito frontal gyrus | 额眶外侧回 |
| RMFG | rostral middle frontal gyrus | 额中回头部 |
| LOG | lateral occipital gyrus | 枕外侧回 |
| CACG | caudal anterior cingulate gyrus | 尾侧前扣带回 |
| IC | isthmus cingulate | 扣带峡部 |
| MOFG | medial orbito frontal gyrus | 额眶内侧回 |
| RACG | rostal anterior cingulate gyrus | 前扣带回头部 |
| PoCiG | posterior cingulate gyrus | 后扣带回 |
| TTG | transverse temporal gyrus | 颞横回 |
| [1] |
VERGANI F, MAHMOOD S, MORRIS C M, et al. Intralobar fibres of the occipital lobe: a post mortem dissection study[J]. Cortex, 2014, 56: 145-156.
doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2014.03.002 pmid: 24768339 |
| [2] | REVELEY C, SETH A K, PIERPAOLI C, et al. Superficial white matter fiber systems impede detection of long-range cortical connections in diffusion MR tractography[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2015, 112(21): E2820-E2828. |
| [3] | VAN DYKEN P C, KHAN A R, PALANIYAPPAN L. Imaging of the superficial white matter in health and disease[J]. Imaging Neurosci, 2024, 2: 1-35. |
| [4] | KIRILINA E, HELBLING S, MORAWSKI M, et al. Superficial white matter imaging: Contrast mechanisms and whole-brain in vivo mapping[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(41): eaaz9281. |
| [5] |
ZHU Y, WANG Y. Brain fiber structure estimation based on principal component analysis and RINLM filter[J]. Med Biol Eng Comput, 2024, 62(3): 751-771.
doi: 10.1007/s11517-023-02972-2 pmid: 37996628 |
| [6] | CONTURO T E, LORI N F, CULL T S, et al. Tracking neuronal fiber pathways in the living human brain[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 1999, 96(18): 10422-10427. |
| [7] | CATANI M, JONES D K, DONATO R, et al. Occipito-temporal connections in the human brain[J]. Brain, 2003, 126(9): 2093-2107. |
| [8] | GUEVARA P, DUCLAP D, POUPON C, et al. Segmentation of short association bundles in massive tractography datasets using a multi-subject bundle atlas[C]// Iberoamerican Congress on Pattern Recognition, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011: 701-708. |
| [9] | XUE T, ZHANG F, ZHANG C, et al. Supwma: consistent and efficient tractography parcellation of superficial white matter with deep learning[C]// International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, ITC Royal Bengal, Kolkata, India: IEEE, 2022: 1-5. |
| [10] | FENG Y J, WANG Z J, ZHANG G J, et al. Global white matter tractography using swarm optimization[J]. J Image Graph, 2012, 17(10): 1312-1318. |
| 冯远静, 王哲进, 张贵军, 等. 全局脑白质纤维群智能跟踪算法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2012, 17(10): 1312-1318. | |
| [11] | 张军. 基于邻域字典基模型的脑纤维流线微分方程跟踪算法[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2017. |
| [12] | YUE Q, WANG Y J. A fiber tracking algorithm based on non-local constrained spherical deconvolution[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2020, 37(4): 422-433. |
|
岳晴, 王远军. 基于非局部约束球面反卷积模型的纤维追踪算法[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2020, 37(4): 422-433.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20192798 |
|
| [13] |
ZHANG T, CHEN H, GUO L, et al. Characterization of U-shape streamline fibers: methods and applications[J]. Med Image Anal, 2014, 18(5): 795-807.
doi: 10.1016/j.media.2014.04.005 pmid: 24835185 |
| [14] |
WU Y, SUN D, WANG Y, et al. Tracing short connections of the temporo-parieto-occipital region in the human brain using diffusion spectrum imaging and fiber dissection[J]. Brain Res, 2016, 1646: 152-159.
