
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 33-42.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20212903
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhi-chao WANG1,Ji-lei ZHANG2,Yu ZHAO3,Ting HUA4,Guang-yu TANG4,Jian-qi LI1,*( )
)
Received:2021-03-30
Published:2022-03-05
Online:2021-05-16
Contact:
Jian-qi LI
E-mail:jqli@phy.ecnu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Zhi-chao WANG,Ji-lei ZHANG,Yu ZHAO,Ting HUA,Guang-yu TANG,Jian-qi LI. CEST Imaging of the Abdomen with Neural Network Fitting[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(1): 33-42.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
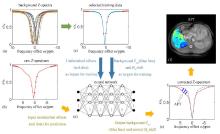
Fig.1
Schematic of data processing. (a) Simulated background Z-spectra; (b) The acquired raw Z-spectrum, in which the red solid dots are inputted into the neural network to produce background reference Z-spectrum and water peak offset for correcting Z-spectrum later; (c) A simulated background Z-spectrum, in which the data marked as red solid dots are inputs for training and the complete Z-spectrum represented by blue line as well as the water peak offset are targets for training; (d) The feedforward neural network generated and applied; (e) The water peak offset and the background Z-spectrum (marked as bluish violet dashed curve) are obtained from the network and used to correct the raw Z-spectrum. The shaded part indicated by the arrow is the difference between bluish violet dashed curve and red solid curve, which is contributed from APT effect; (f) The APT map
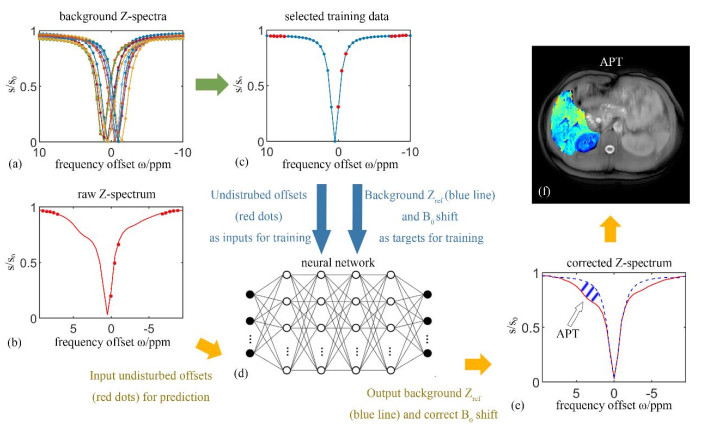
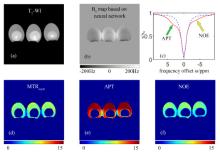
Fig.2
The CEST imaging results of egg white. (a) T1 weighted image; (b) B0 map based on neural network; (c) The corrected Z-spectrum in egg white (red solid curve) and the background reference Z-spectrum (bluish violet dashed curve) obtained by neural network prediction, where the green arrow and yellow arrow indicate the positions of APT and NOE exchange, respectively; (d) MTRasym map of egg white; (e) APT map; (f) NOE map
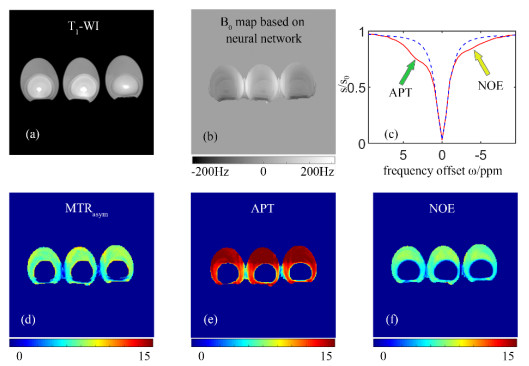
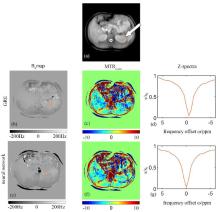
Fig.3
Abdominal B0 maps and the corresponding CEST results of a healthy volunteer obtained by gradient recalled echo (GRE) sequence (the 2nd row) and neural network based method (the 3rd row). (a) The reference image while the CEST saturation radio frequency pulse was not applied; (b) & (e) B0 maps obtained by GRE sequence and neural network fitting, respectively; (c) & (f) MTRasym maps based on GRE sequence and neural network fitting, respectively; (d) & (g) The Z-spectrum analysis of tissue located in the orange circle in the left kidney based on GRE sequence and neural network fitting, respectively
