
Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance ›› 2022, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 220-229.doi: 10.11938/cjmr20202870
• Review Articles & Perspectives • Previous Articles Next Articles
Min-xiong ZHOU1,Hui-ting ZHANG2,Yi-da WANG3,Guang YANG3,Xu-feng YAO1,An-kang GAO4,Jing-liang CHENG4,Jie BAI4,Xu YAN2,*( )
)
Received:2020-11-05
Published:2022-06-05
Online:2022-05-28
Contact:
Xu YAN
E-mail:maxwell4444@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
Min-xiong ZHOU, Hui-ting ZHANG, Yi-da WANG, Guang YANG, Xu-feng YAO, An-kang GAO, Jing-liang CHENG, Jie BAI, Xu YAN. Evaluation of the Influence of Data Sampling Schemes on Neural Diffusion Models[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2022, 39(2): 220-229.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 1
Meanings of regular parameters used in diffusion models
| 模型 | 参数 | 全名(英文/中文) | 物理含义 |
| DTI | FA | fractional anisotropy各向异性分数 | 反映扩散系数在空间上分布不均匀的程度. |
| MD\AD\RD | mean\axial\radial diffusivity平均\轴向\径向扩散系数 | 反映平均、轴向(神经纤维方向)和垂直于轴向平面的扩散速率. | |
| DKI | MD\AD\RD | mean\axial\radial diffusivity 平均\轴向\径向扩散系数 | 与DTI的MD\AD\RD参数类似,但为校正后的扩散速率. |
| MK\AK\RK | mean\axial\radial kurtosis 平均\轴向\径向扩散峰度 | 反映平均、轴向(神经纤维方向)和垂直于轴向平面的扩散偏离正态分布的程度,与扩散受限和多组织成分混杂有关. | |
| NODDI | ICVF | intra-cellular volume fraction 细胞内容积比 | 为细胞内信号占总扩散信号的比例,与神经突密度相关. |
| ISOVF | isotropic volume fraction 各向同性容积比 | 为各向同性信号占总扩散信号的比例,通常反映脑脊液信号 | |
| ODI | orientation dispersion index 方向分散指数 | 量化神经轴突方向角度的不一致性,其值在单方向的神经组织中趋近于0,在各向同性组织趋近于1. | |
| MAP | RTOP | return-to-the-origin probability 返回原点概率 | 水分子在扩散过程中不发生净位移的概率,反映扩散受限程度. |
| MSD | mean squared displacement 平均平方位移 | 单位时间内水分子的均方位移,反映扩散速率,与DTI/DKI的MD参数接近. | |
| QIV | Q space inverse variance Q空间逆方差 | Q空间信号几何平均值的逆方差 | |
| NG | no-Gaussianity 非高斯性 | 含义与DKI中的MK接近,反映扩散偏离正态分布的程度. |
Fig.1
Based on the mean values in ROIs, the influence of different sampling schemes on the quantitative parameters of various diffusion models was compared. The sampling schemes included QGrid, Free and MDDW. The diffusion models included DTI, DKI, NODDI and MAP. ROIs were selected in gray matter and white matter regions respectively (Each parameter is in different value range, thus a rescale is applied to display them together)
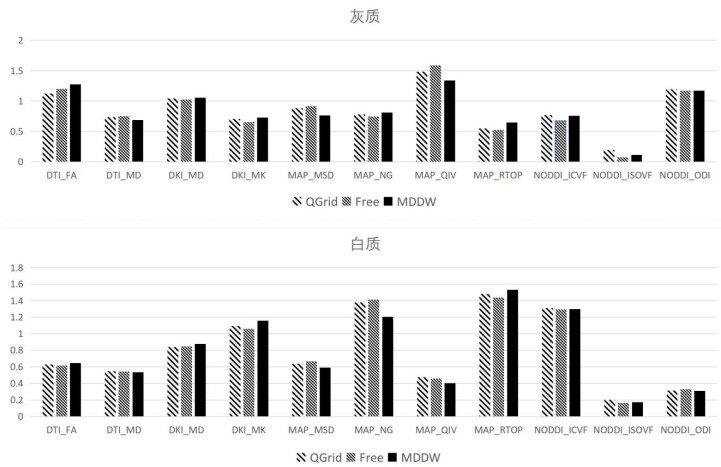
Table 2
The coefficients of variation of quantitative diffusion parameters among 3 sampling schemes, namely QGrid, Free, MDDW
| DTI | DKI | MAP | NODDI | |||||||||||
| FA | MD | MD | MK | MSD | NG | QIV | RTOP | ICVF | ISOVF | ODI | ||||
| 灰质 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.47 | 0.01 | |||
| 白质 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.04 | |||
| 1 |
BASSER P J , MATTIELLO J , LEBIHAN D . MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging[J]. Biophys J, 1994, 66 (1): 259- 267.
doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80775-1 |
| 2 | JIANG F , WANG Y J . A review on interpolation methods for diffusion tensor images[J]. Chinese J Magn Reson, 2019, 36 (3): 392- 407. |
| 蒋帆, 王远军. 扩散张量图像的插值方法综述[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2019, 36 (3): 392- 407. | |
| 3 | XU Y H , GAO S C , HAO X F . An improved spectral quaternion interpolation method of diffusion tensor imaging[J]. J Biomed Eng, 2016, 33 (2): 362- 367. |
| 徐永红, 高上策, 郝小飞. 一种改进的扩散张量成像谱四元数插值方法[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2016, 33 (2): 362- 367. | |
| 4 |
JENSEN J H , HELPERN J A , RAMANI A , et al. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2005, 53 (6): 1432- 1440.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.20508 |
| 5 |
ZHANG H , SCHNEIDER T , WHEELER-KINGSHOTT C A , et al. NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain[J]. Neuroimage, 2012, 61 (4): 1000- 1016.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.072 |
| 6 | ÖZARSLANE, KOAYC G, SHEPHERDT M, 等. Mean apparent propagator (MAP) MRI: A novel diffusion imaging method for mapping tissue microstructure[J]. Neuroimage, 2013, 78, 16- 32. |
| 7 | FICK R, DAIANU M, PIZZOLATO M, et al. Comparison of biomarkers in transgenic alzheimer rats using multi-shell diffusion MRI[C] //MICCAI, 2017: 187-199. |
| 8 |
PINES A R , CIESLAK M , LARSEN B , et al. Leveraging multi-shell diffusion for studies of brain development in youth and young adulthood[J]. Dev Cogn Neurosci, 2020, 43, 100788.
doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2020.100788 |
| 9 |
MA K R , ZHANG X N , ZHANG H T , et al. Mean apparent propagator-MRI: A new diffusion model which improves temporal lobe epilepsy lateralization[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2020, 126, 108914.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108914 |
| 10 |
LE H B , ZENG W K , ZHANG H H , et al. Mean apparent propagator MRI is better than conventional diffusion tensor imaging for the Evaluation of Parkinson's disease: a prospective pilot study[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2020, 12, 563595.
doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.563595 |
| 11 |
WEDEEN V J , HAGMANN P , TSENG W Y I , et al. Mapping complex tissue architecture with diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2005, 54 (6): 1377- 1386.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.20642 |
| 12 |
CARUYER E , LENGLET C , SAPIRO G , et al. Design of multishell sampling schemes with uniform coverage in diffusion MRI[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 69 (6): 1534- 1540.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.24736 |
| 13 |
JONES D K , HORSFIELD M A , SIMMONS A . Optimal strategies for measuring diffusion in anisotropic systems by magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1999, 42 (3): 515- 525.
doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199909)42:3<515::AID-MRM14>3.0.CO;2-Q |
| 14 |
PAPADAKIS N G , MURRILLS C D , HALL L D , et al. Minimal gradient encoding for robust estimation of diffusion anisotropy[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2000, 18 (6): 671- 679.
doi: 10.1016/S0730-725X(00)00151-X |
| 15 |
TABESH A , JENSEN J H , ARDEKANI B A , et al. Estimation of tensors and tensor-derived measures in diffusional kurtosis imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2011, 65 (3): 823- 836.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.22655 |
| 16 |
WU Y C , ALEXANDER A L . Hybrid diffusion imaging[J]. Neuroimage, 2007, 36 (3): 617- 629.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.050 |
| 17 |
HUTCHINSON E B , AVRAM A V , IRFANOGLU M O , et al. Analysis of the effects of noise, DWI sampling, and value of assumed parameters in diffusion MRI models[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2017, 78 (5): 1767- 1780.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26575 |
| 18 |
ANDICA C , KAMAGATA K , HATANO T , et al. MR biomarkers of degenerative brain disorders derived from diffusion imaging[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2020, 52 (6): 1620- 1636.
doi: 10.1002/jmri.27019 |
| 19 |
FIGINI M , RIVA M , GRAHAM M , et al. Prediction of isocitrate dehydrogenase genotype in brain gliomas with MRI: Single-shell versus multishell diffusion models[J]. Radiology, 2018, 289 (3): 788- 796.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018180054 |
| 20 |
SOTIROPOULOS S N , JBABDI S , XU J Q , et al. Advances in diffusion MRI acquisition and processing in the Human Connectome Project[J]. Neuroimage, 2013, 80, 125- 143.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.057 |
| 21 |
JENKINSON M , BECKMANN C F , BEHRENS T E , et al. FSL[J]. Neuroimage, 2012, 62 (2): 782- 790.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015 |
| 22 |
XIE S M , CHEN L F , ZUO N M , et al. DiffusionKit: A light one-stop solution for diffusion MRI data analysis[J]. J Neurosci Methods, 2016, 273, 107- 119.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.08.011 |
| 23 | GARYFALLIDIS E , BRETT M , AMIRBEKIAN B , et al. Dipy, a library for the analysis of diffusion MRI data[J]. Front Neuroinform, 2014, 8, 8. |
| 24 |
DADUCCI A , CANALES-RODRÍGUEZ E J , ZHANG H , et al. Accelerated microstructure imaging via convex optimization (AMICO) from diffusion MRI data[J]. Neuroimage, 2015, 105, 32- 44.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.10.026 |
| 25 |
KLEIN S , STARING M , MURPHY K , et al. elastix: a toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2010, 29 (1): 196- 205.
doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2035616 |
| 26 |
LE BIHAN D , TURNER R . Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging using spin echoes[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1991, 19 (2): 221- 227.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910190206 |
| 27 |
BENNETT K M , SCHMAINDA K M , BENNETT R T , et al. Characterization of continuously distributed cortical water diffusion rates with a stretched-exponential model[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2003, 50 (4): 727- 734.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.10581 |
| 28 | WANG Y , WANG Q , HALDAR J P , et al. Quantification of increased cellularity during inflammatory demyelination[J]. Brain, 2011, 134 (Pt 12): 3590- 3601. |
| 29 |
PARK J E , KIM H S , PARK S Y , et al. Prediction of core signaling pathway by using diffusionand perfusion-based MRI radiomics and next-generation sequencing in isocitrate dehydrogenase wild-type glioblastoma[J]. Radiology, 2020, 294 (2): 388- 397.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019190913 |
| [1] | MA Yingxue, ZHAO Yanqiang, YANG Xiaodong, JIANG Bin, TAO Cheng. Opportunities and Challenges of High-field and Ultra-high-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 334-344. |
| [2] | SHU Wei. Diagnostic Efficacy Comparison of B-scan Ultrasonography and MRI in Fetal Skeletal Abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 265-274. |
| [3] | SUI Meiju, ZHANG Lei, WANG Ruifang, LUO Yingying, LI Sha, QIU Maosong, XU Qiuyi, CHEN Daiqin, CHEN Shizhen, ZHOU Xin. MRI-traceable Nanoenzyme for Cascade Catalysis-enhanced Immunotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(3): 231-248. |
| [4] | MENG Jingxin, WANG Yuanjun. Research Progress on Tractography of Superficial White Matter Based on Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 205-220. |
| [5] | CHEN Qun, YANG Zijian, CHENG Xinyi, JIA Siyi, DU Xiaoxia, WANG Mengxing. Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technology in Pediatric Exercise Intervention Research [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 195-204. |
| [6] | ZUO Bingyu, SHI Lili, SONG Jia, ZHAO Yang, LI Qian. Application of Estrogen and Tumor Markers Combined with DCE-MRI in Diagnosis and Clinical Staging of Cervical Cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(2): 164-173. |
| [7] | YANG Jiacheng, WANG Yuanjun. Improved Constrained Spherical Deconvolution for Microstructural Imaging of Brain Gray Matter [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2025, 42(1): 67-79. |
| [8] | PANG Qifan, WANG Zhichao, WU Yupeng, LI Jianqi. The Impact of K-Space Filling Strategy on Fat Artifacts in APT Imaging Based on FLASH Sequence [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 443-453. |
| [9] | HUANG Min, ZHU Junlin, KAO Yuchen, ZHOU Dao, TANG Qiling. Multi-Coil MRI Image Reconstruction Based on ISTAVS-Net of Physical Model [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(4): 418-429. |
| [10] | XU Zhenshun, YUAN Xiaohan, HUANG Ziheng, SHAO Chengwei, WU Jie, BIAN Yun. Multi-source Feature Classification Model of Pancreatic Mucinous and Serous Cystic Neoplasms Based on Deep Learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 19-29. |
| [11] | LIU Ying, LIN Ling, YUAN Binhua, ZHANG Haowei. Research Progress of MRI Gradient Waveform Generator [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 99-115. |
| [12] | ZHOU Minxiong, QI Xuan, DU Bin, QI Dong, WANG Haijie, YANG Guang, Cai Wenmei, LIU Mengxiao, ZHANG Huiting, YAN Xu, NIE Shengdong, HE Yongsheng. Evaluation of the Impact of b-Value Ranges on Six Body Diffusion Models in Prostate Application [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2024, 41(1): 9-18. |
| [13] | ZHOU Tianli, ZHANG Dian, WU Jizhi, JIA Huihui, CHANG Yan, SHENG Mao, YANG Xiaodong. Application of MRI-based Finite Element Modeling and Analysis in Periacetabular Osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 397-409. |
| [14] | CHEN Mengying, WU Yupeng, PANG Qifan, ZHONG Haodong, LI Gaiying, LI Jianqi. Simultaneously Neuromelanin-sensitive Imaging and Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping in the Whole Brain [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 385-396. |
| [15] | REN Hongjin, MA Yan, XIAO Liang. Knee Joint Model Construction and Local Specific Absorption Rate Estimation Based on Generative Adversarial Networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2023, 40(4): 410-422. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||