doi: S0006-8993(16)30408-5 pmid: 27235864 |
| [15] | ZHANG D, ZONG F, ZHANG Q, et al. Anat-SFSeg: Anatomically-guided superficial fiber segmentation with point-cloud deep learning[J]. Med Image Anal, 2024, 95: 103165. |
| [16] | LI M, HE J Z, FENG Y J. Research progress of neural fiber tracking[J]. J Image Graph, 2020, 25(8): 1513-1528. |
| 李茂, 何建忠, 冯远静. 神经纤维跟踪算法研究进展[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(8): 1513-1528. | |
| [17] | NIE X, RUAN J, OTADUY M C G, et al. Surface-based probabilistic fiber tracking in superficial white matter[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2024, 43(3): 1113-1124. |
| [18] | GUEVARA M, GUEVARA P, ROMÁN C, et al. Superficial white matter: A review on the dMRI analysis methods and applications[J]. NeuroImage, 2020, 212: 116673. |
| [19] |
UĞURBIL K, XU J, AUERBACH E J, et al. Pushing spatial and temporal resolution for functional and diffusion MRI in the Human Connectome Project[J]. NeuroImage, 2013, 80: 80-104.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.012 pmid: 23702417 |
| [20] | YE W H, WANG Y J. Review of neural fiber tracking with diffusion magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Chinese Comput Sys, 2022, 43(7): 1458-1463. |
| 叶伟红, 王远军. 扩散磁共振图像的神经纤维追踪算法研究综述[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2022, 43(7): 1458-1463. | |
| [21] |
TOURNIER J D, CALAMANTE F, KING M D, et al. Limitations and requirements of diffusion tensor fiber tracking: an assessment using simulations[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2002, 47(4): 701-708.
pmid: 11948731 |
| [22] | AYDOGAN D B, SHI Y. Parallel transport tractography[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2020, 40(2): 635-647. |
| [23] | GAHM J K, SHI Y. Surface-based tracking of U-fibers in the superficial white matter[C]// Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 538-546. |
| [24] |
SCHILLING K, GAO Y, JANVE V, et al. Confirmation of a gyral bias in diffusion MRI fiber tractography[J]. Hum Brain Mapp, 2018, 39(3): 1449-1466.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.23936 pmid: 29266522 |
| [25] |
SOTIROPOULOS S N, HERNÁNDEZ-FERNÁNDEZ M, VU A T, et al. Fusion in diffusion MRI for improved fibre orientation estimation: An application to the 3T and 7T data of the Human Connectome Project[J]. NeuroImage, 2016, 134: 396-409.
doi: S1053-8119(16)30047-7 pmid: 27071694 |
| [26] |
SONG A W, CHANG H C, PETTY C, et al. Improved delineation of short cortical association fibers and gray/white matter boundary using whole-brain three-dimensional diffusion tensor imaging at submillimeter spatial resolution[J]. Brain Connect, 2014, 4(9): 636-640.
doi: 10.1089/brain.2014.0270 pmid: 25264168 |
| [27] |
ST-ONGE E, DADUCCI A, GIRARD G, et al. Surface-enhanced tractography (SET)[J]. NeuroImage, 2018, 169: 524-539.
doi: S1053-8119(17)31058-3 pmid: 29258891 |
| [28] |
BASTIANI M, COTTAAR M, DIKRANIAN K, et al. Improved tractography using asymmetric fibre orientation distributions[J]. NeuroImage, 2017, 158: 205-218.
doi: S1053-8119(17)30521-9 pmid: 28669902 |
| [29] | WU Y, HONG Y, FENG Y, et al. Mitigating gyral bias in cortical tractography via asymmetric fiber orientation distributions[J]. Med Image Anal, 2020, 59: 101543. |
| [30] | SHASTIN D, GENC S, PARKER G D, et al. Surface-based tracking for short association fibre tractography[J]. NeuroImage, 2022, 260: 119423. |
| [31] | COTTAAR M, BASTIANI M, BODDU N, et al. Modelling white matter in gyral blades as a continuous vector field[J]. NeuroImage, 2021, 227: 117693. |
| [32] |
RHEAULT F, DE BENEDICTIS A, DADUCCI A, et al. Tractostorm: The what, why, and how of tractography dissection reproducibility[J]. Hum Brain Mapp, 2020, 41(7): 1859-1874.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.24917 pmid: 31925871 |
| [33] |
WAKANA S, JIANG H, NAGAE-POETSCHER L M, et al. Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy[J]. Radiology, 2004, 230(1): 77-87.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2301021640 pmid: 14645885 |
| [34] |
CATANI M, DELL’ACQUA F, VERGANI F, et al. Short frontal lobe connections of the human brain[J]. Cortex, 2012, 48(2): 273-291.
doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2011.12.001 pmid: 22209688 |
| [35] |
ROJKOVA K, VOLLE E, URBANSKI M, et al. Atlasing the frontal lobe connections and their variability due to age and education: a spherical deconvolution tractography study[J]. Brain Struct Funct, 2016, 221: 1751-1766.