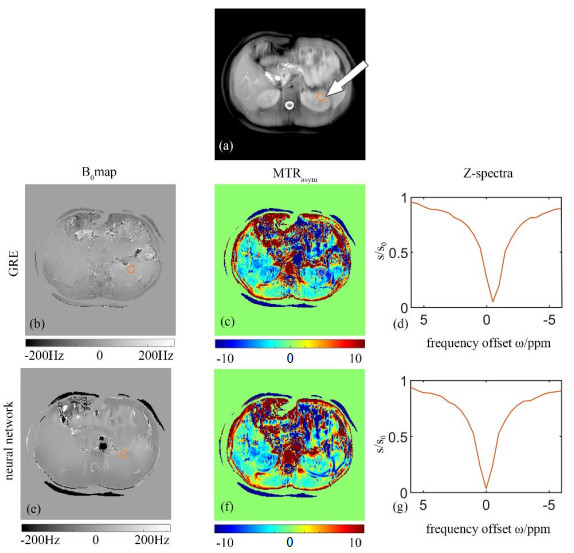
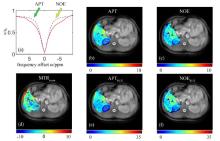
Fig.4
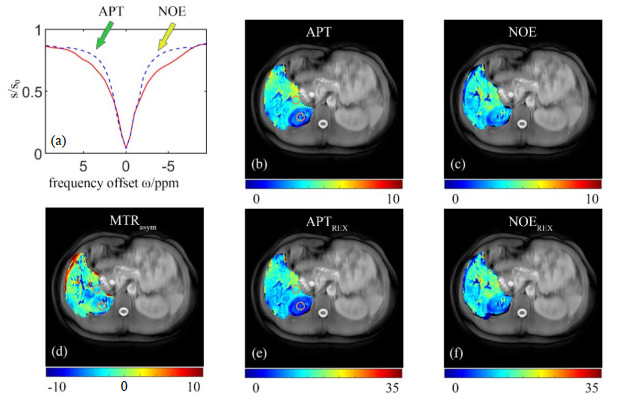
The CEST results of a healthy volunteer obtained by the method based on neural network. (a) The corrected Z-spectrum (red solid curve) and background reference Z-spectrum (bluish violet dashed line), where the green arrow and yellow arrow indicate the positions APT and NOE, respectively; (b) APT map; (c) NOE map; (d) MTRasym map; (e) APTREX map; (f) NOEREX map
| 1 |
FORSéN S , HOFFMAN R A . Study of moderately rapid chemical exchange reactions by means of nuclear magnetic double resonance[J]. J Chem Phys, 1963, 39 (11): 2892- 2901.
doi: 10.1063/1.1734121 |
| 2 | CHEN L Q , PAGEL M D . Evaluating pH in the extracellular tumor microenvironment using CEST MRI and other imaging methods[J]. Adv Radio, 2015, 206405. |
| 3 | TAO Q , YI P W , WEI G J , et al. pH Imaging based on chemical exchange saturation transfer: Principles, methods, applications and recent progresses[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2018, 35 (4): 505- 519. |
| 陶泉, 易佩伟, 魏国境, 等. 基于CEST机制的pH成像方法、原理和应用[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2018, 35 (4): 505- 519. | |
| 4 |
ZHOU J Y , PAYEN J F , WILSON D A , et al. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI[J]. Nat Med, 2003, 9 (8): 1085- 1090.
doi: 10.1038/nm907 |
| 5 | YANG Y G , CHEN Z , CAI C B , et al. Factors affecting chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging on 1.5 T clinical MRI scanners[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2017, 34 (3): 275- 282. |
| 杨永贵, 陈忠, 蔡聪波, 等. 1.5 T磁共振化学交换饱和转移成像的影响因素分析[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2017, 34 (3): 275- 282. | |
| 6 |
ZHOU J , BLAKELEY J O , HUA J , et al. Practical data acquisition method for human brain tumor amide proton transfer (APT) imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2008, 60 (4): 842- 849.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.21712 |
| 7 | WEI G J , Y P W , TAO Q , et al. Comparisons of different CEST quantification metrics applied in acute parkinson's disease mouse model[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2019, 36 (2): 195- 207. |
| 魏国境, 易佩伟, 陶泉, 等. CEST成像不同量化方式在急性帕金森氏病小鼠模型研究中的应用比较[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2019, 36 (2): 195- 207. | |
| 8 |
ZHANG J X , ZHU W Z , TAIN R W , et al. Improved differentiation of low-grade and high-grade gliomas and detection of tumor proliferation using APT contrast fitted from Z-spectrum[J]. Mol Imaging Biol, 2018, 20 (4): 623- 631.
doi: 10.1007/s11307-017-1154-y |
| 9 | CAI K , SINGH A , POPTANI H , et al. CEST signal at 2 ppm (CEST@2 ppm) from Z-spectral fitting correlates with creatine distribution in brain tumor[J]. NMR Biomed, 2015, 28 (1): 1- 8. |
| 10 |
JONES K M , POLLARD A C , PAGEL M D . Clinical applications of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, 47 (1): 11- 27.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.25838 |
| 11 |
ZHOU J Y , HEO H Y , KNUTSSON L , et al. APT-weighted MRI: Techniques, current neuro applications, and challenging issues[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 50 (2): 347- 364.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.26645 |
| 12 |
SEO N , JEONG H K , CHOI J Y , et al. Liver MRI with amide proton transfer imaging: feasibility and accuracy for the characterization of focal liver lesions[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31 (1): 222- 231.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07122-y |
| 13 |
CHEN S Z , YUAN J , DENG M , et al. Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MR technique for in-vivo liver imaging at 3.0 tesla[J]. Eur Radiol, 2016, 26 (6): 1792- 1800.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3972-0 |
| 14 |
LIN Y , LUO X J , YU L , et al. Amide proton transfer-weighted MRI for predicting histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with diffusion-weighted imaging[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2019, 9 (10): 1641- 1651.
doi: 10.21037/qims.2019.08.07 |
| 15 |
WANG Y , GRIMM R C , FELMLEE J P , et al. Algorithms for extracting motion information from navigator echoes[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1996, 36 (1): 117- 123.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910360120 |
| 16 |
KIM M , GILLEN J , LANDMAN B A , et al. Water saturation shift referencing (WASSR) for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) experiments[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2009, 61 (6): 1441- 1450.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.21873 |
| 17 |
SUN P Z , FARRAR C T , SORENSEN A G . Correction for artifacts induced by B0 and B1 field inhomogeneities in pH-sensitive chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) Imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2007, 58 (6): 1207- 1215.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.21398 |
| 18 |
LI W , AVRAM A V , WU B , et al. Integrated Laplacian-based phase unwrapping and background phase removal for quantitative susceptibility mapping[J]. NMR Biomed, 2014, 27 (2): 219- 227.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.3056 |
| 19 |
LIM I A L , LI X , JONES C K , et al. Quantitative magnetic susceptibility mapping without phase unwrapping using WASSR[J]. Neuroimage, 2014, 86, 265- 279.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.09.072 |
| 20 |
MELACINI G , KAPTEIN R , BOELENS R . Editing of chemical exchange-relayed NOEs in NMR experiments for the observation of protein-water interactions[J]. J Magn Reson, 1999, 136 (2): 214- 218.
doi: 10.1006/jmre.1998.1646 |
| 21 |
JIN T , WANG P , ZONG X , et al. MR imaging of the amide-proton transfer effect and the pH-insensitive nuclear overhauser effect at 9.4 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 69 (3): 760- 770.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24315 |
| 22 |
ZAISS M , SCHMITT B , BACHERT P . Quantitative separation of CEST effect from magnetization transfer and spillover effects by Lorentzian-line-fit analysis of Z-spectra[J]. J Magn Reson, 2011, 211 (2): 149- 155.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2011.05.001 |
| 23 |
MORRISON C , HENKELMAN R M . A model for magnetization transfer in tissues[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1995, 33 (4): 475- 482.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910330404 |
| 24 |
ZAISS M , SCHUPPERT M , DESHMANE A , et al. Chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI contrast in the human brain at 9.4 T[J]. Neuroimage, 2018, 179, 144- 155.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.06.026 |
| 25 |
HENKELMAN R M , HUANG X , XIANG Q S , et al. Quantitative interpretation of magnetization transfer[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1993, 29 (6): 759- 766.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910290607 |
| 26 |
WOESSNER D E , ZHANG S R , MERRITT M E , et al. Numerical solution of the Bloch equations provides insights into the optimum design of PARACEST agents for MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2005, 53 (4): 790- 799.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.20408 |
| 27 |
ZAISS M , ZU Z , XU J , et al. A combined analytical solution for chemical exchange saturation transfer and semi-solid magnetization transfer[J]. NMR Biomed, 2015, 28 (2): 217- 230.