doi: 10.1007/s00429-015-1001-3 pmid: 25682261 |
| [36] | BURKS J D, BOETTCHER L B, CONNER A K, et al. White matter connections of the inferior parietal lobule: a study of surgical anatomy[J]. Brain Behav, 2017, 7(4): e00640. |
| [37] |
CATANI M, ROBERTSSON N, BEYH A, et al. Short parietal lobe connections of the human and monkey brain[J]. Cortex, 2017, 97: 339-357.
doi: S0010-9452(17)30370-2 pmid: 29157936 |
| [38] |
SHINOHARA H, LIU X, NAKAJIMA R, et al. Pyramid-shape crossings and intercrossing fibers are key elements for construction of the neural network in the superficial white matter of the human cerebrum[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2020, 30(10): 5218-5228.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa080 pmid: 32324856 |
| [39] |
OISHI K, ZILLES K, AMUNTS K, et al. Human brain white matter atlas: identification and assignment of common anatomical structures in superficial white matter[J]. NeuroImage, 2008, 43(3): 447-457.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.07.009 pmid: 18692144 |
| [40] |
ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, OISHI K, et al. Atlas-guided tract reconstruction for automated and comprehensive examination of the white matter anatomy[J]. NeuroImage, 2010, 52(4): 1289-1301.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.05.049 pmid: 20570617 |
| [41] | PARDO E, GUEVARA P, DUCLAP D, et al. Study of the variability of short association bundles on a HARDI database[C]// Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Osaka, Japan: IEEE, 2013: 77-80. |
| [42] | OUYANG M, JEON T, MISHRA V, et al. Global and regional cortical connectivity maturation index (CCMI) of developmental human brain with quantification of short-range association tracts[C]// International Society for Optical Engineering, San Diego, CA, United States: SPIE, 2016, 9788: 328-334. |
| [43] | MOVAHEDIAN ATTAR F, KIRILINA E, HAENELT D, et al. Mapping short association fibers in the early cortical visual processing stream using in vivo diffusion tractography[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2020, 30(8): 4496-4514. |
| [44] |
VERGANI F, LACERDA L, MARTINO J, et al. White matter connections of the supplementary motor area in humans[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2014, 85(12): 1377-1385.
doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2013-307492 pmid: 24741063 |
| [45] |
MAGRO E, MOREAU T, SEIZEUR R, et al. Characterization of short white matter fiber bundles in the central area from diffusion tensor MRI[J]. Neuroradiology, 2012, 54: 1275-1285.
doi: 10.1007/s00234-012-1073-1 pmid: 22854806 |
| [46] | YANG Z, LI X, ZHOU J, et al. Functional clustering of whole brain white matter fibers[J]. J Neurosci Meth, 2020, 335: 108626. |
| [47] | GUEVARA M, SUN Z Y, GUEVARA P, et al. Disentangling the variability of the superficial white matter organization using regional-tractogram-based population stratification[J]. NeuroImage, 2022, 255: 119197. |
| [48] | VINDAS N, AVILA N L, ZHANG F, et al. GeoLab: geometry-based tractography parcellation of superficial white matter[C]// International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Cartagena de Indias, Colombia: IEEE, 2023: 1-5. |
| [49] |
GUEVARA P, DUCLAP D, POUPON C, et al. Automatic fiber bundle segmentation in massive tractography datasets using a multi-subject bundle atlas[J]. NeuroImage, 2012, 61(4): 1083-1099.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.02.071 pmid: 22414992 |
| [50] |
ROMÁN C, GUEVARA M, VALENZUELA R, et al. Clustering of whole-brain white matter short association bundles using HARDI data[J]. Front Neuroinform, 2017, 11: 73.
doi: 10.3389/fninf.2017.00073 pmid: 29311886 |
| [51] |
DESIKAN R S, SÉGONNE F, FISCHL B, et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest[J]. NeuroImage, 2006, 31(3): 968-980.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021 pmid: 16530430 |
| [52] |
ZHANG F, WU Y, NORTON I, et al. An anatomically curated fiber clustering white matter atlas for consistent white matter tract parcellation across the lifespan[J]. NeuroImage, 2018, 179: 429-447.
doi: S1053-8119(18)30534-2 pmid: 29920375 |
| [53] | PRON A, BRUN L, DERUELLE C, et al. Dense and structured representations of U-shape fiber connectivity in the central sulcus[C]// International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Washington, DC, USA: IEEE, 2018: 700-703. |
| [54] |
PRON A, DERUELLE C, COULON O. U-shape short-range extrinsic connectivity organisation around the human central sulcus[J]. Brain Struct Funct, 2021, 226(1): 179-193.