doi: 10.1002/nbm.3237 |
| 28 |
ZAISS M , WINDSCHUH J , PAECH D , et al. Relaxation-compensated CEST-MRI of the human brain at 7 T: Unbiased insight into NOE and amide signal changes in human glioblastoma[J]. Neuroimage, 2015, 112, 180- 188.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.040 |
| 29 |
TOGAO O , KEUPP J , HIWATASHI A , et al. Amide proton transfer imaging of brain tumors using a self-corrected 3D fast spin-echo Dixon method: Comparison with separate B0 correction[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2017, 77 (6): 2272- 2279.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26322 |
| 30 | KIM H , WU Y , VILLANO D , et al. Analysis protocol for the quantification of renal pH using chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2021, 2216, 667- 688. |
| 31 |
KLEIN S , STARING M , MURPHY K , et al. elastix: A toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2010, 29 (1): 196- 205.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2035616 |
| 32 | SHAMONIN D P , BRON E E , LELIEVELDT B P F , et al. Fast parallel image registration on CPU and GPU for diagnostic classification of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Front Neuroinform, 2013, 7, 50. |
| [1] | MA Yingxue, ZHAO Yanqiang, YANG Xiaodong, JIANG Bin, TAO Cheng. Opportunities and Challenges of High-field and Ultra-high-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 334-344. |
| [2] | SUI Meiju, ZHANG Lei, WANG Ruifang, LUO Yingying, LI Sha, QIU Maosong, XU Qiuyi, CHEN Daiqin, CHEN Shizhen, ZHOU Xin. MRI-traceable Nanoenzyme for Cascade Catalysis-enhanced Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 231-248. |
| [3] | CHEN Qun, YANG Zijian, CHENG Xinyi, JIA Siyi, DU Xiaoxia, WANG Mengxing. Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technology in Pediatric Exercise Intervention Research [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 195-204. |
| [4] | GU Jiajia, WANG Yuanjun. Hybrid Attention and Multiscale Module for Alzheimer's Disease Classification [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 103-116. |
| [5] | PANG Qifan, WANG Zhichao, WU Yupeng, LI Jianqi. The Impact of K-Space Filling Strategy on Fat Artifacts in APT Imaging Based on FLASH Sequence [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 443-453. |
| [6] | ZHANG Haowei, WANG Yuncheng, LIU Ying. Brain Age Assessment of Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Based on Convolutional Neural Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(2): 139-150. |
| [7] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [8] | LIU Ying, LIN Ling, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Research Progress of MRI Gradient Waveform Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 99-115. |
| [9] | SHI Weicheng,JIN Zhaoyang,YE Zheng. Fast Multi-channel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based on PCAU-Net [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 39-51. |
| [10] | LI Pan,FANG Delei,ZHANG Junxia,MA Debei. Magnetic Resonance Compatibility Analysis Method of Surgical Robotic System Based on Image Quality Evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(1): 79-91. |
| [11] | Yi-feng YANG, Zhang-xuan QI, Sheng-dong NIE. Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions Based on Multimodal MRI and Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(4): 401-412. |
| [12] |
De-gang TANG,Hong-chuang LI,Xiao-ling LIU,Lei SHI,Hai-dong LI,Chao-hui YE,Xin ZHOU.
A Simulation Study on the Effect of the High Permittivity Materials Geometrical Structure on the Transmit Field |
| [13] | Zhen-yu WANG, Ying-shan WANG, Jin-ling MAO, Wei-wei MA, Qing LU, Jie SHI, Hong-zhi WANG. Magnetic Resonance Images Segmentation of Synovium Based on Dense-UNet++ [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 208-219. |
| [14] | Yan MA, Cang-ju XING, Liang XIAO. Knee Joint Image Segmentation and Model Construction Based on Cascaded Network [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 184-195. |
| [15] | Jun LUO, Sheng-ping LIU, Xing YANG, Jia-sheng WANG, Ye LI. Design of a 5 T Non-magnetic Magnetic Resonance Radio Frequency Power Amplifier [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 163-173. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||