doi: 10.1007/s00429-020-02177-5 pmid: 33245395 |
| [55] | XUE T, ZHANG F, ZHANG C, et al. Superficial white matter analysis: An efficient point-cloud-based deep learning framework with supervised contrastive learning for consistent tractography parcellation across populations and dMRI acquisitions[J]. Med Image Anal, 2023, 85: 102759. |
| [56] |
GUEVARA M, ROMÁN C, HOUENOU J, et al. Reproducibility of superficial white matter tracts using diffusion-weighted imaging tractography[J]. NeuroImage, 2017, 147: 703-725.
doi: S1053-8119(16)30684-X pmid: 28034765 |
| [57] | ROMÁN C, HERNÁNDEZ C, FIGUEROA M, et al. Superficial white matter bundle atlas based on hierarchical fiber clustering over probabilistic tractography data[J]. NeuroImage, 2022, 262: 119550. |
| [58] | JIANG F, WANG Y J. Construction of human brain templates with diffusion tensor imaging data: A review[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2018, 35(4): 520-530. |
|
蒋帆, 王远军. 扩散张量成像的人脑模板构建[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2018, 35(4): 520-530.
doi: 10.11938/cjmr20182662 |
| [1] | WEI Zhihong, KONG Xudong, KONG Yan, YAN Shiju, DING Yang, WEI Xianding, KONG Dong, YANG Bo. Application of Generative Adversarial Networks Based on Global and Local Feature Information in Hippocampus Segmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 143-153. |
| [2] | YANG Jiacheng, WANG Yuanjun. Improved Constrained Spherical Deconvolution for Microstructural Imaging of Brain Gray Matter [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 67-79. |
| [3] | Dai Junlong, He Cong, Wu Jie, Bian Yun. Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms Segmentation Network Combining Dual Decoding and Global Attention Upsampling Modules [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 151-161. |
| [4] | CHANG Bo, SUN Haoyun, GAO Qingyu, WANG Lijia. Research Progress on Cardiac Segmentation in Different Modal Medical Images by Traditional Methods and Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 224-244. |
| [5] | REN Hongjin, MA Yan, XIAO Liang. Knee Joint Model Construction and Local Specific Absorption Rate Estimation Based on Generative Adversarial Networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 410-422. |
| [6] | WANG Hui, WANG Tiantian, WANG Lijia. Squeeze-and-excitation Residual U-shaped Network for Left Myocardium Segmentation Based on Cine Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 435-447. |
| [7] | ZHANG Jiajun, LU Yucheng, BAO Yifang, LI Yuxin, GENG Chen, HU Fuyuan, DAI Yakang. An Automatic Segmentation Method of Cerebral Arterial Tree in TOF-MRA Based on DBCNet [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 320-331. |
| [8] | ZHAO Xin, ZHANG Xin, LI Xinjie, WANG Hongkai. Multimodal Glioma Segmentation with Fusion of Multiple Self-attention and Deformable Convolutions [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(3): 280-292. |
| [9] | Lan DENG,Yuan-jun WANG. DTI Brain Template Construction Based on Gaussian Averaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 413-427. |
| [10] | Ying-shan WANG, Ao-qi DENG, Jin-ling MAO, Zhong-qi ZHU, Jie SHI, Guang YANG, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Hong-zhi WANG. Automatic Segmentation of Knee Joint Synovial Magnetic Resonance Images Based on 3D VNetTrans [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(3): 303-315. |
| [11] | Zhen-yu WANG, Ying-shan WANG, Jin-ling MAO, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Jie SHI, Hong-zhi WANG. Magnetic Resonance Images Segmentation of Synovium Based on Dense-UNet++ [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 208-219. |
| [12] | Yue QIU, Sheng-dong NIE, Long WEI. Segmentation of Breast Tumors Based on Fully Convolutional Network and Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Image [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 196-207. |
| [13] | Ying LIU,Yi-yun GUO,Jing-cong CHEN,Hao-wei ZHANG. Automatic Precise Segmentation of Cerebellopontine Angle Tumor Based on Faster-RCNN and Level-Set Method [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 381-391. |
| [14] | Lu HUO,Xiao-xin HU,Qin XIAO,Ya-jia GU,Xu CHU,Luan JIANG. Automatic Segmentation of Breast and Fibroglandular Tissues in DCE-MR Images Based on nnU-Net [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 367-380. |
| [15] | Shi-ju YAN,Yong-sen HAN,Guang-yu TANG. An Improved Level Set Algorithm for Prostate Region Segmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2021, 38(3): 356-366. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
